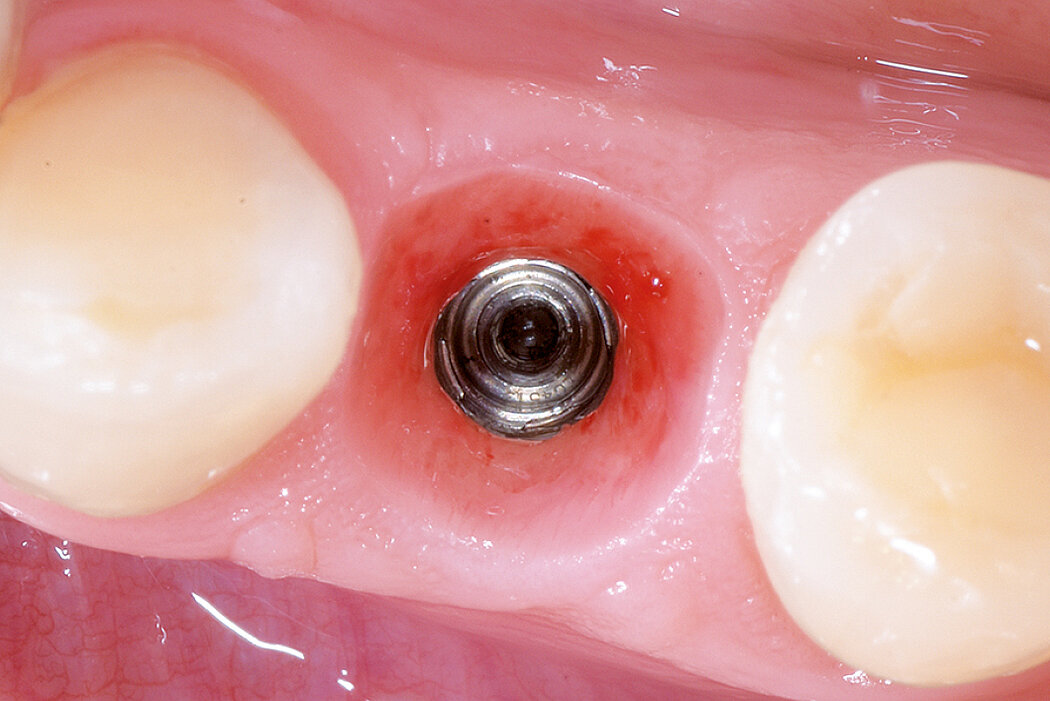
Delayed/late implant placement

Delayed/Late implant placement in combination with Ridge Preservation is a reliable and conventional treatment option for every surgeon. In this approach, Ridge Preservation with Geistlich biomaterials provides sufficient ridge volume for implant placement even several months after tooth extraction.1,2
References:
- Cardaropoli D, et al. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2014 Mar–Apr;34(2):211-7. (Clinical study)
- Vignoletti F, et al. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012 Feb;23 Suppl 5:22-38. (Systematic review)
Clinical Cases
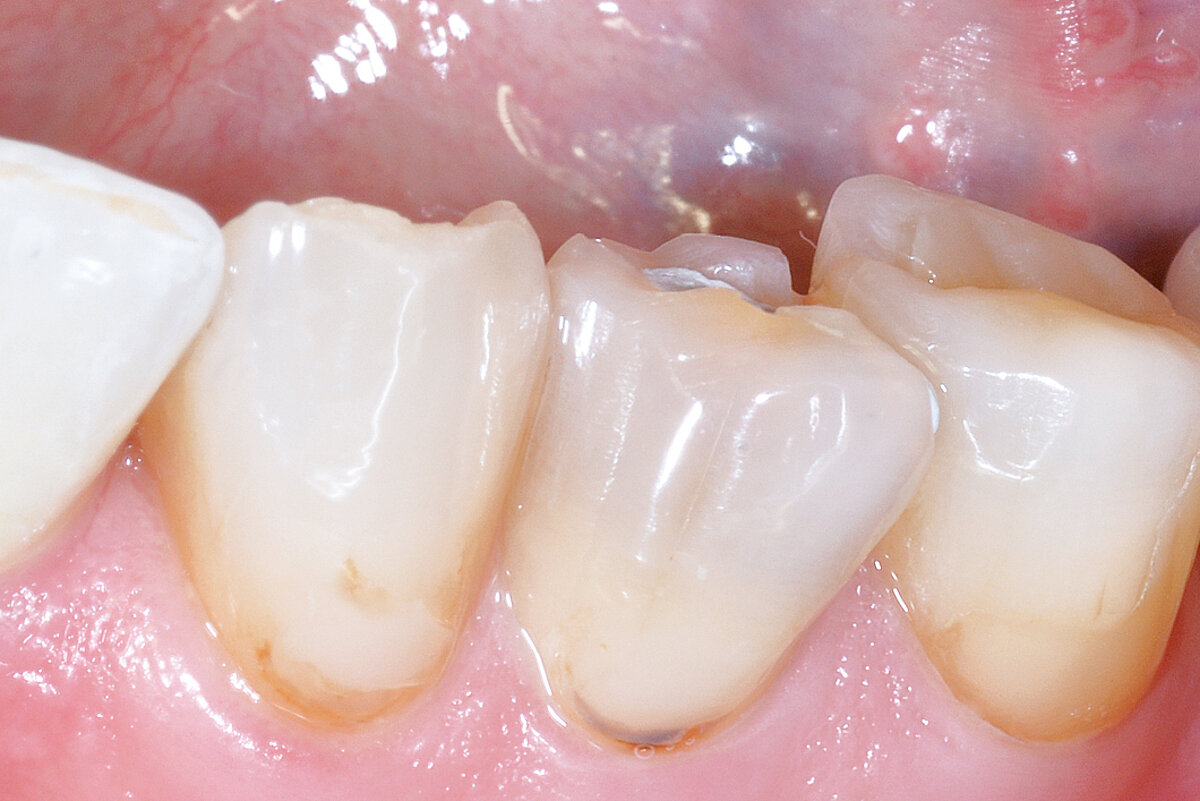
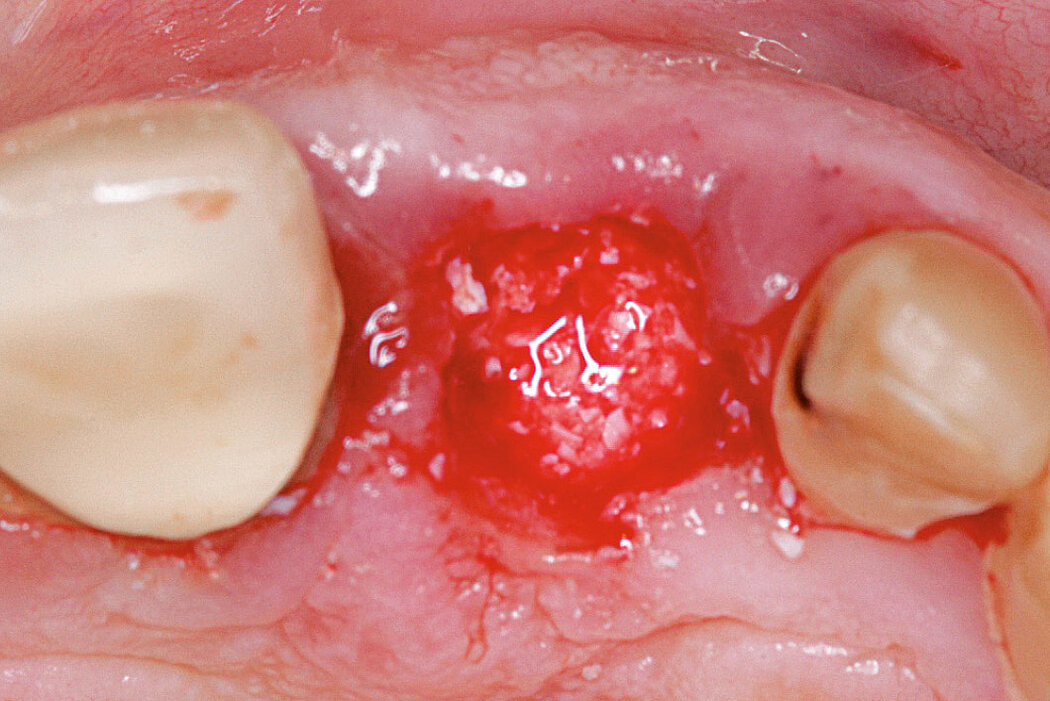
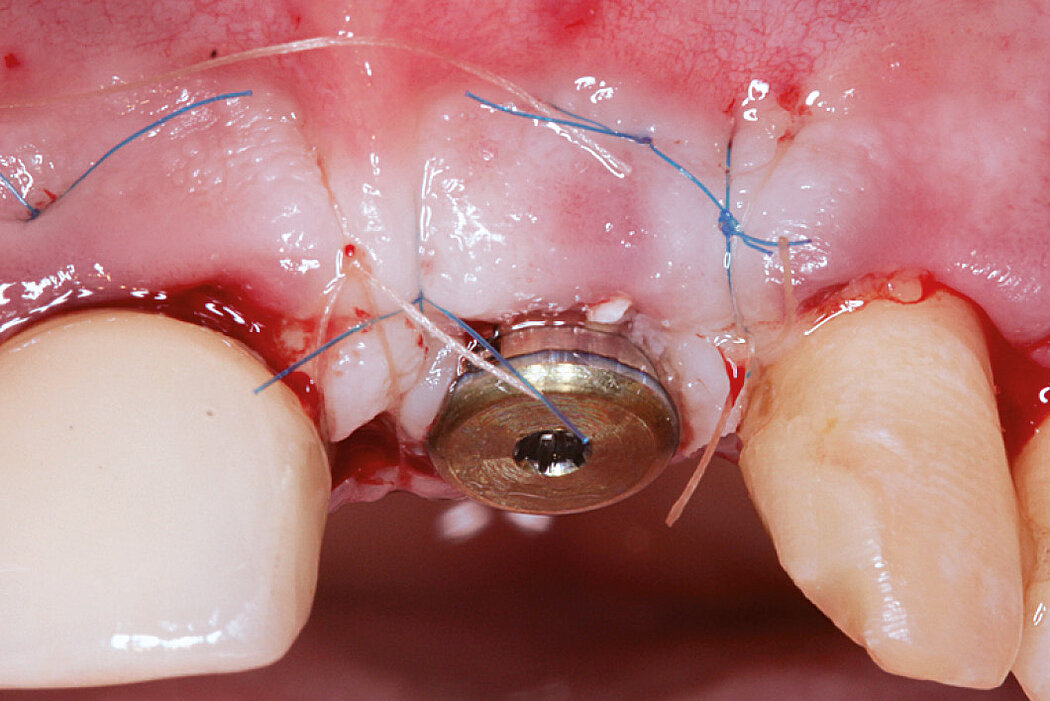
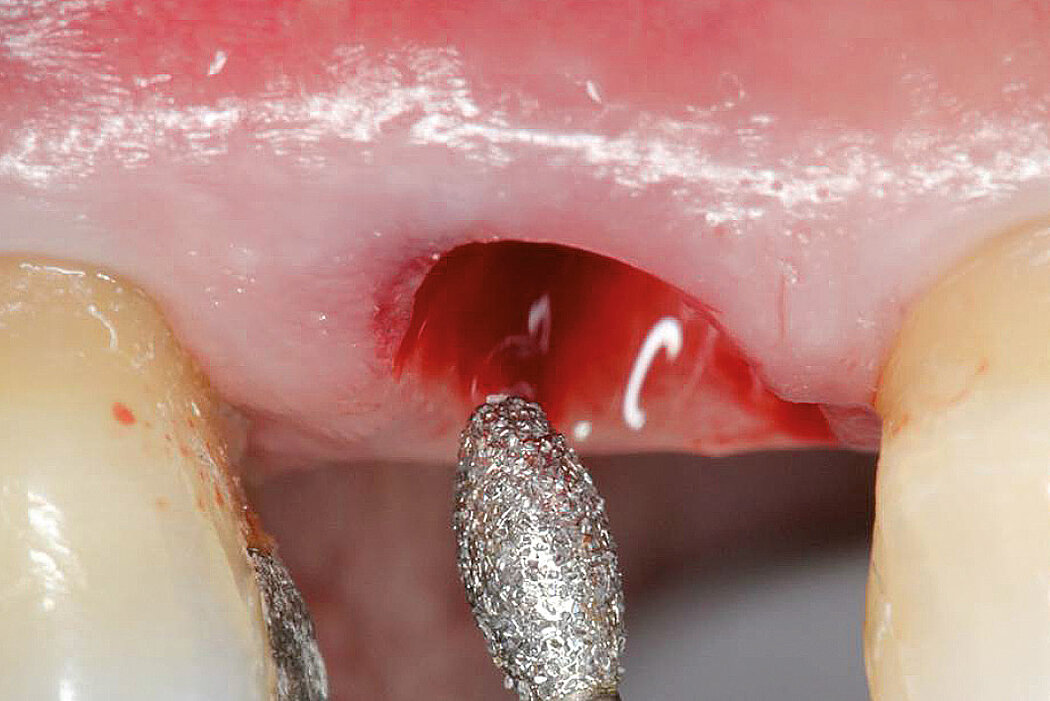
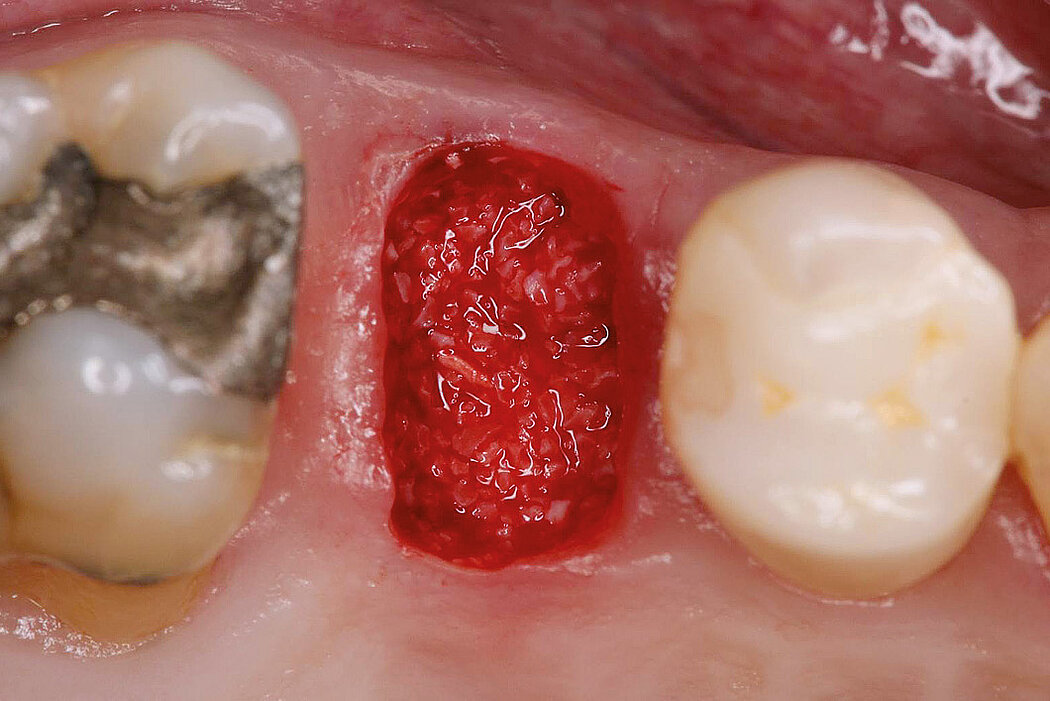
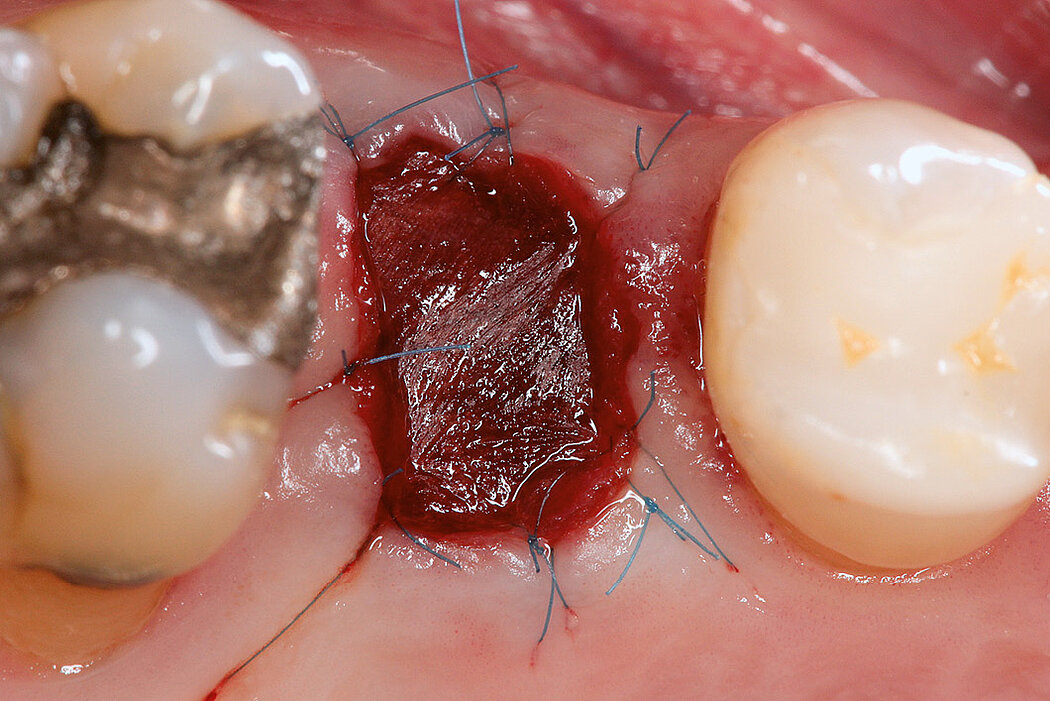
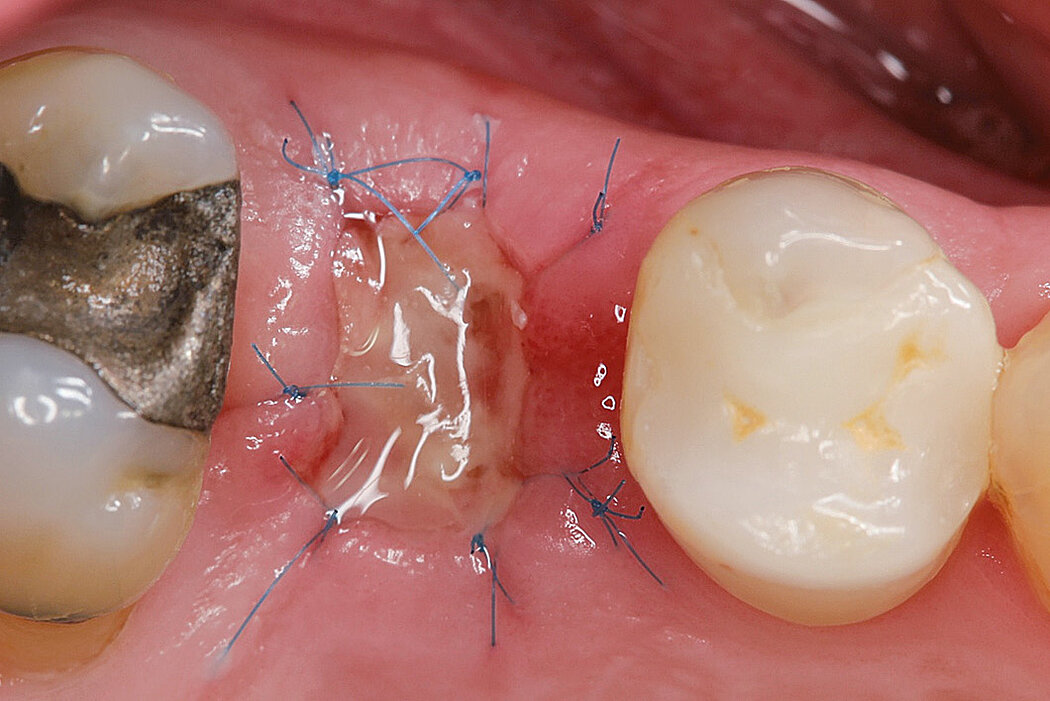
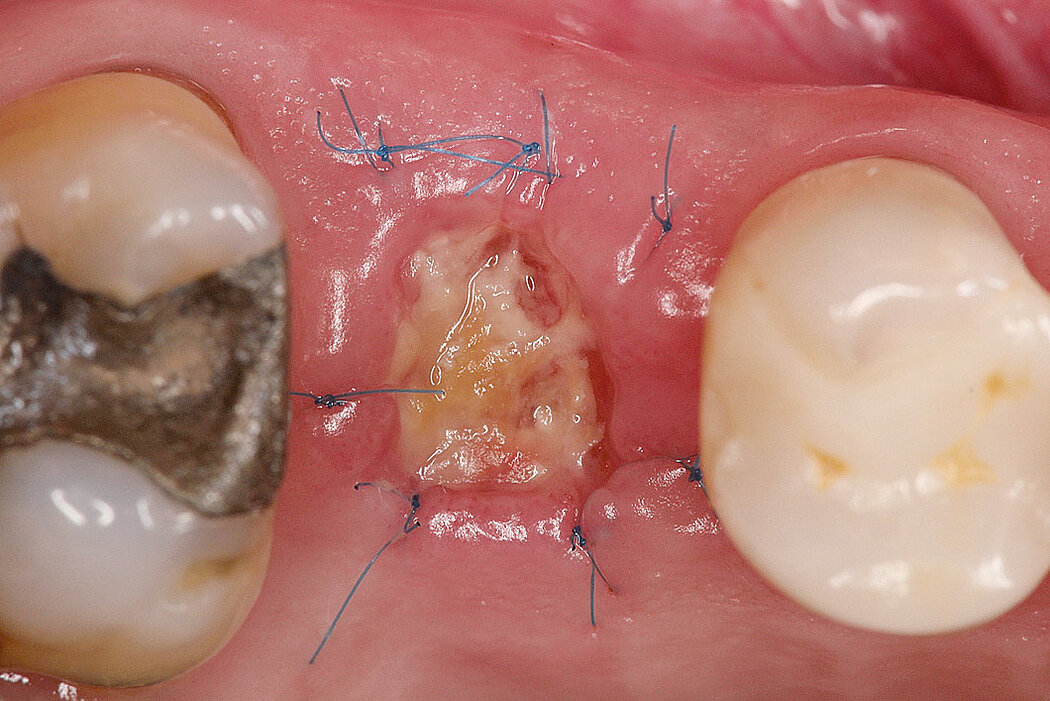
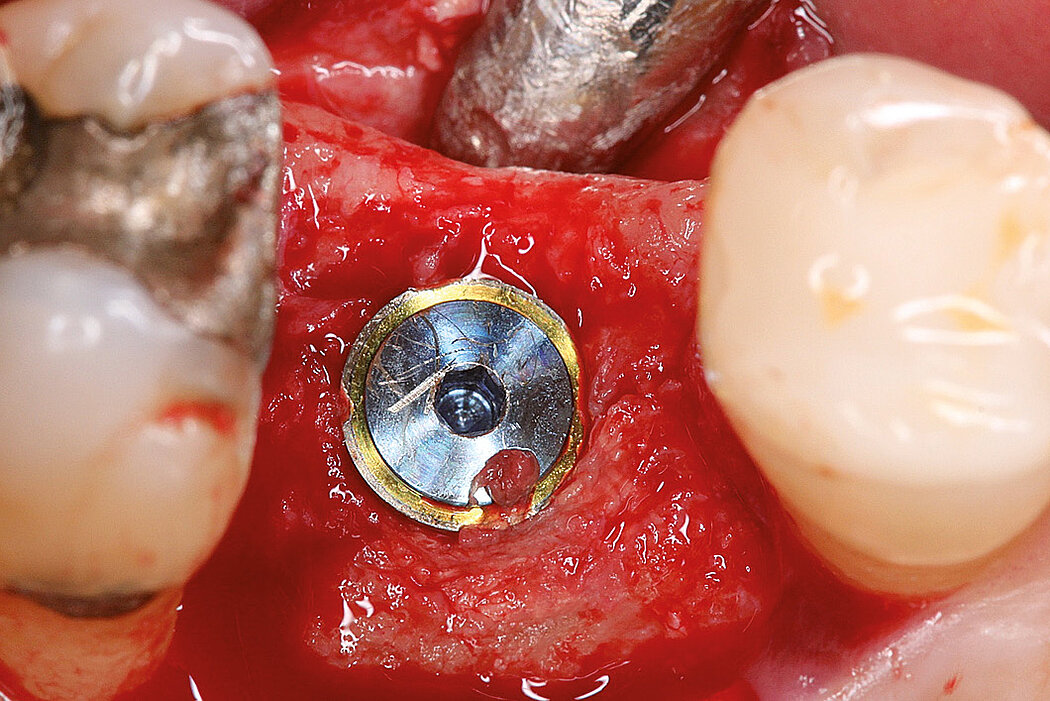
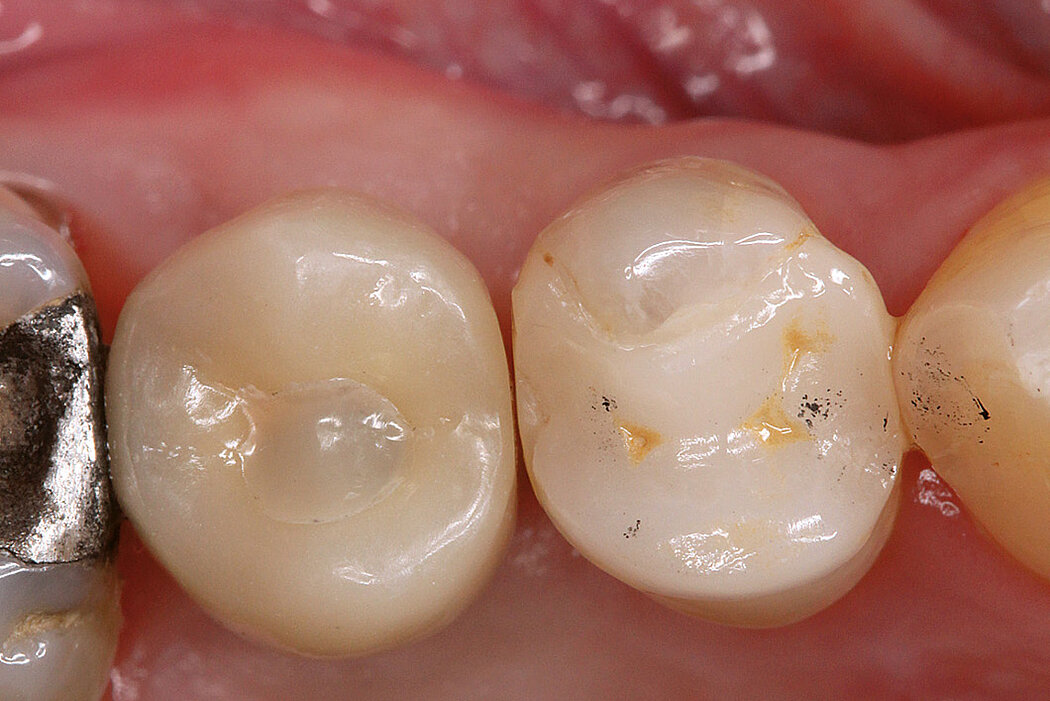
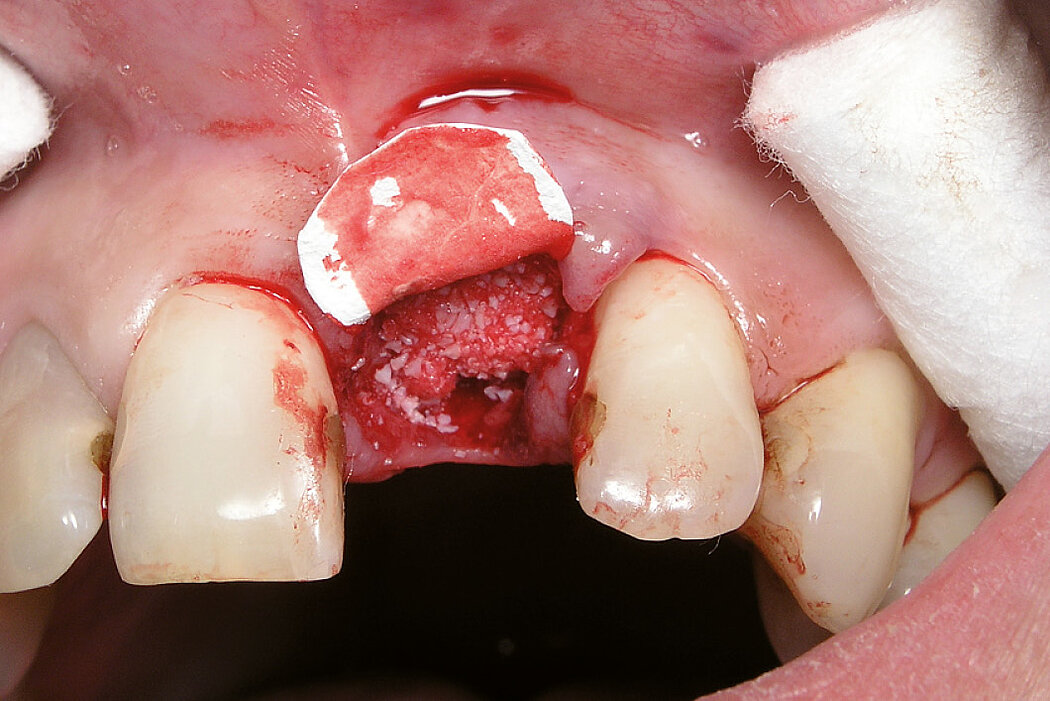
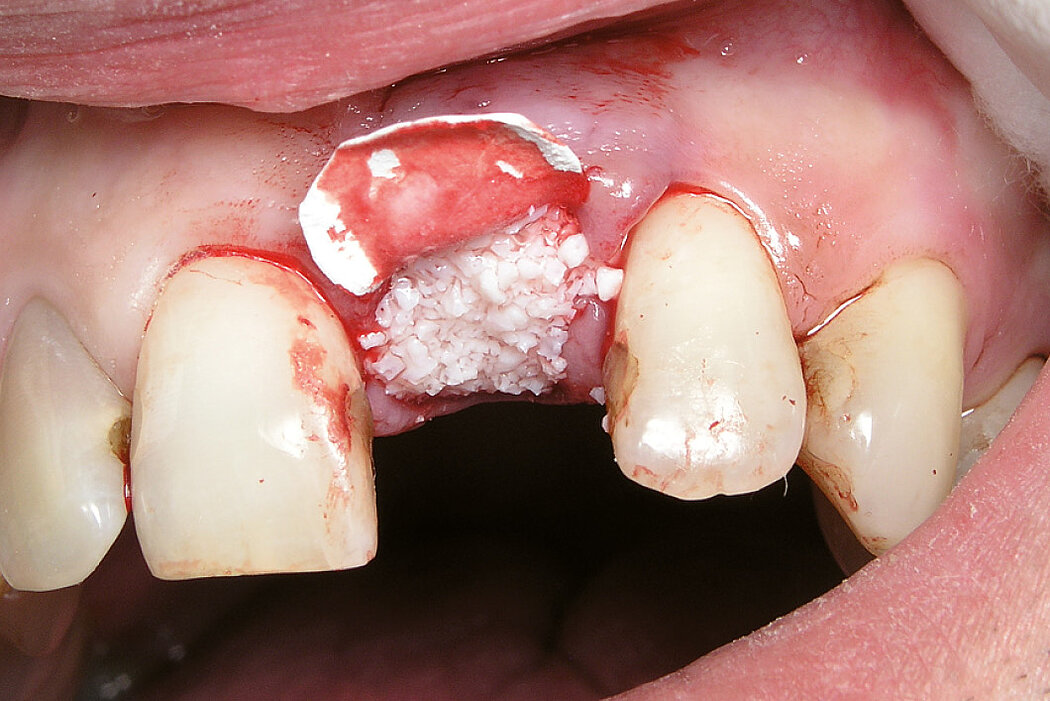
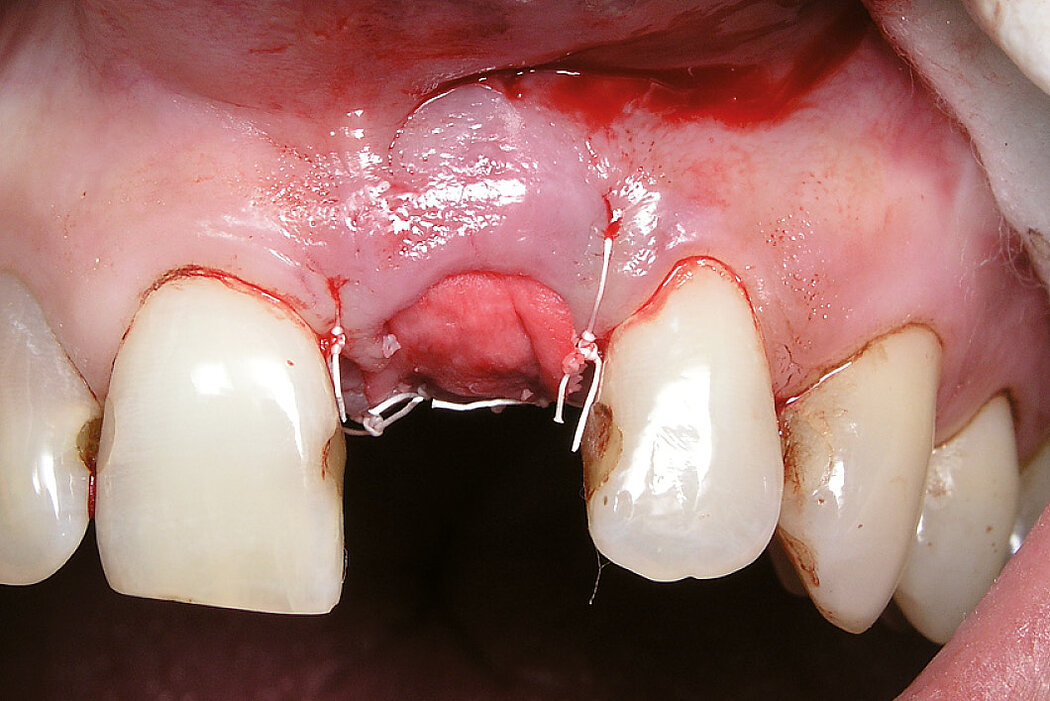
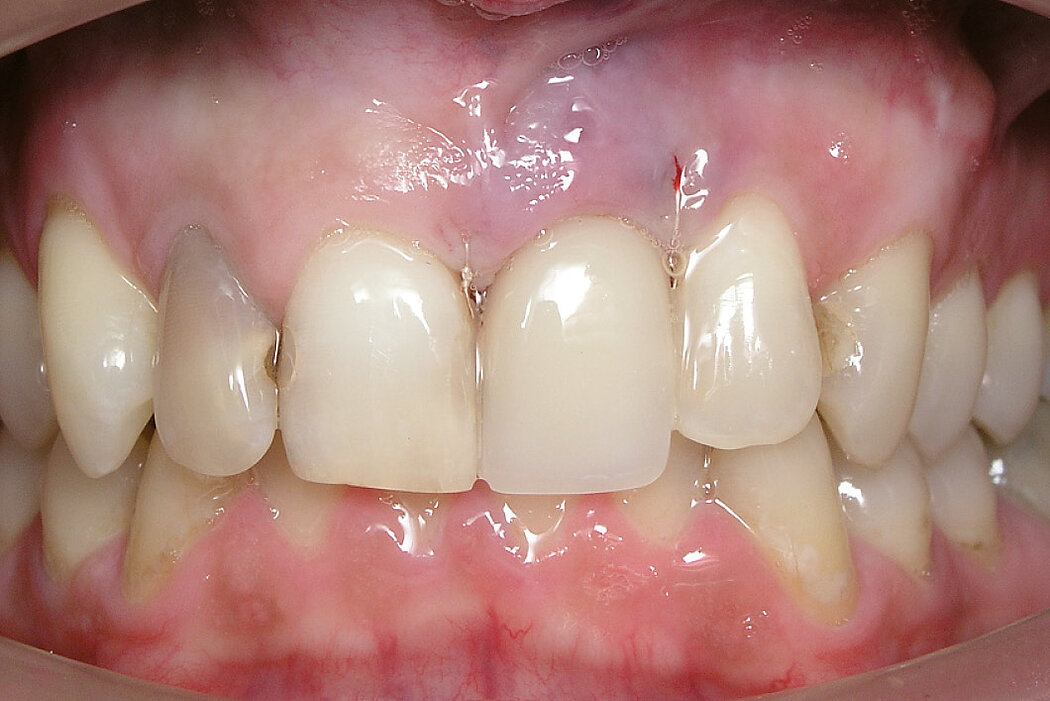
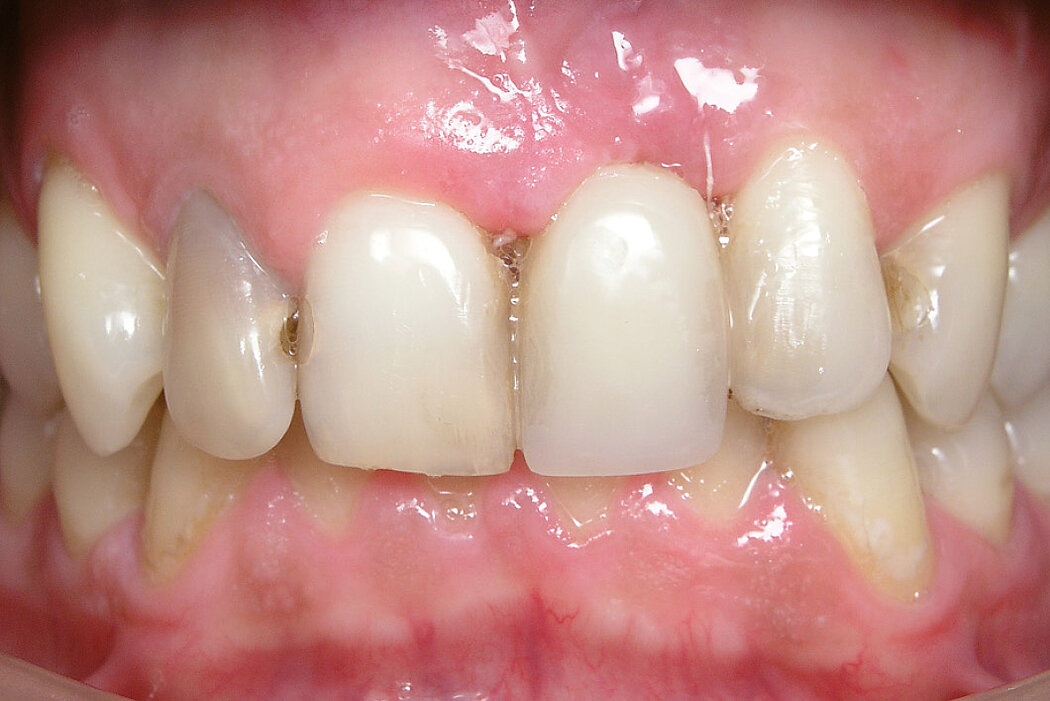
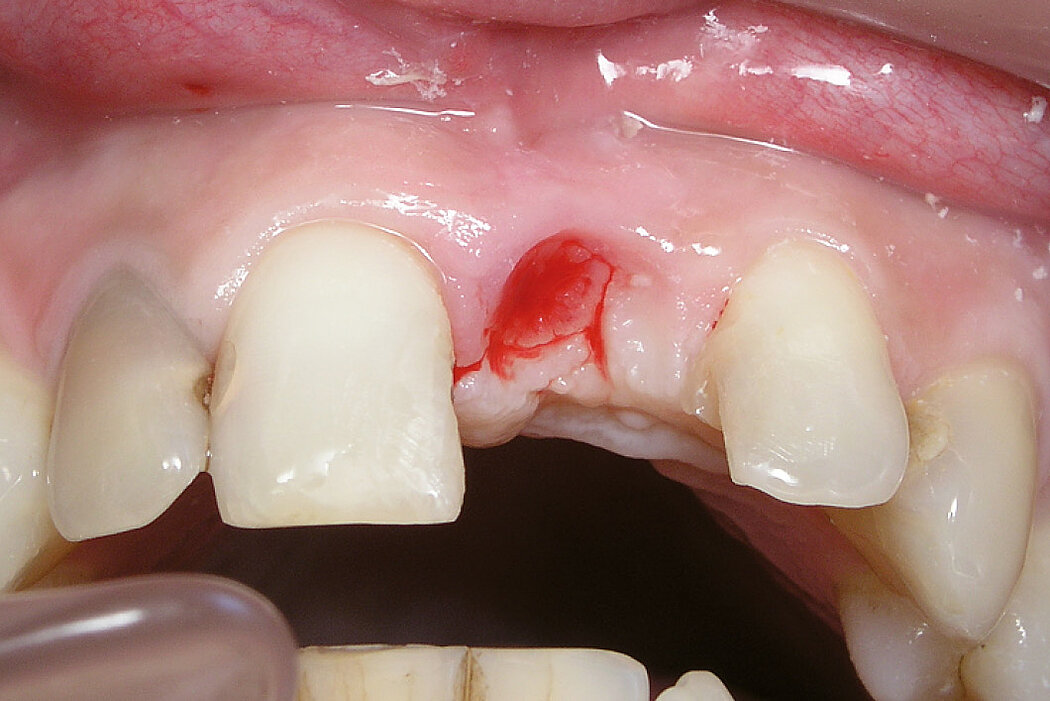
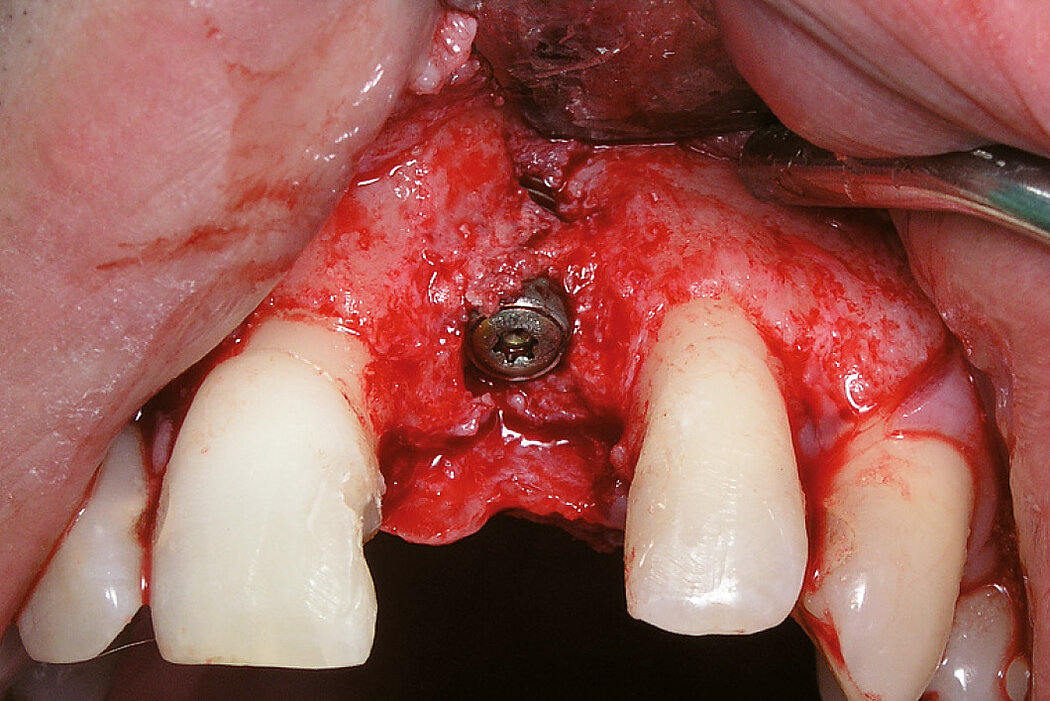
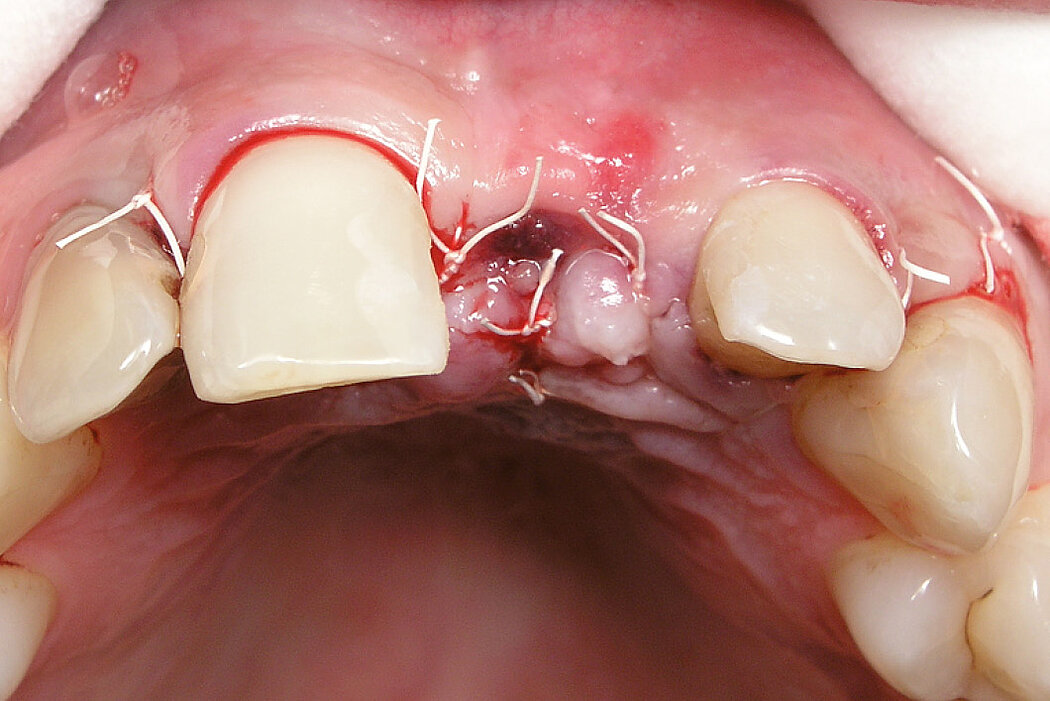
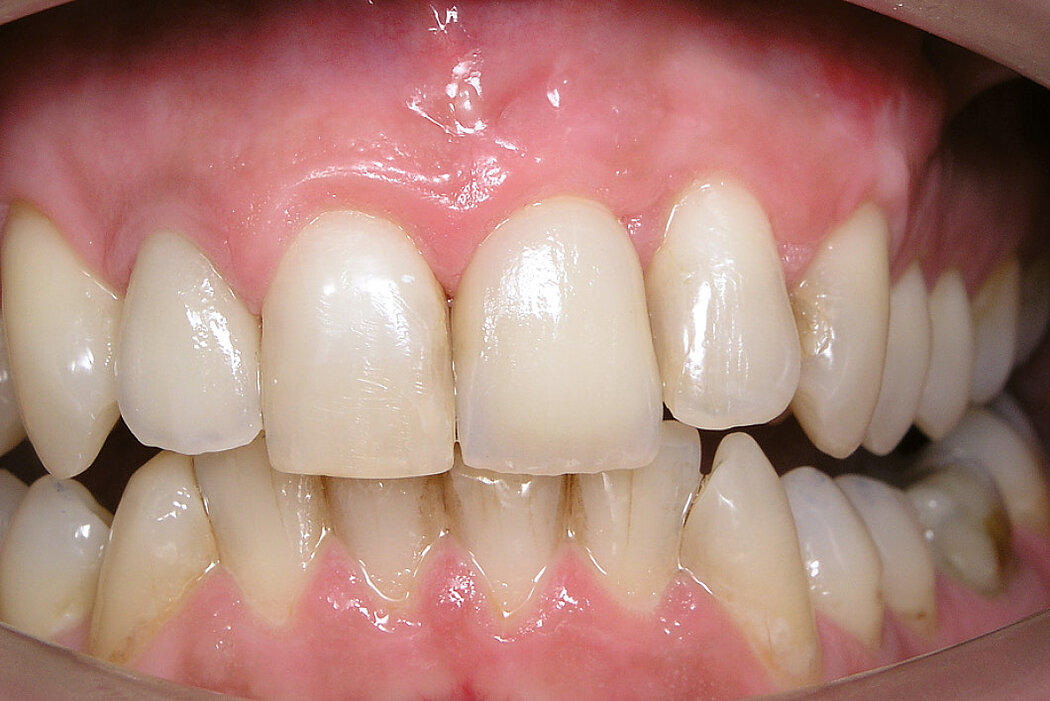
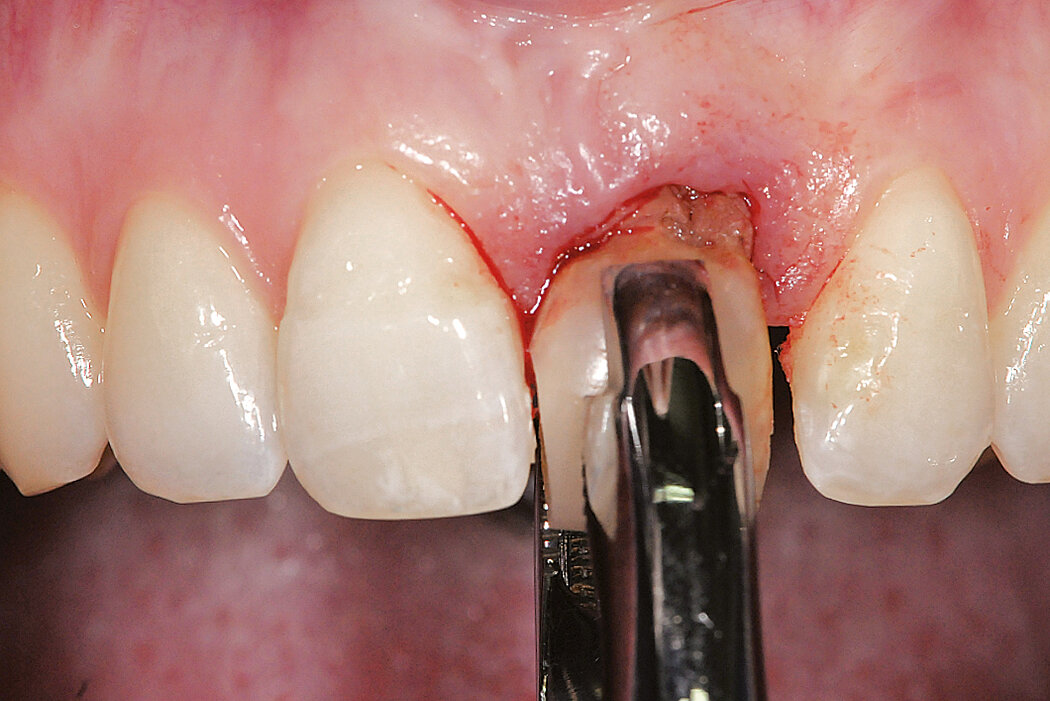
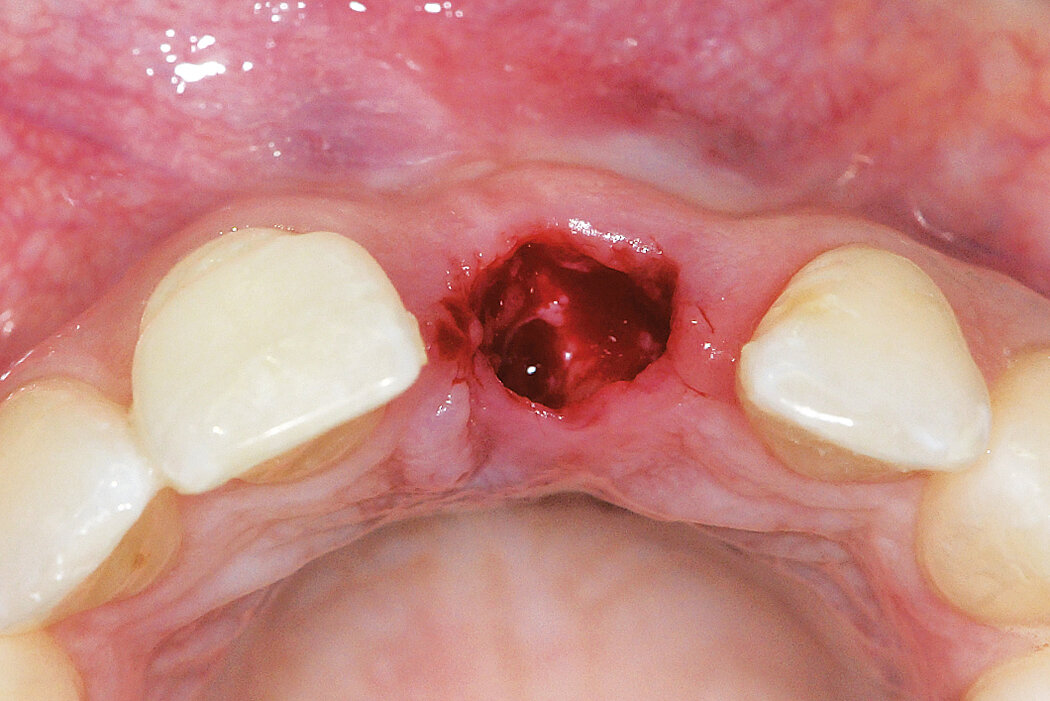
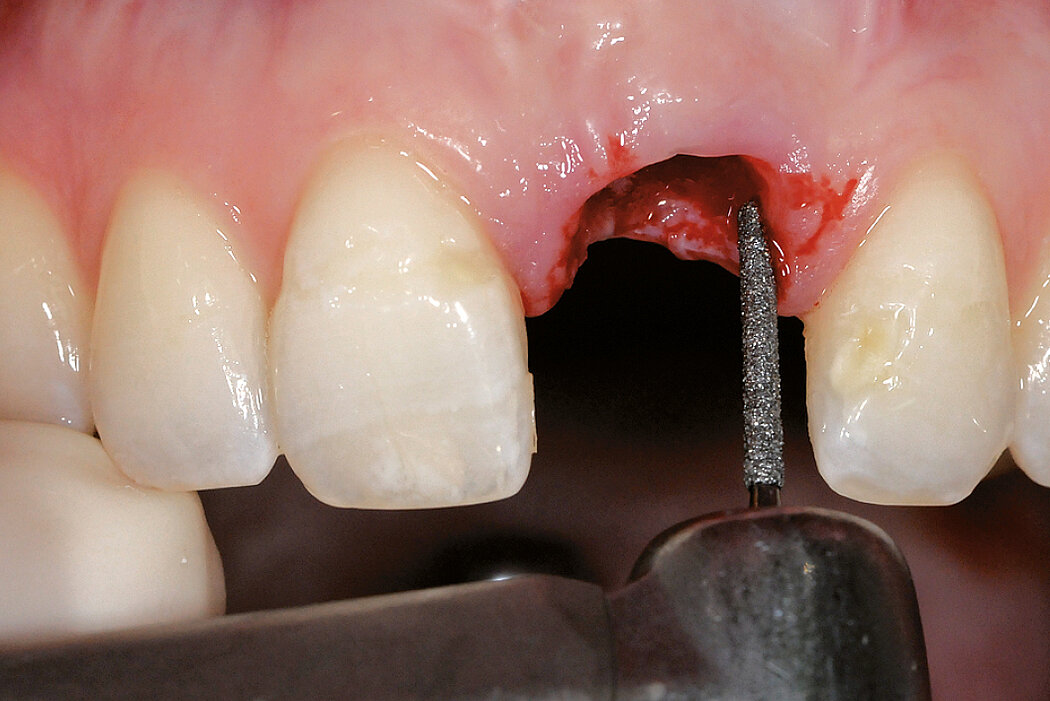
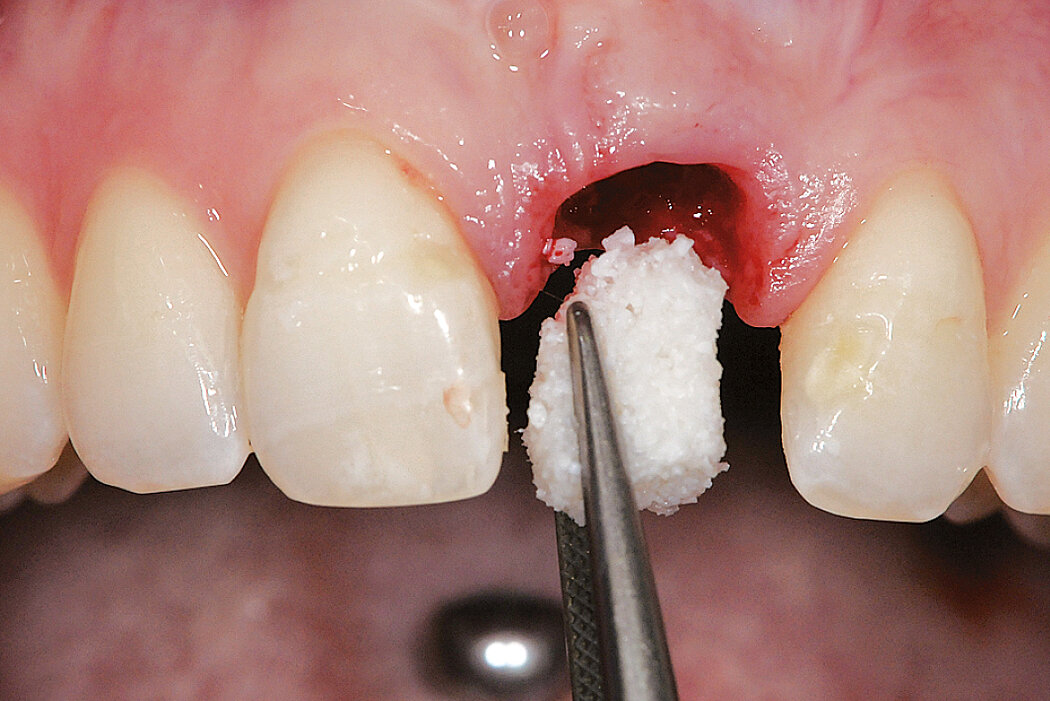
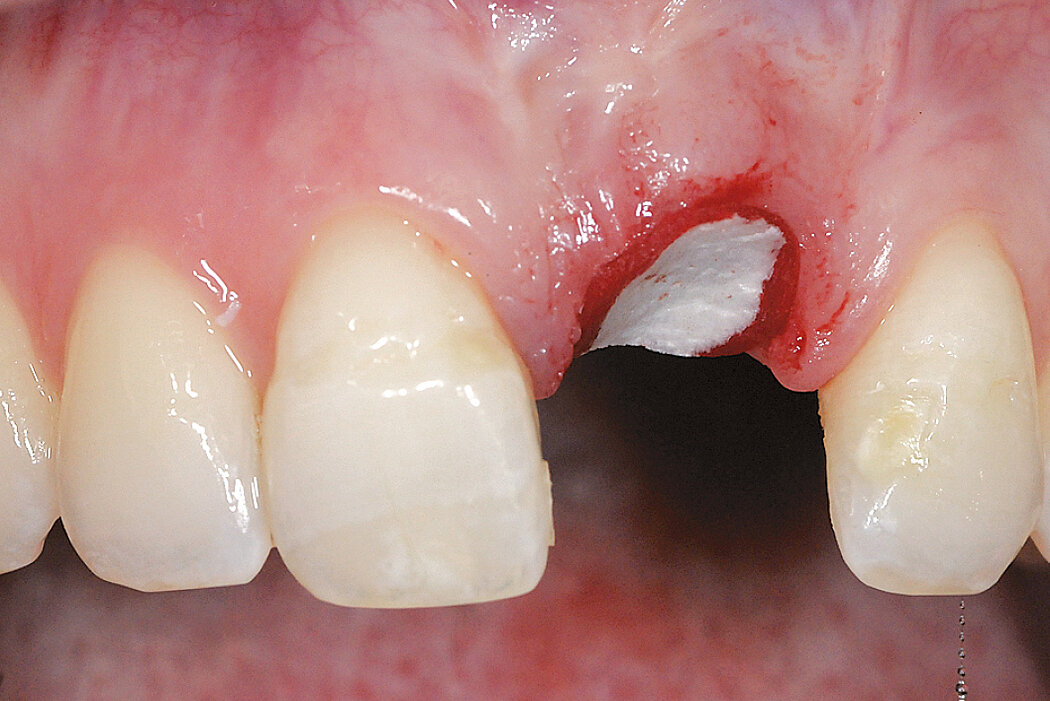
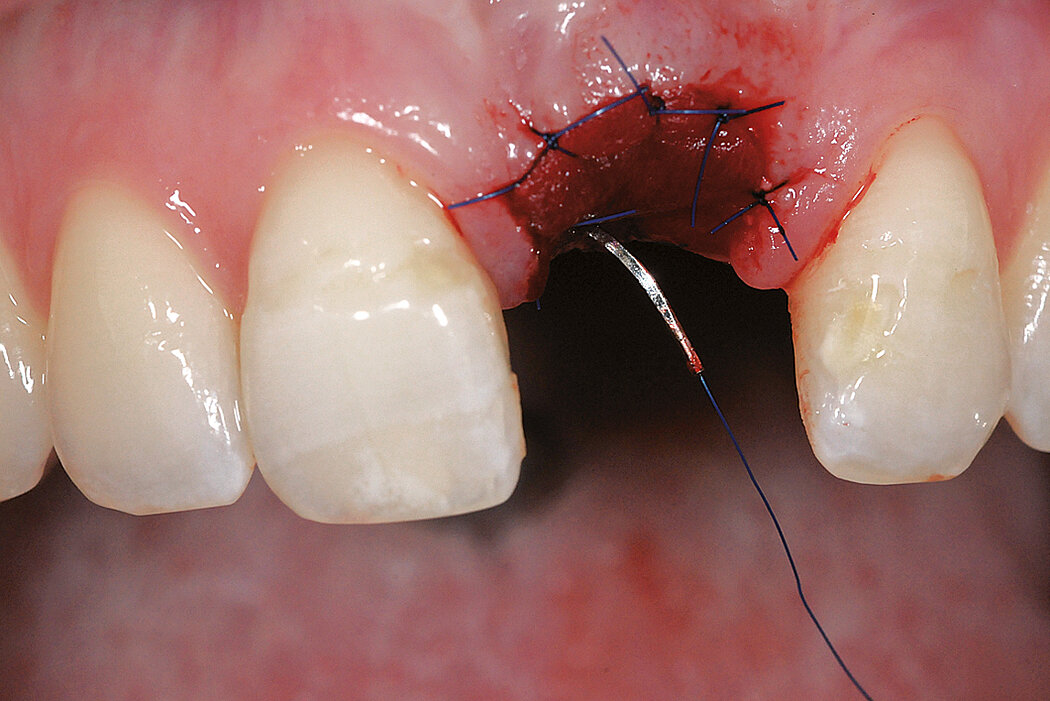
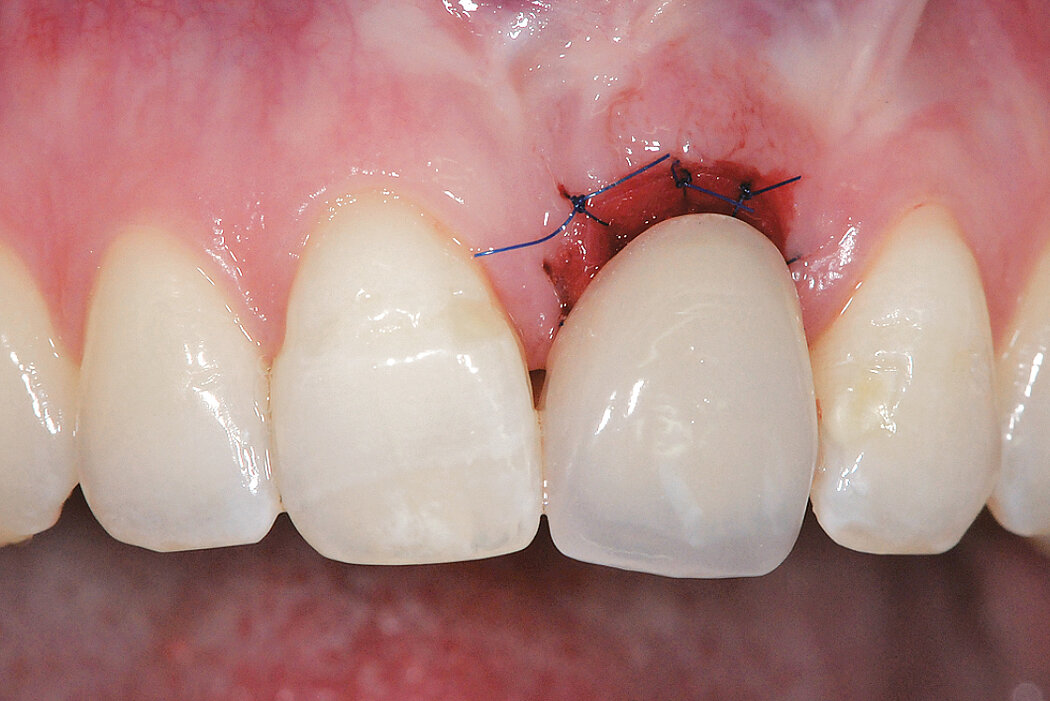
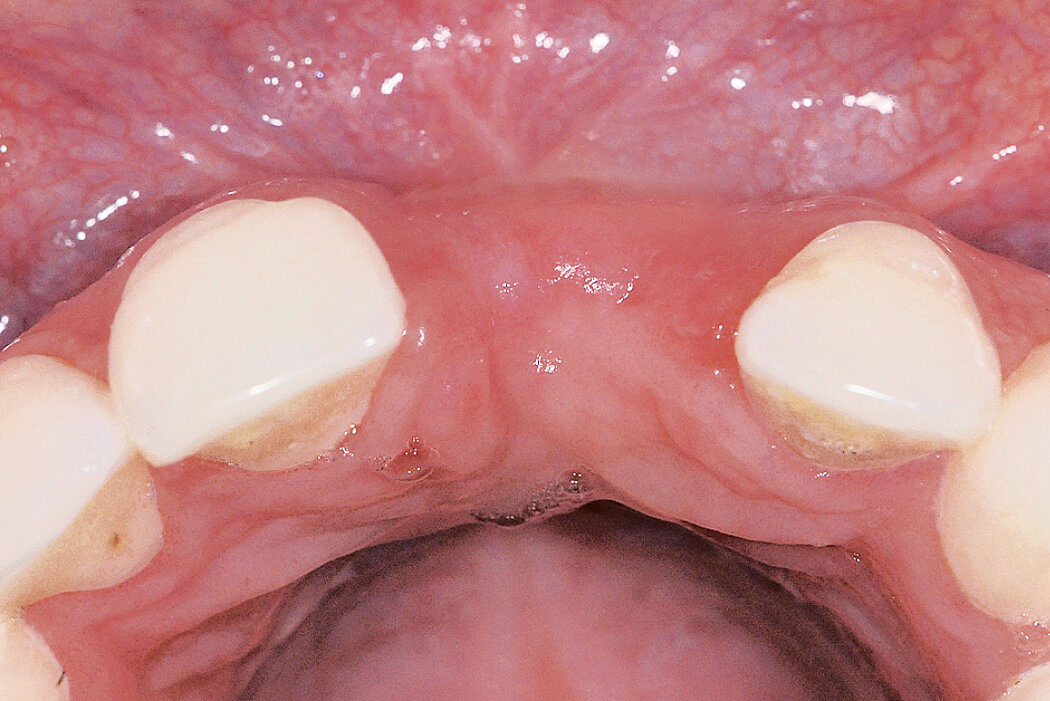
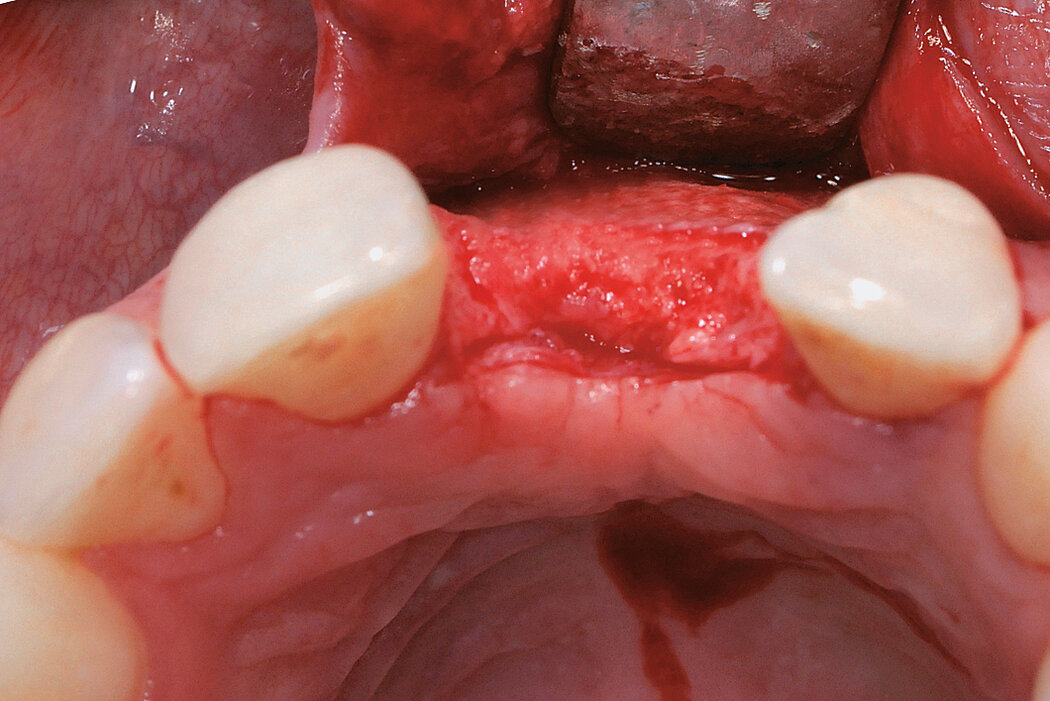
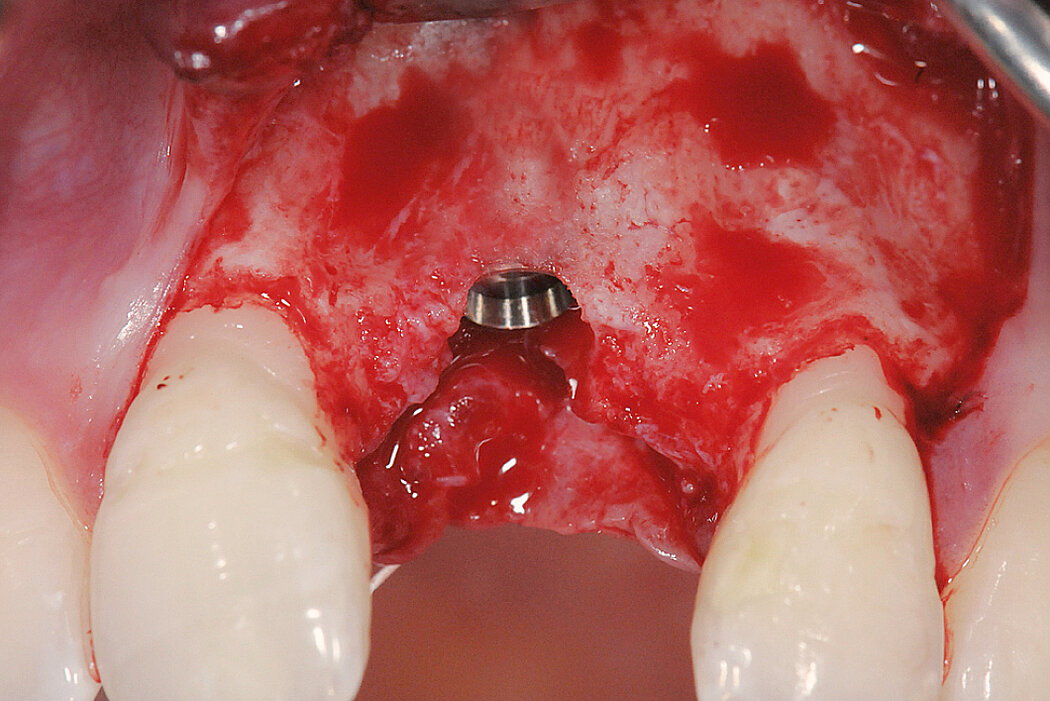
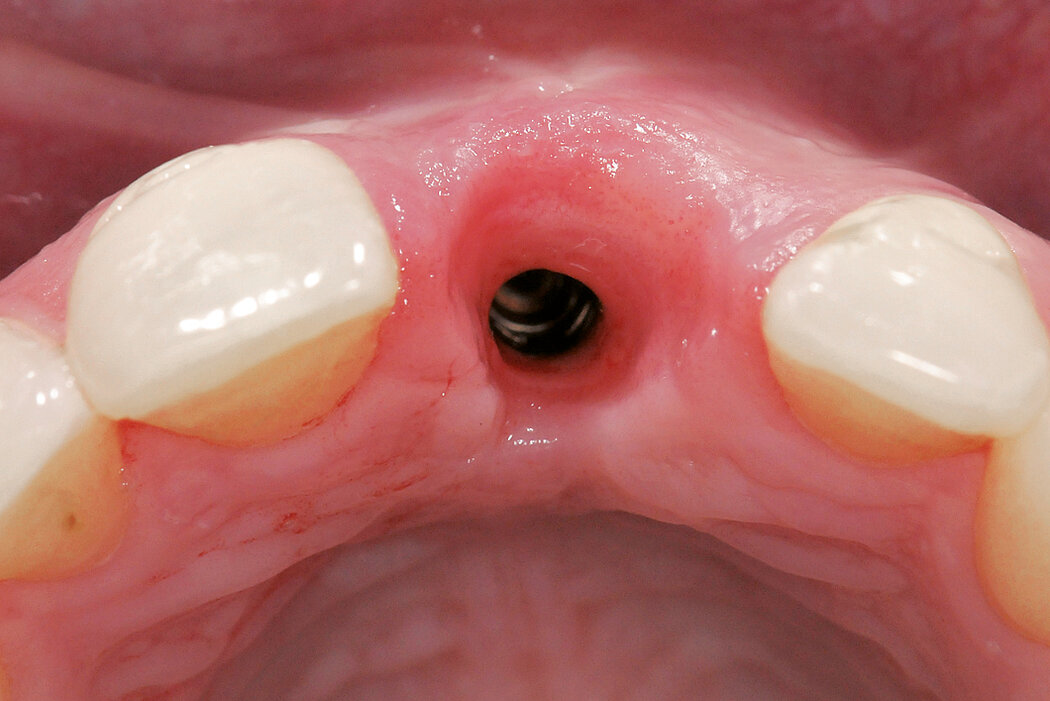
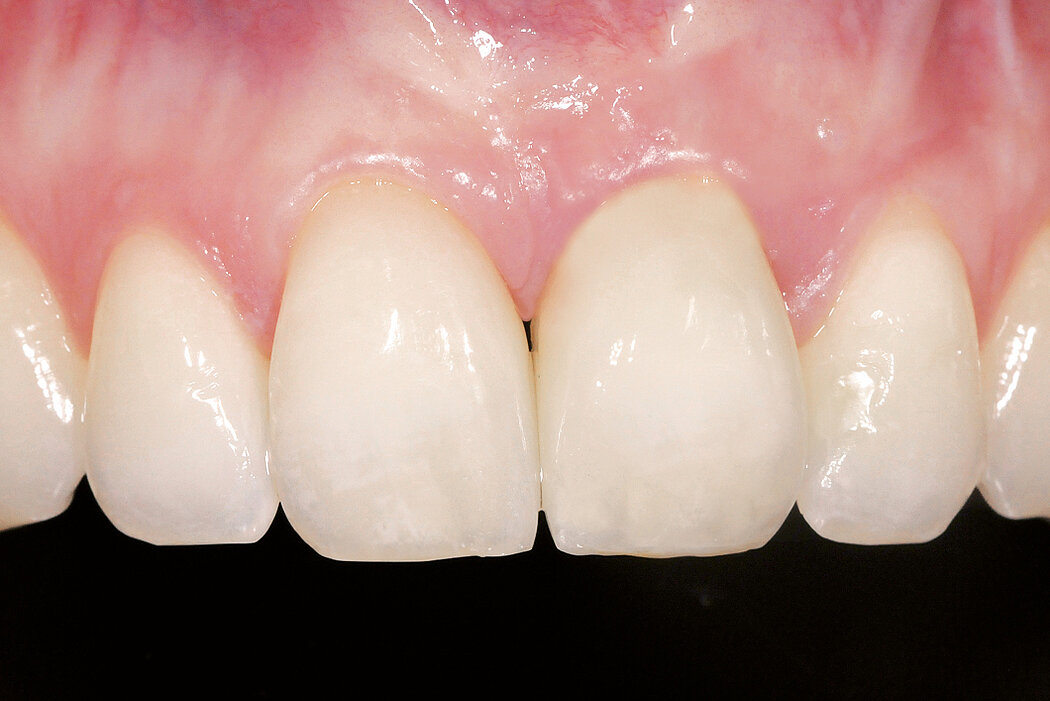
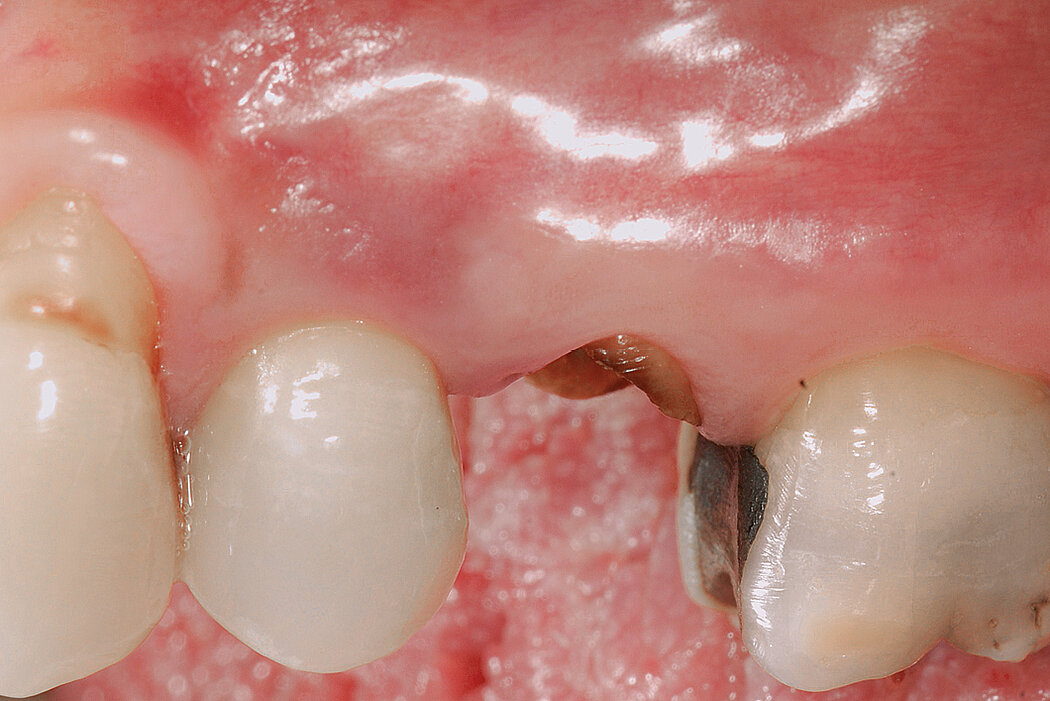
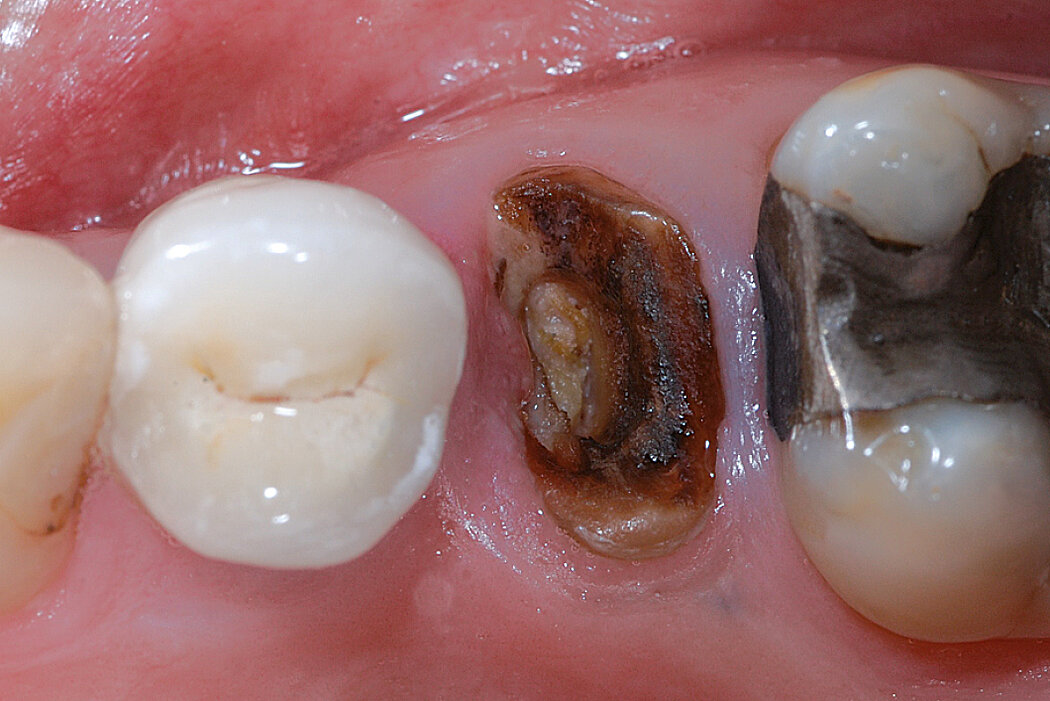
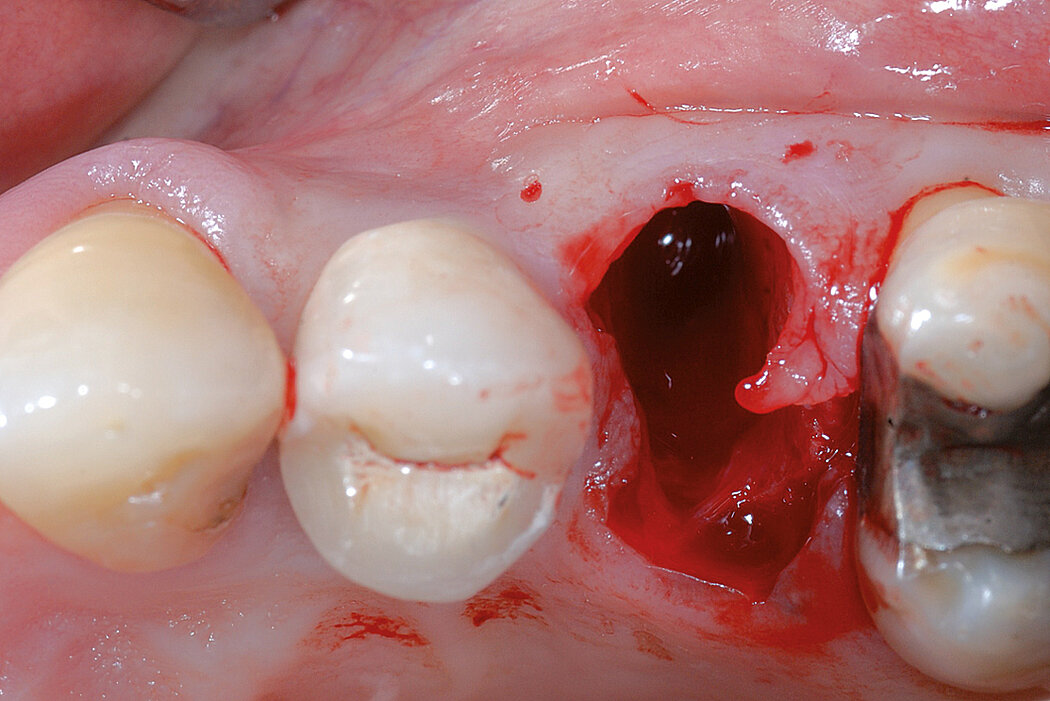
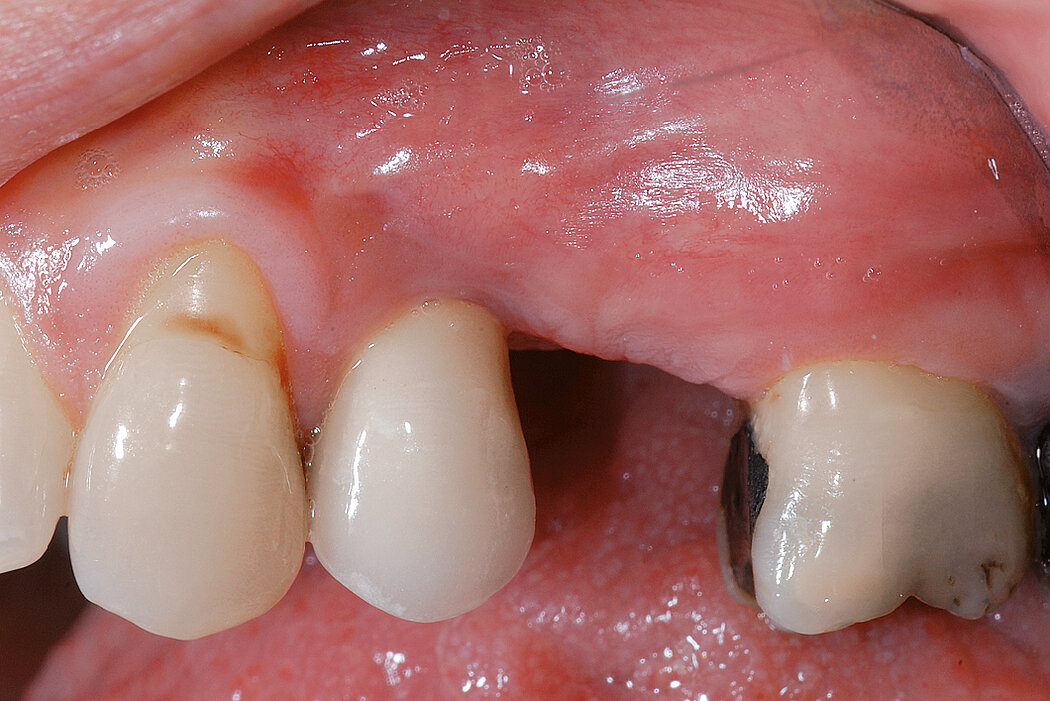
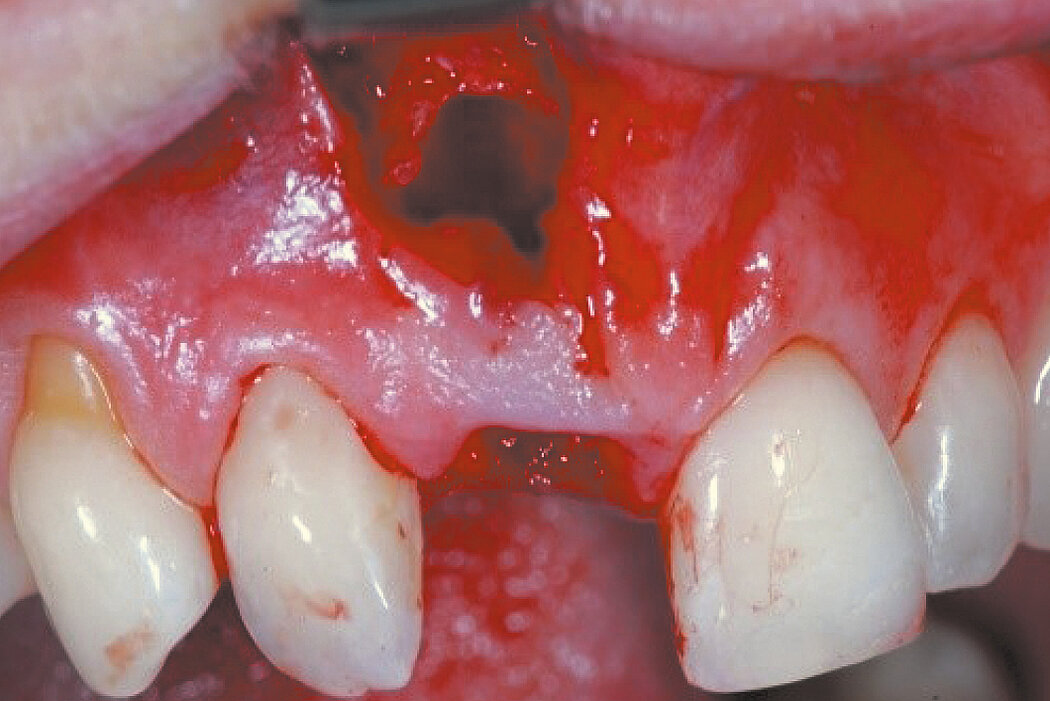
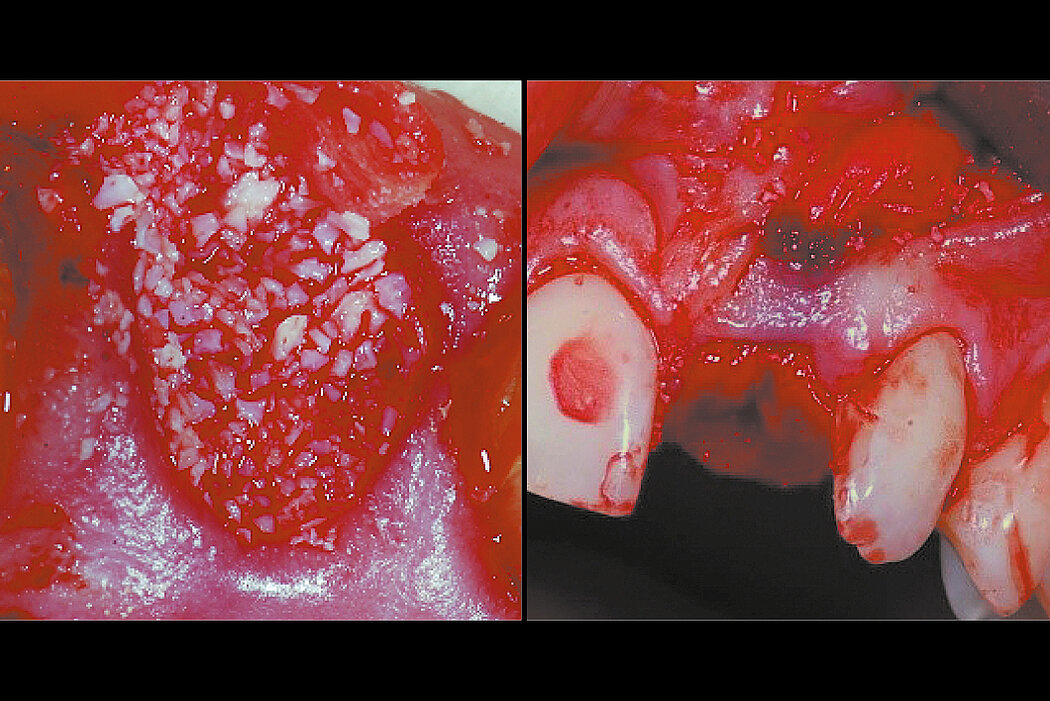
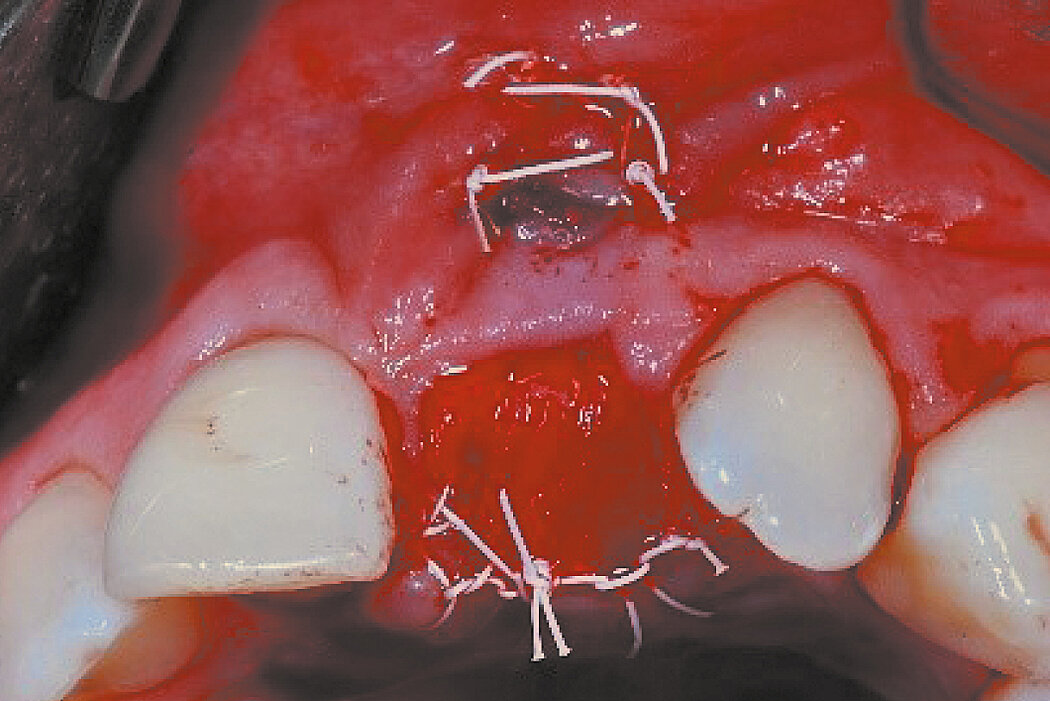
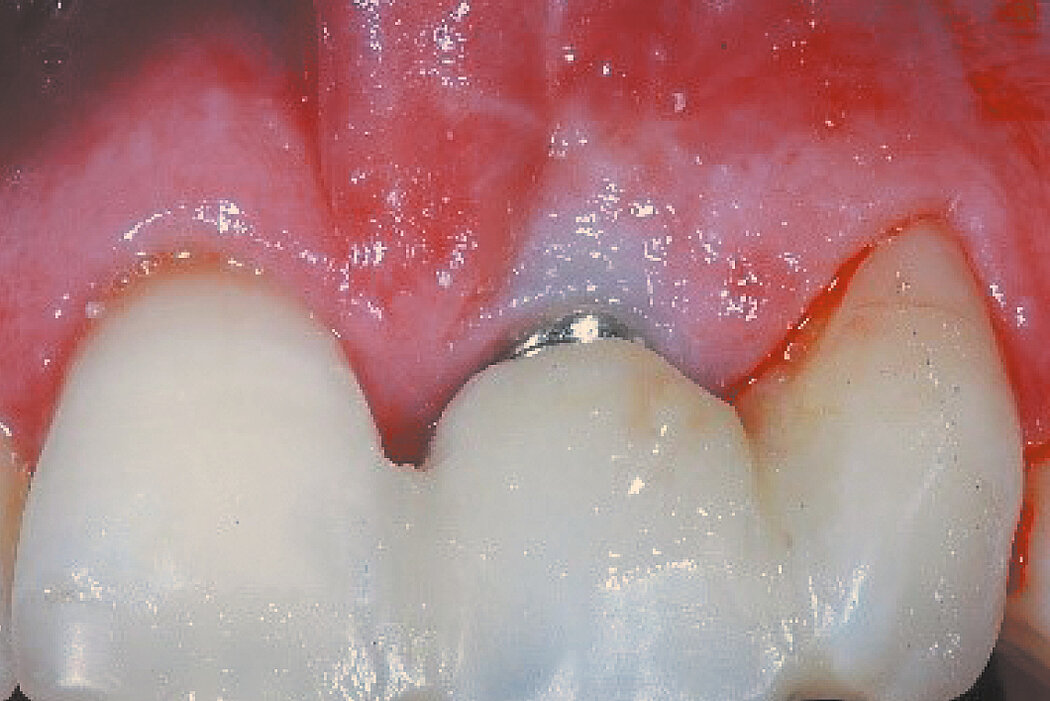
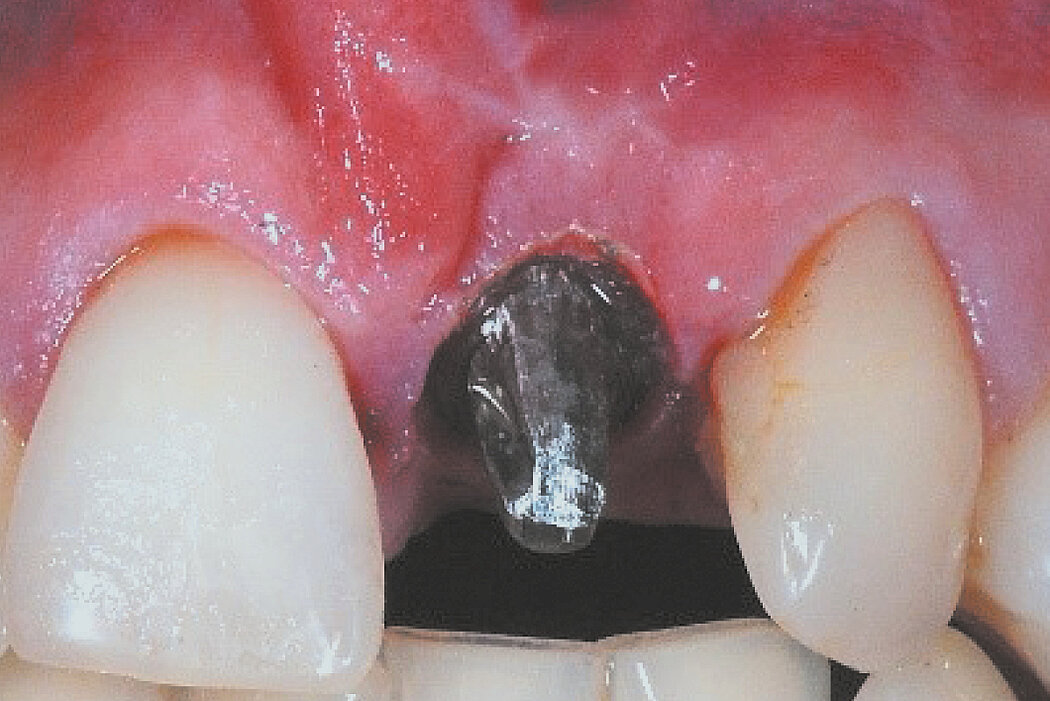
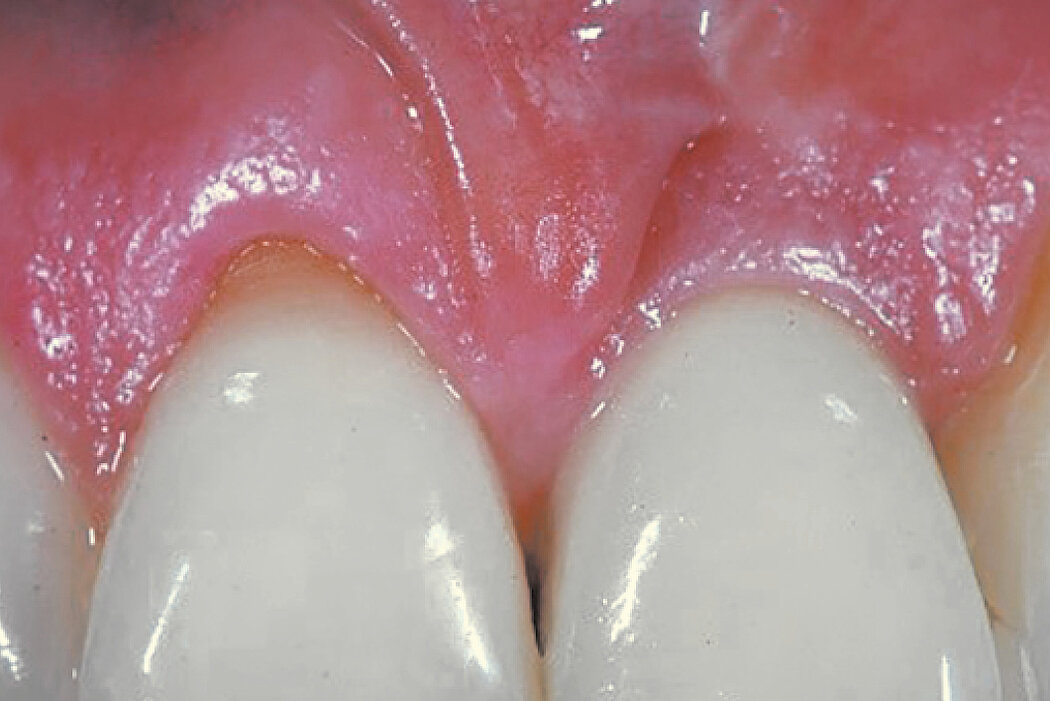
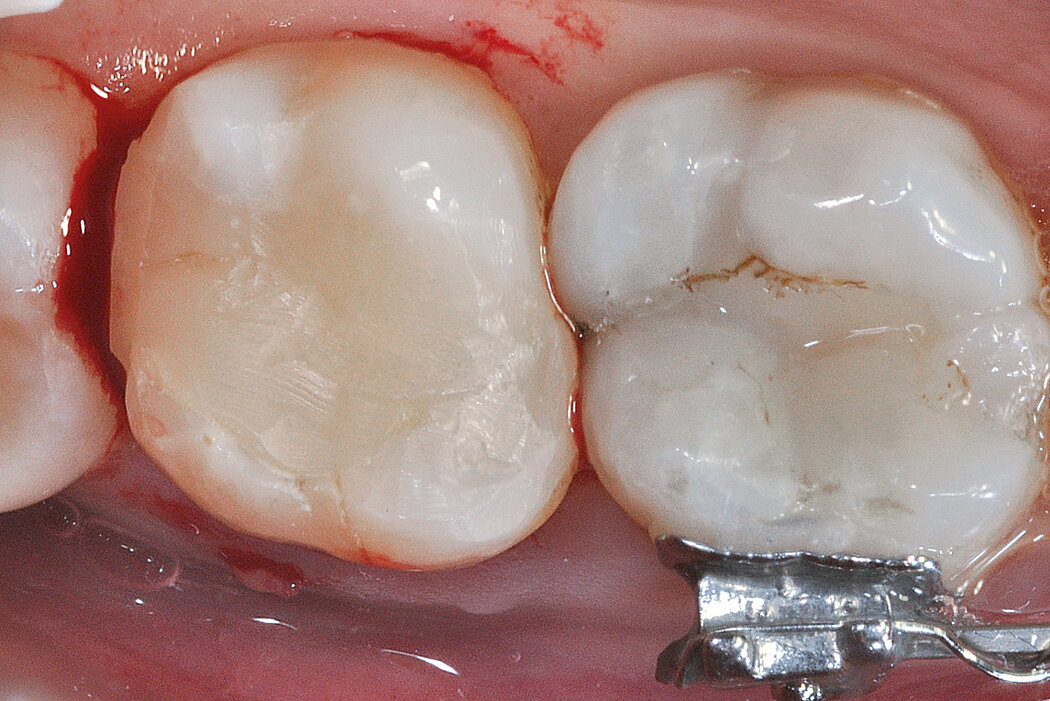
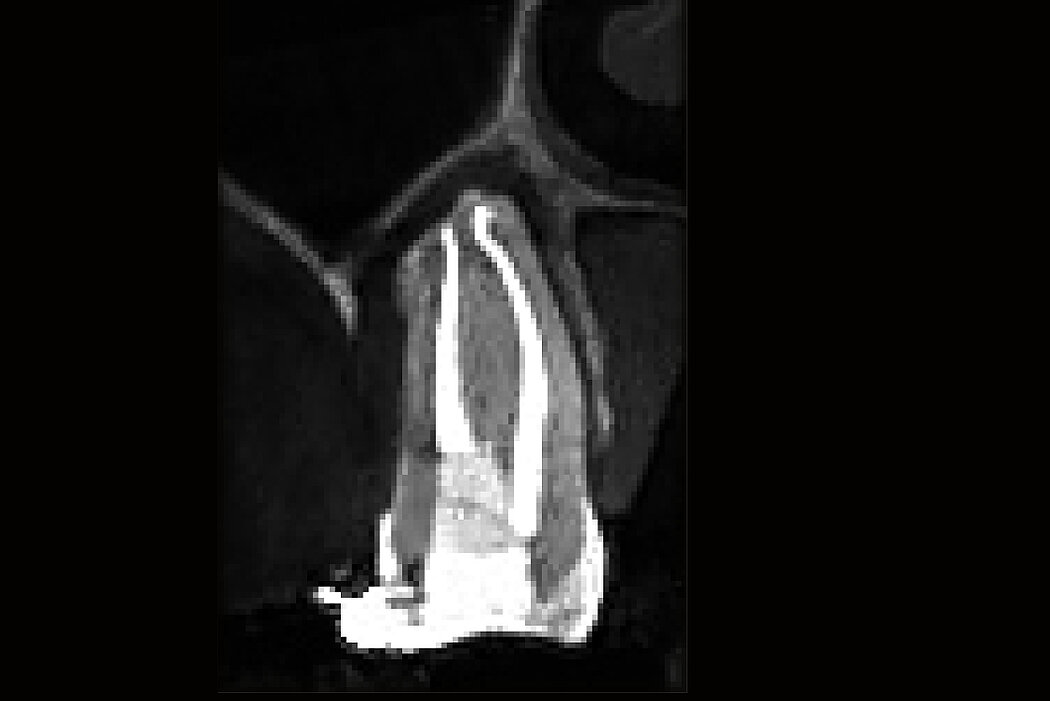
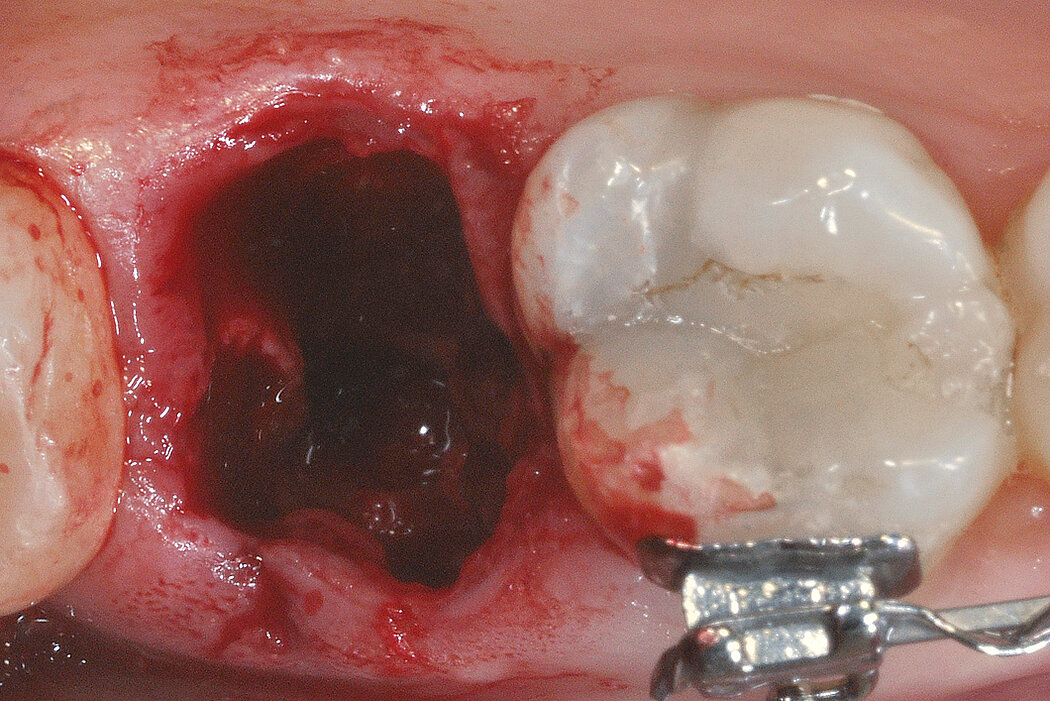
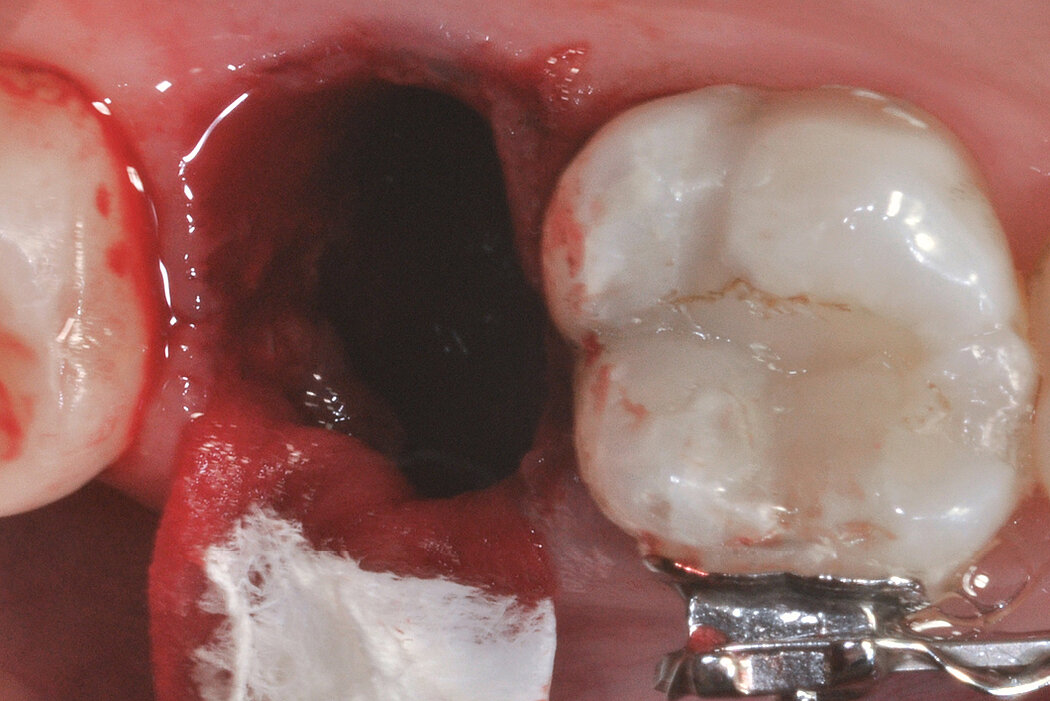
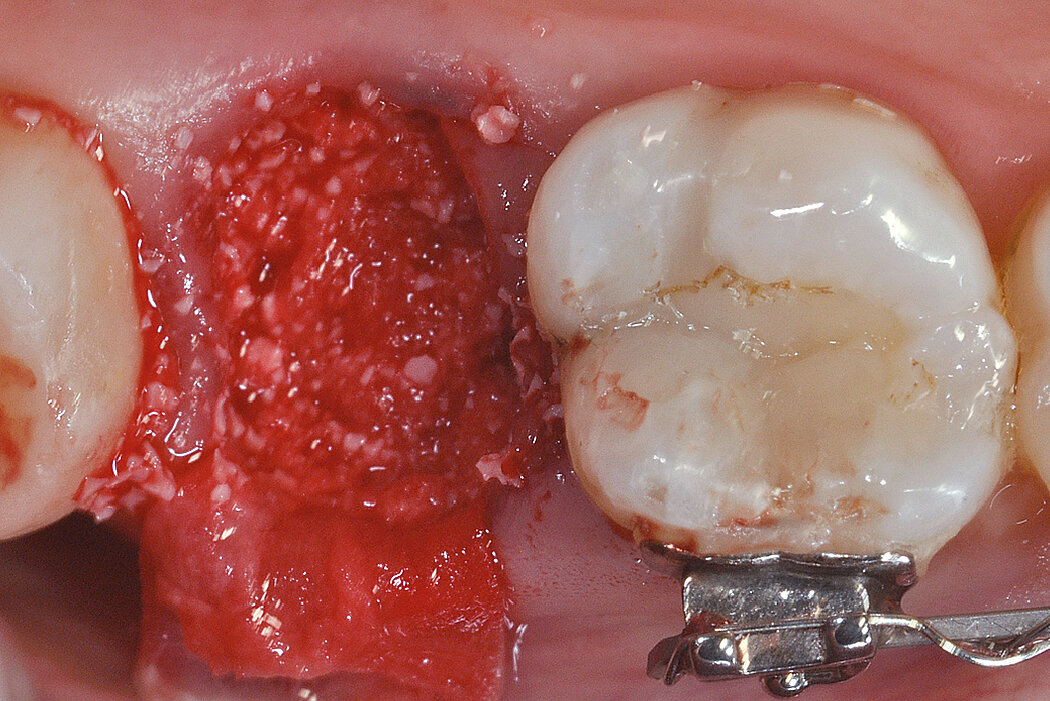
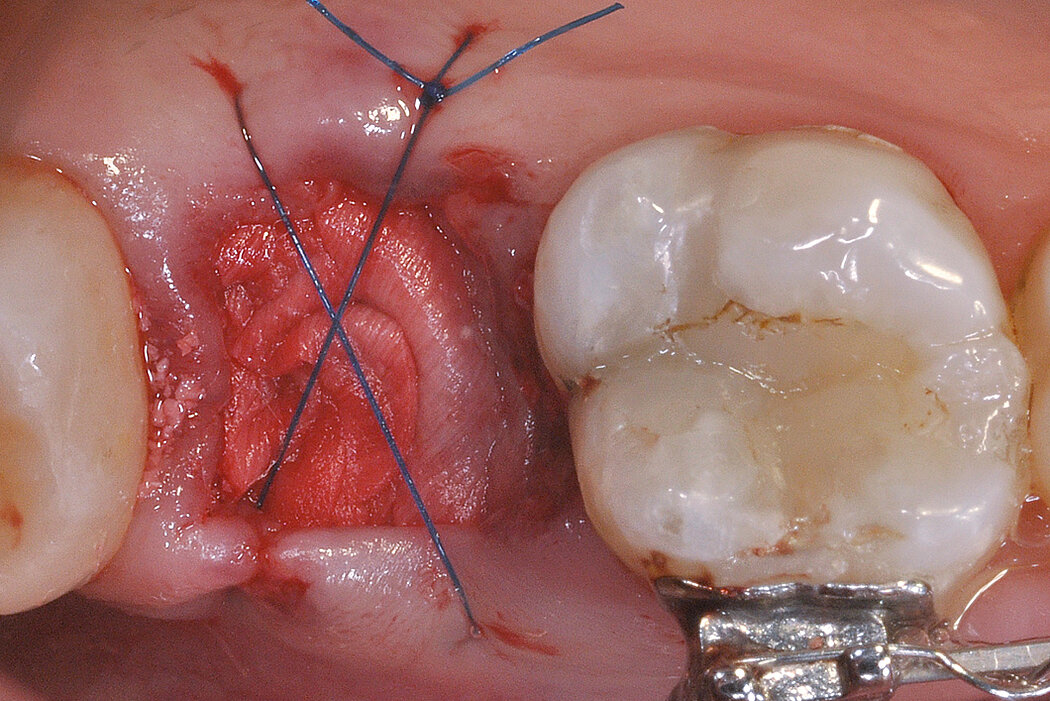
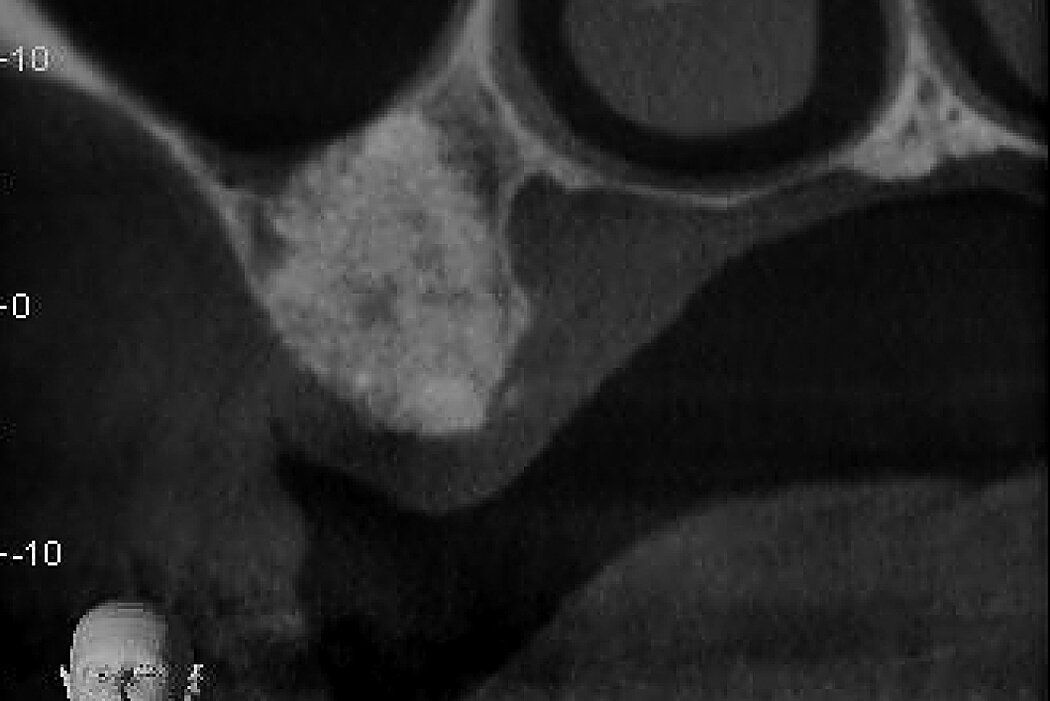
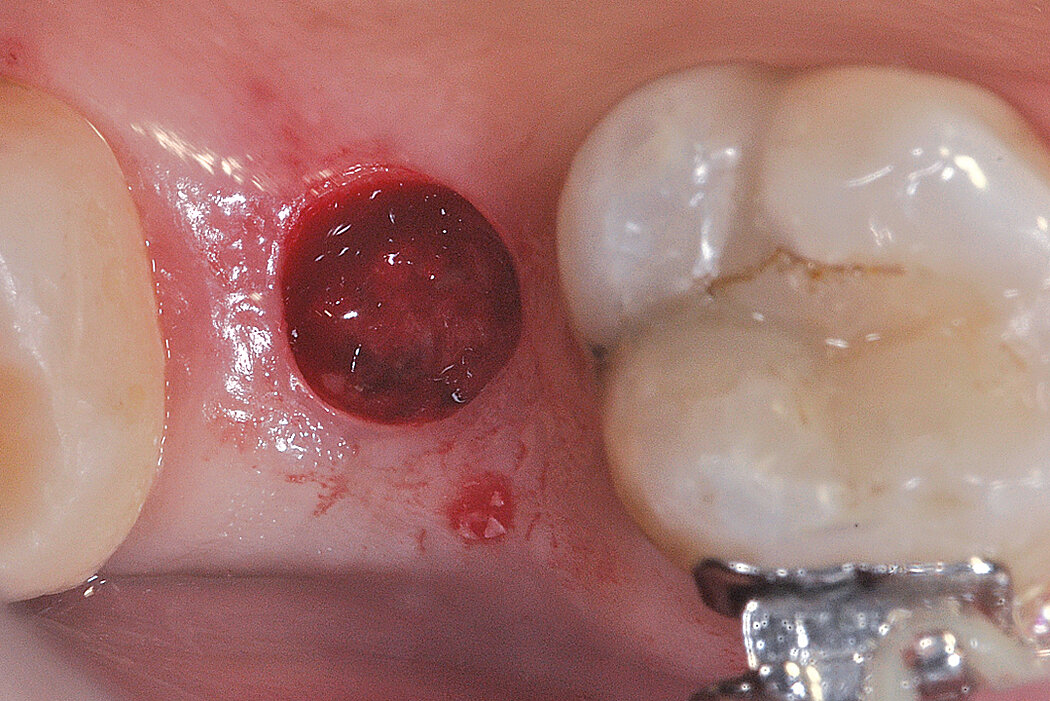
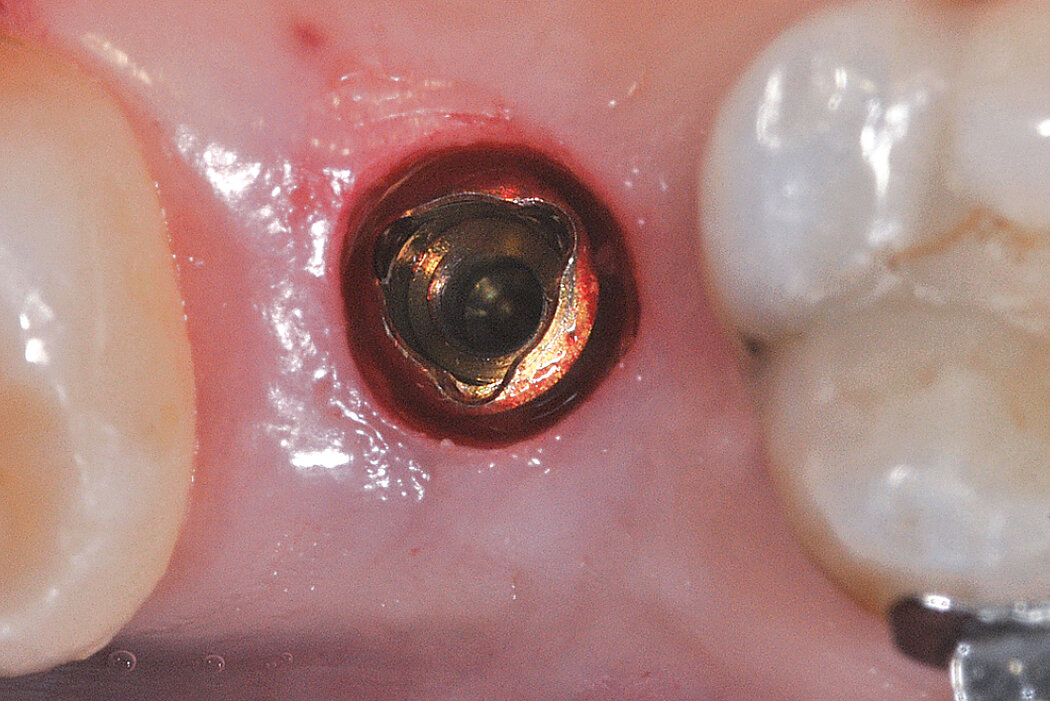
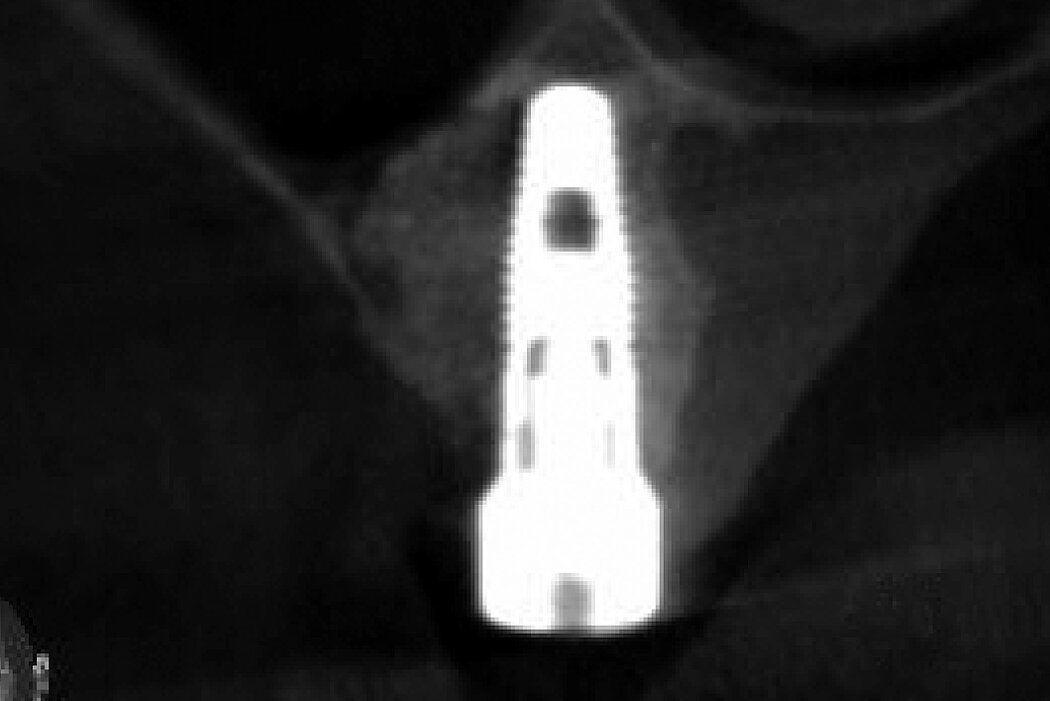
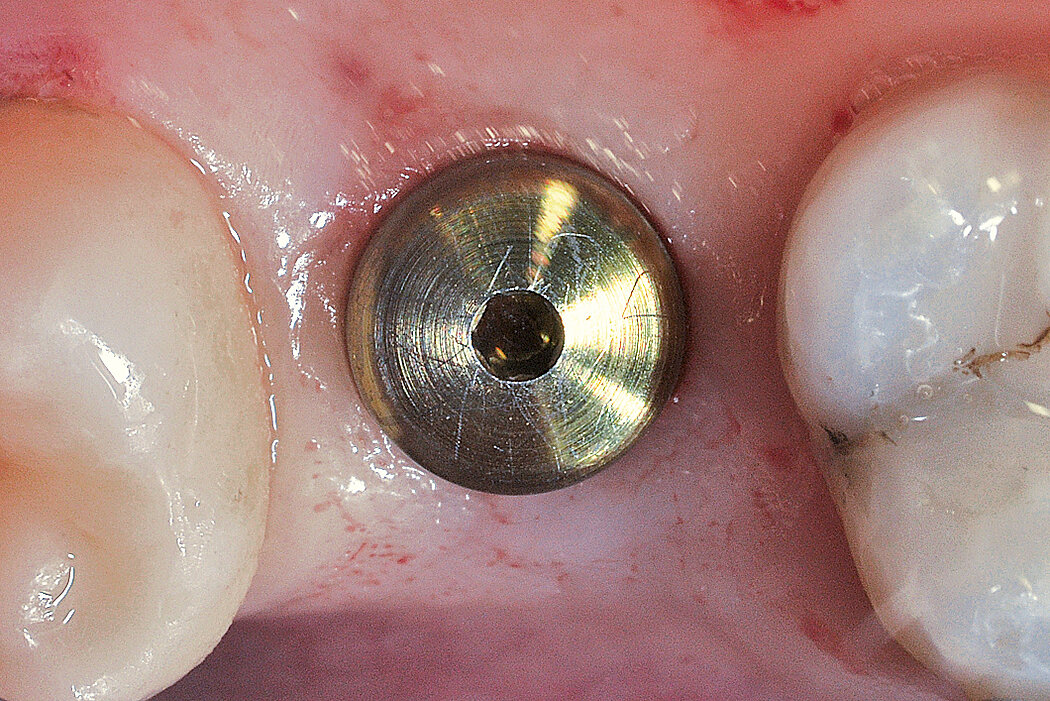
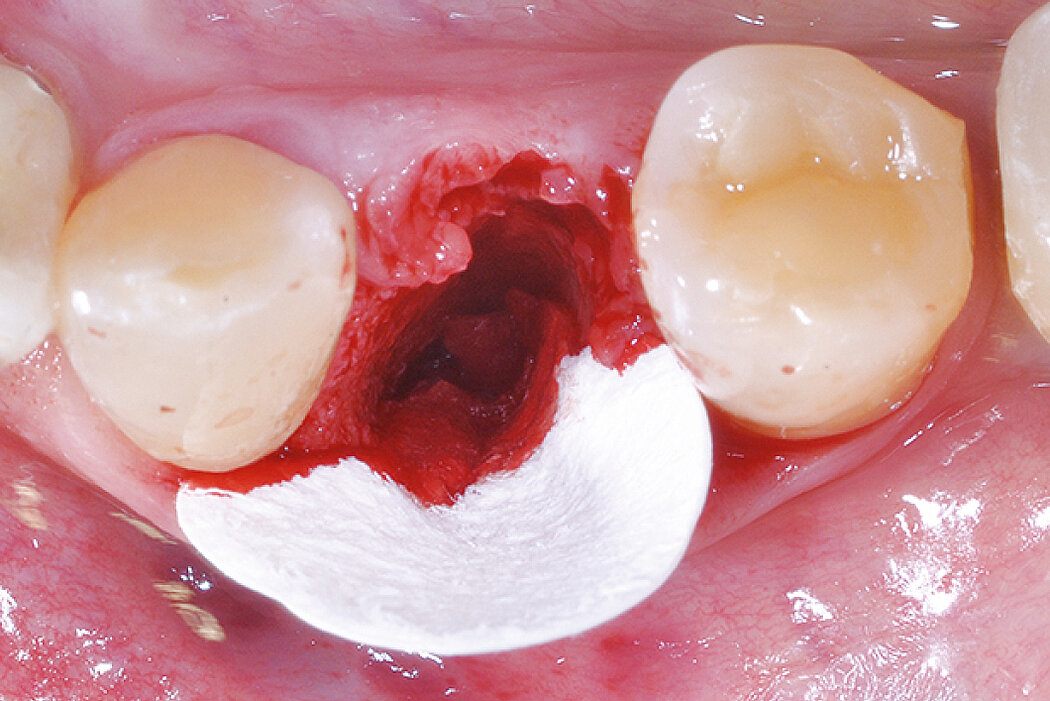
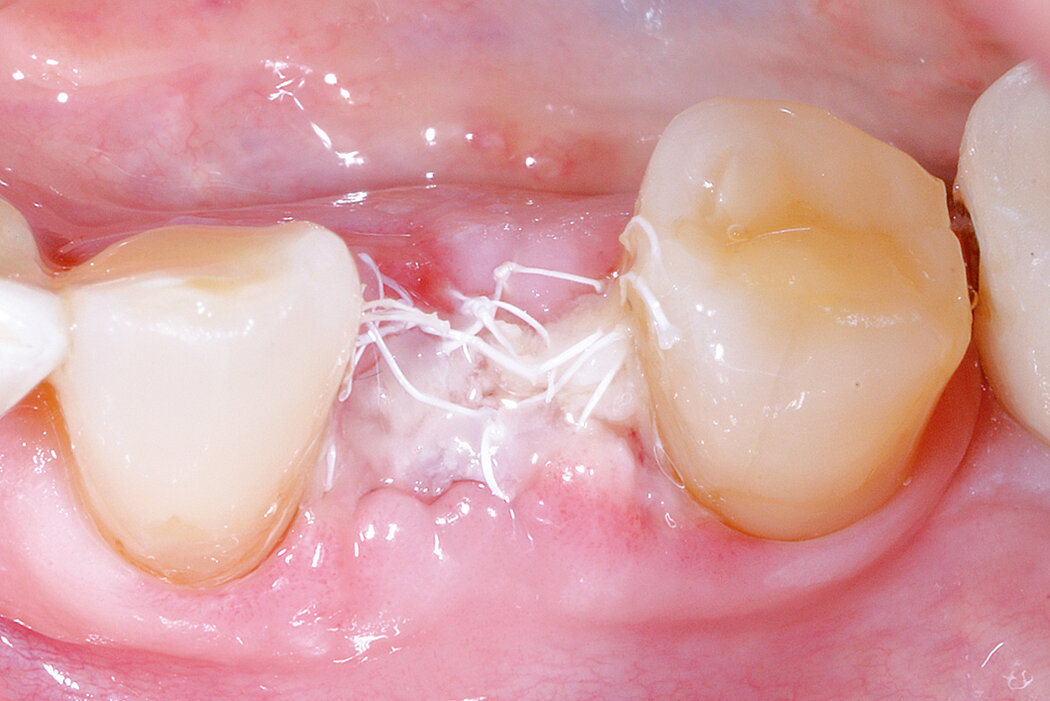
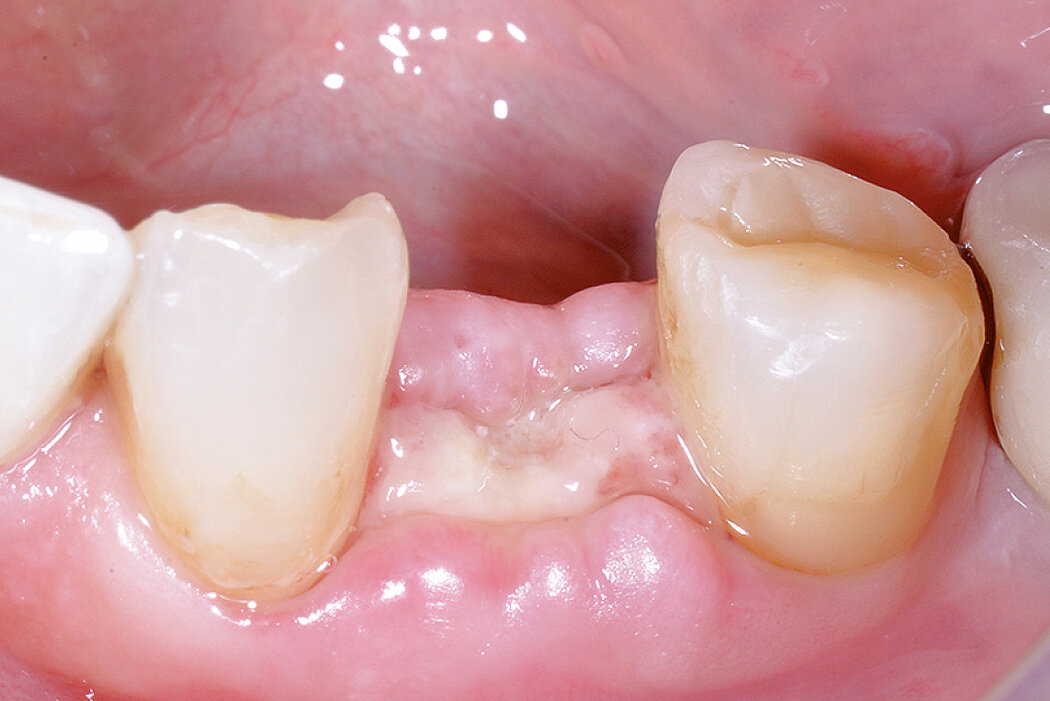
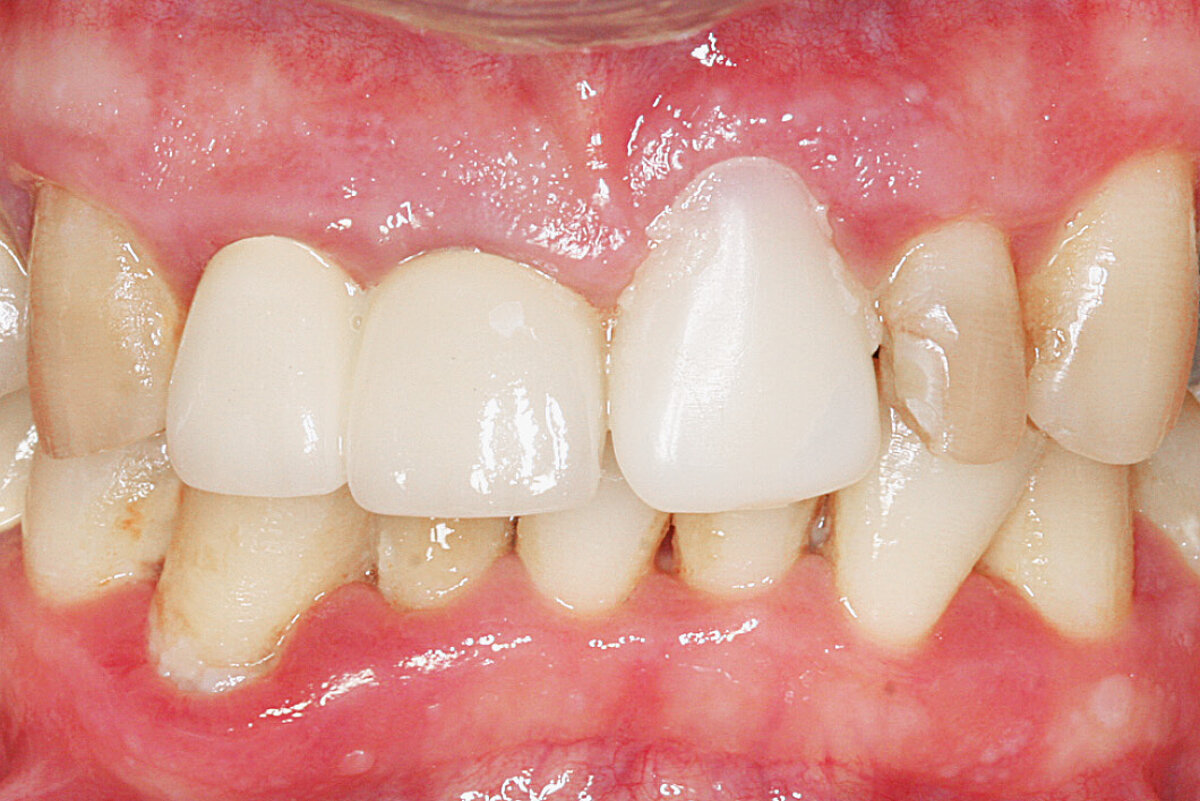
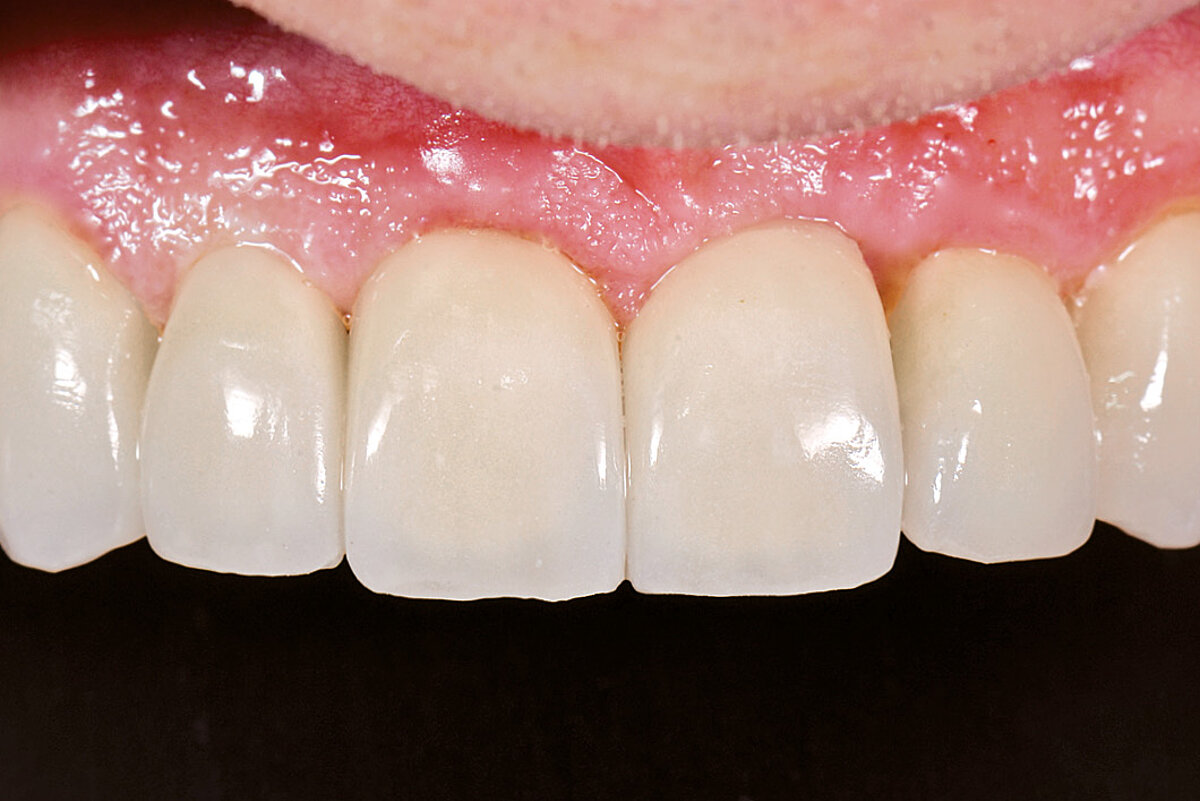
Ridge Preservation in socket with preserved buccal bone wall
Clinical challenge
With the chosen Biomaterials, hard and soft-tissue volume are preserved in the front area for late implantation.
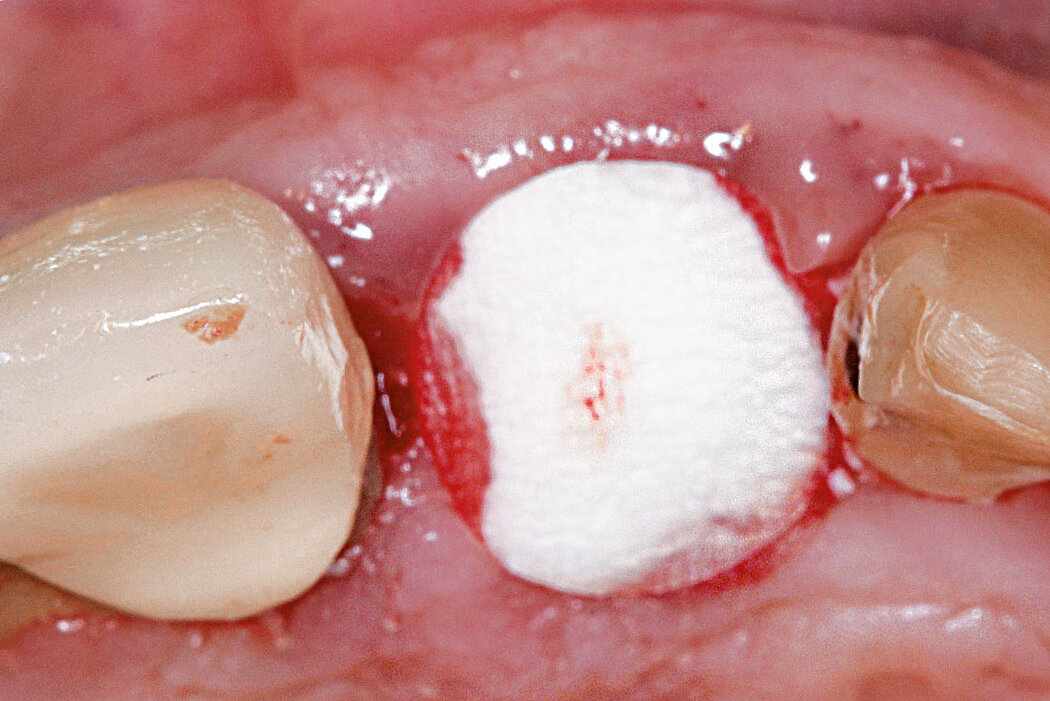
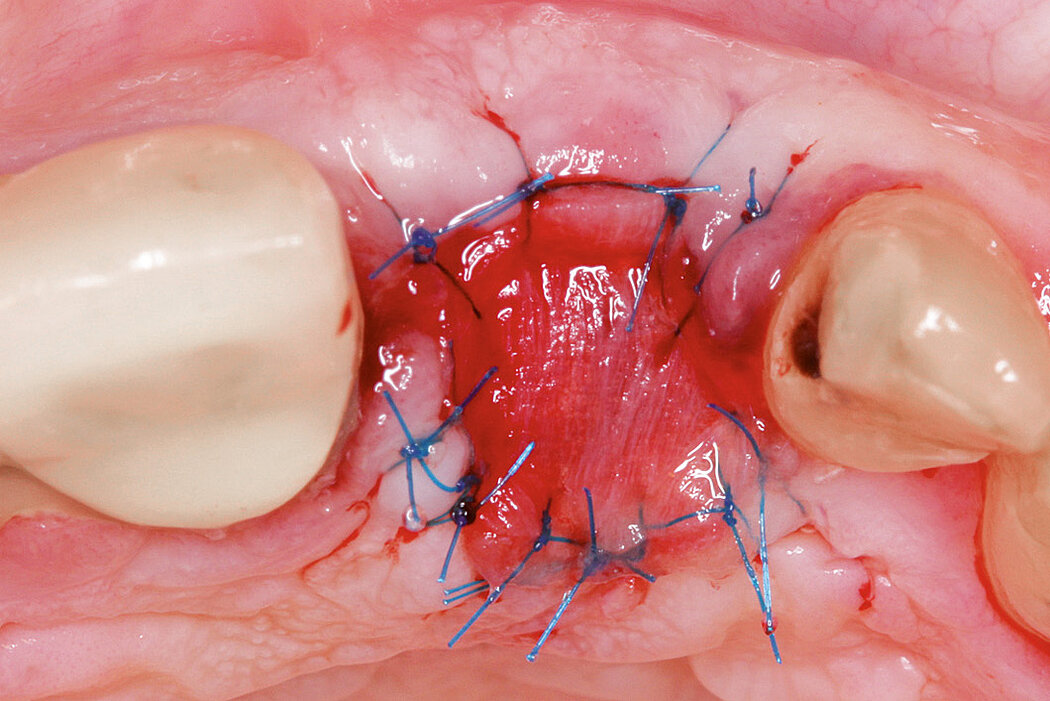
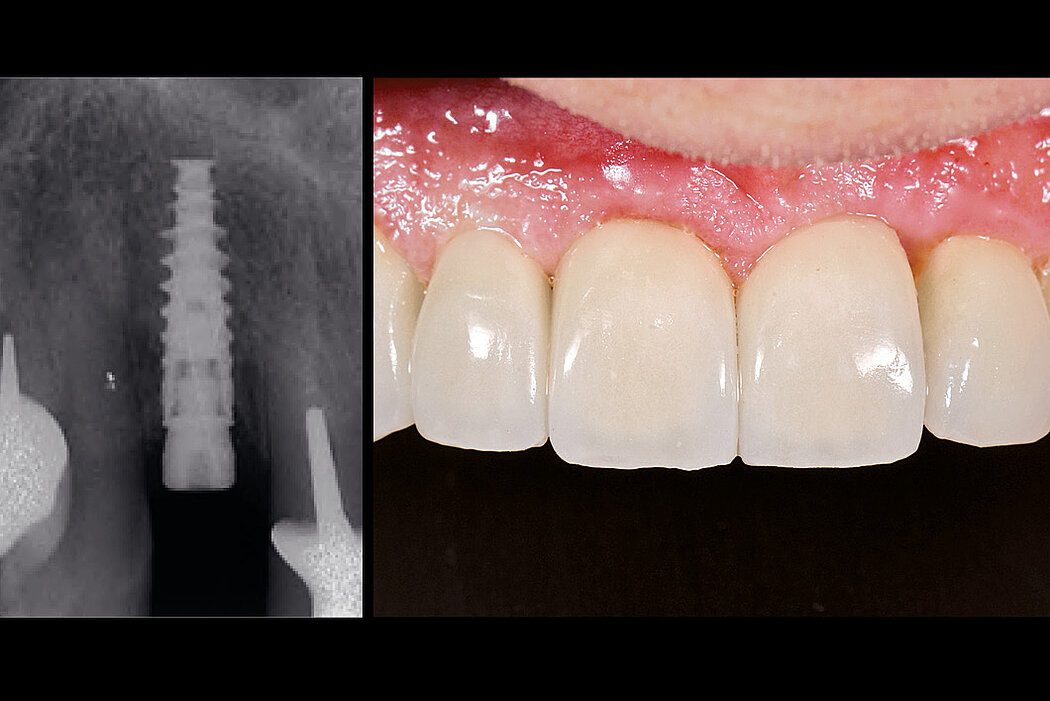
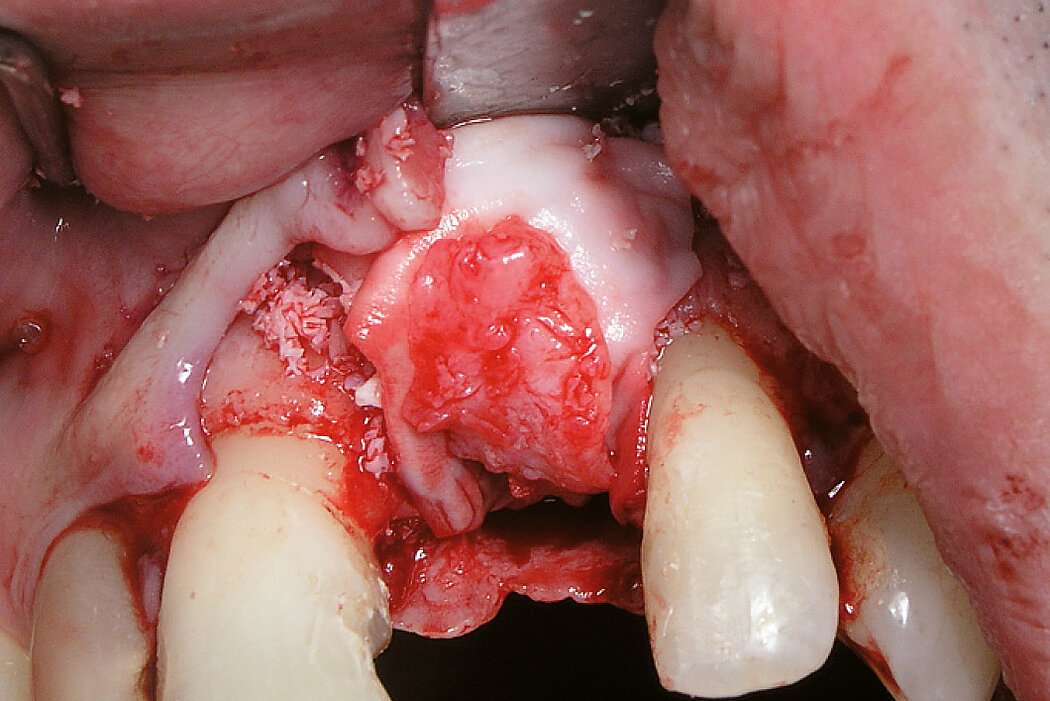
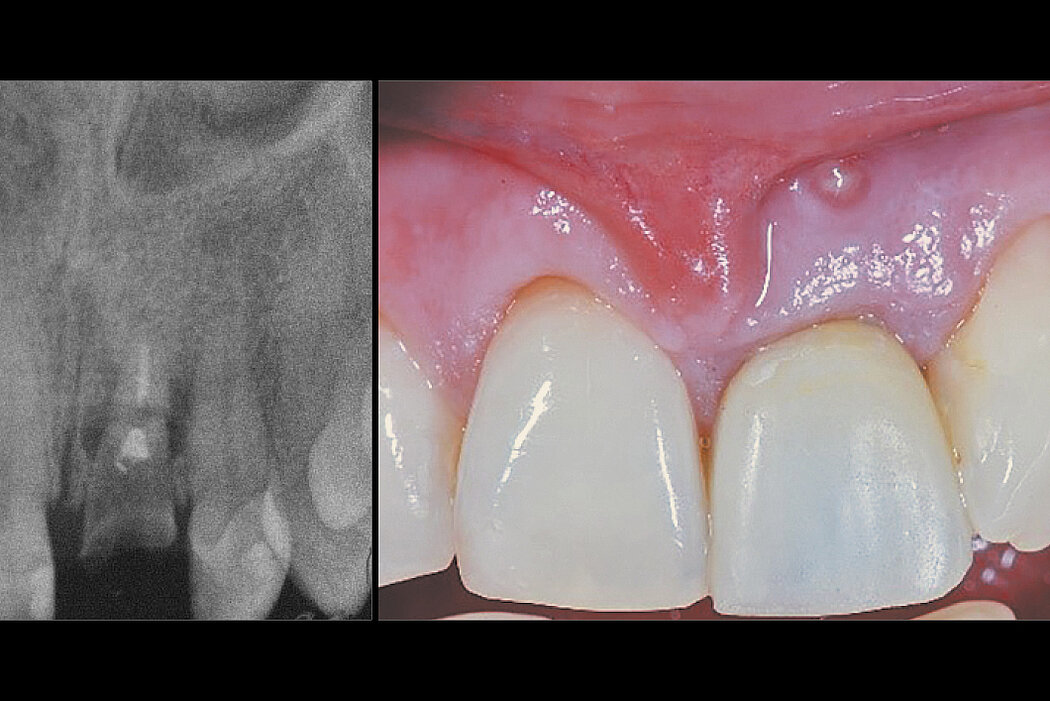
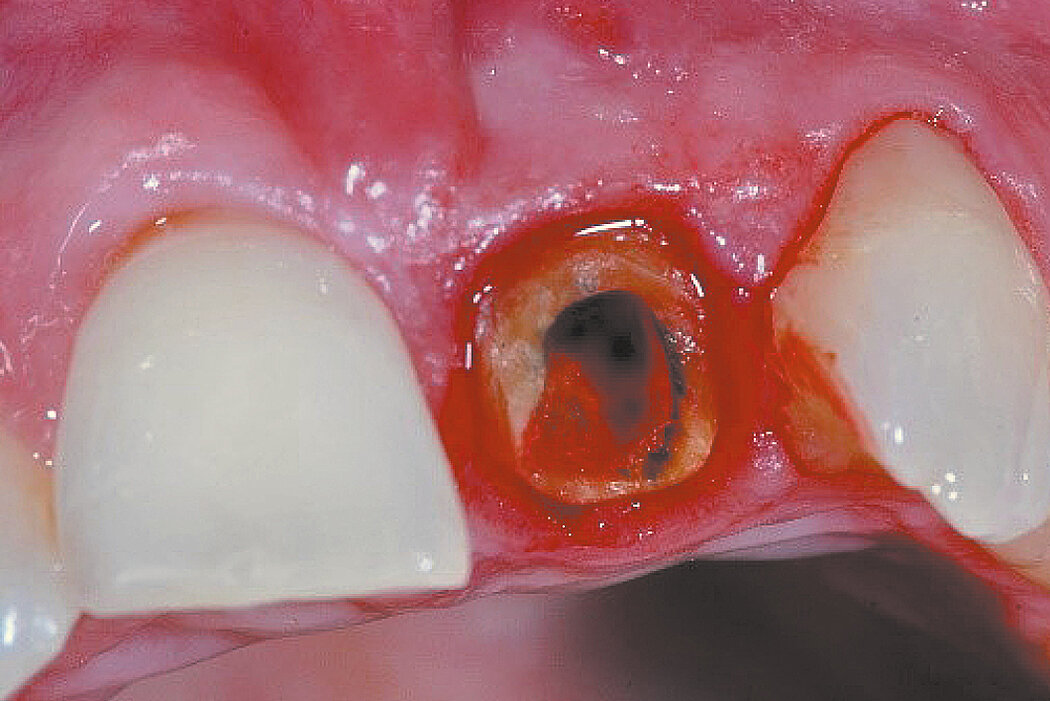
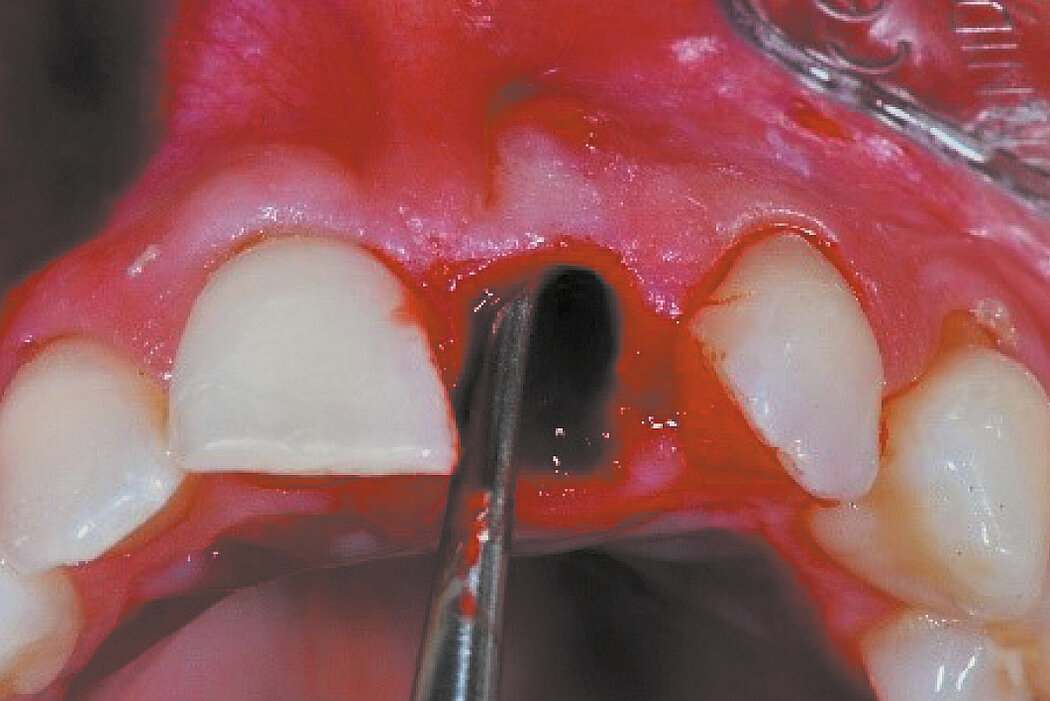
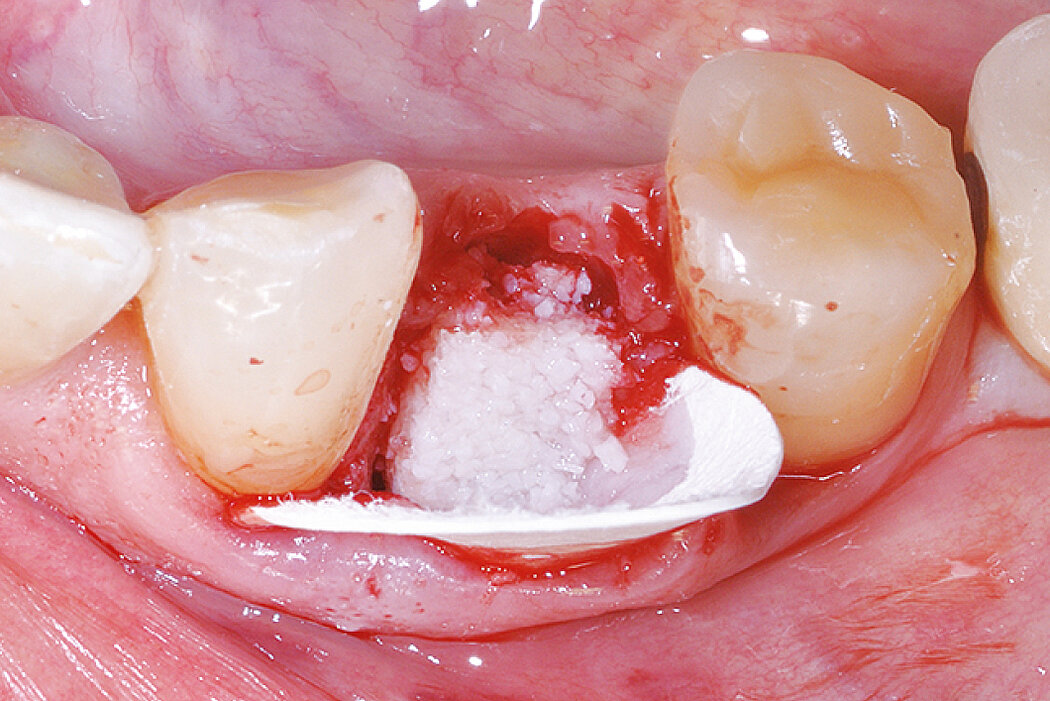
Aim / Approach
Preservation of hard and soft-tissue volume after tooth extraction. Late implant placement, as it is an extremely reliable procedure, which has been proven repeatedly in the international literature.
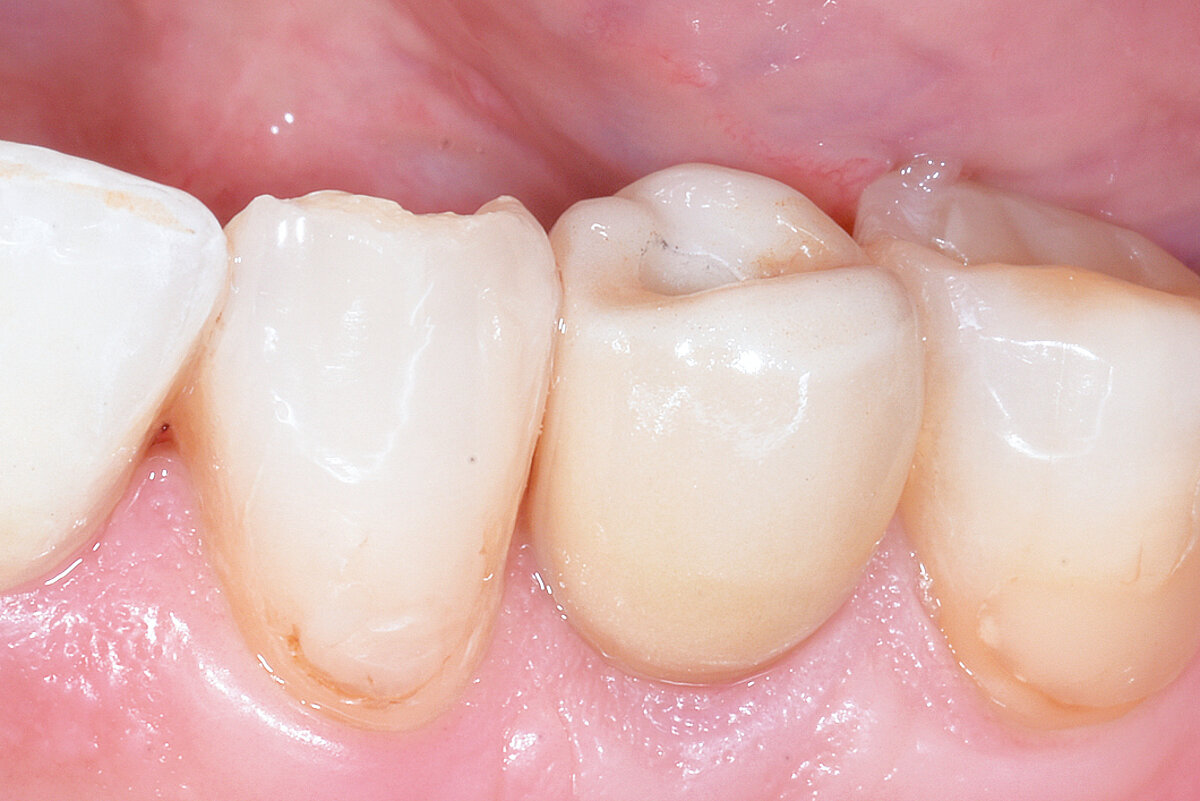
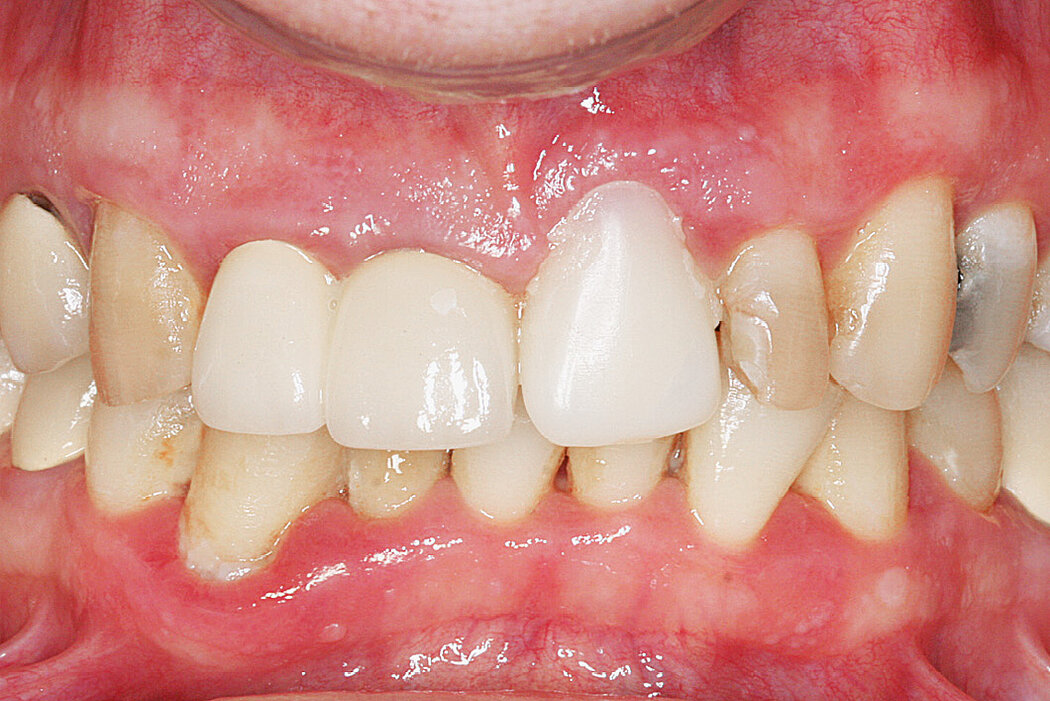
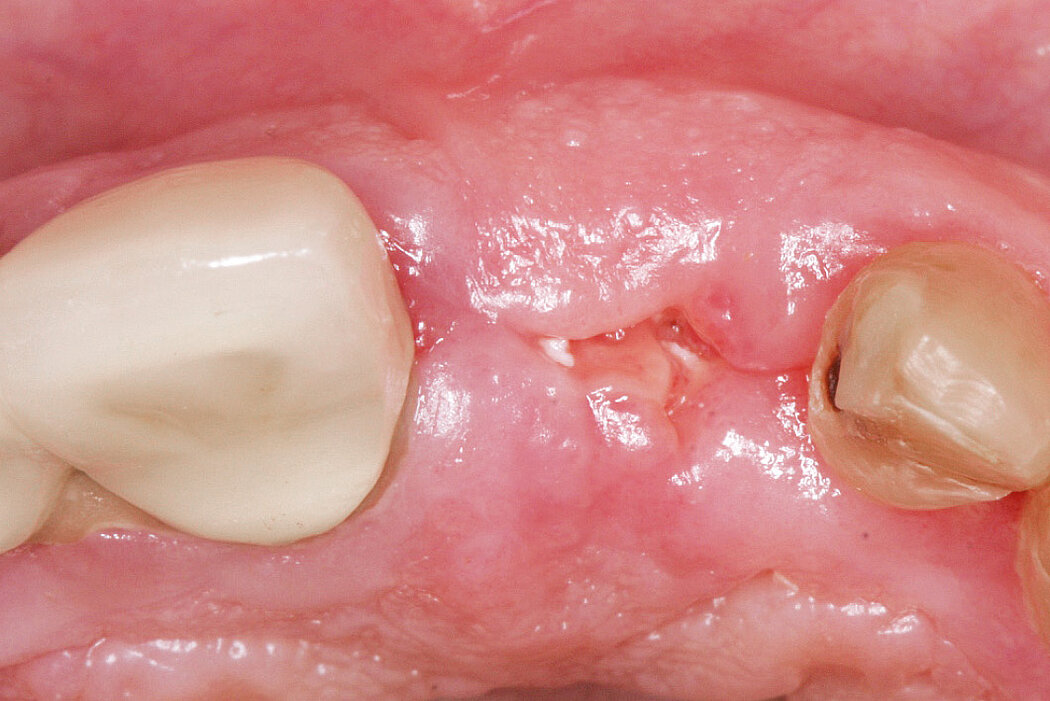
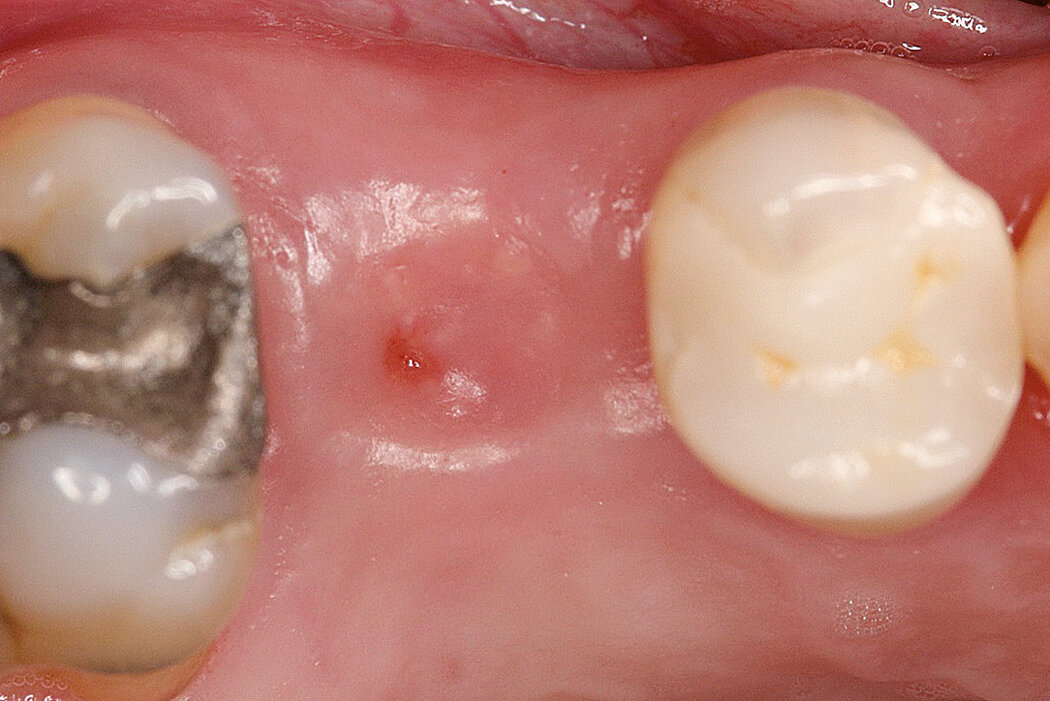
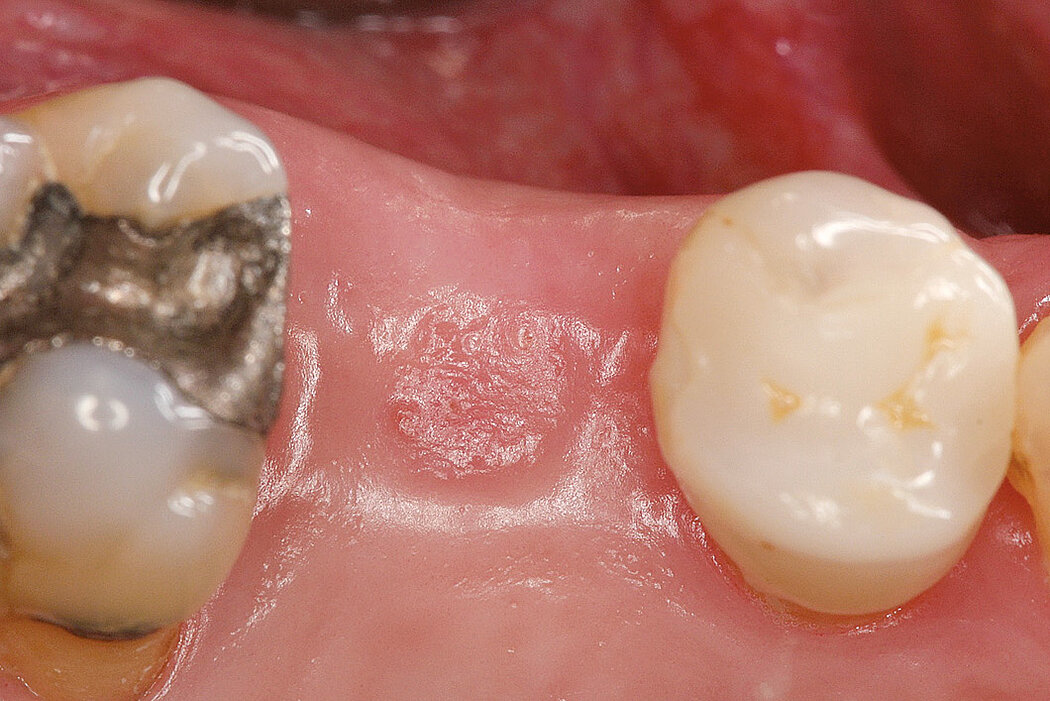
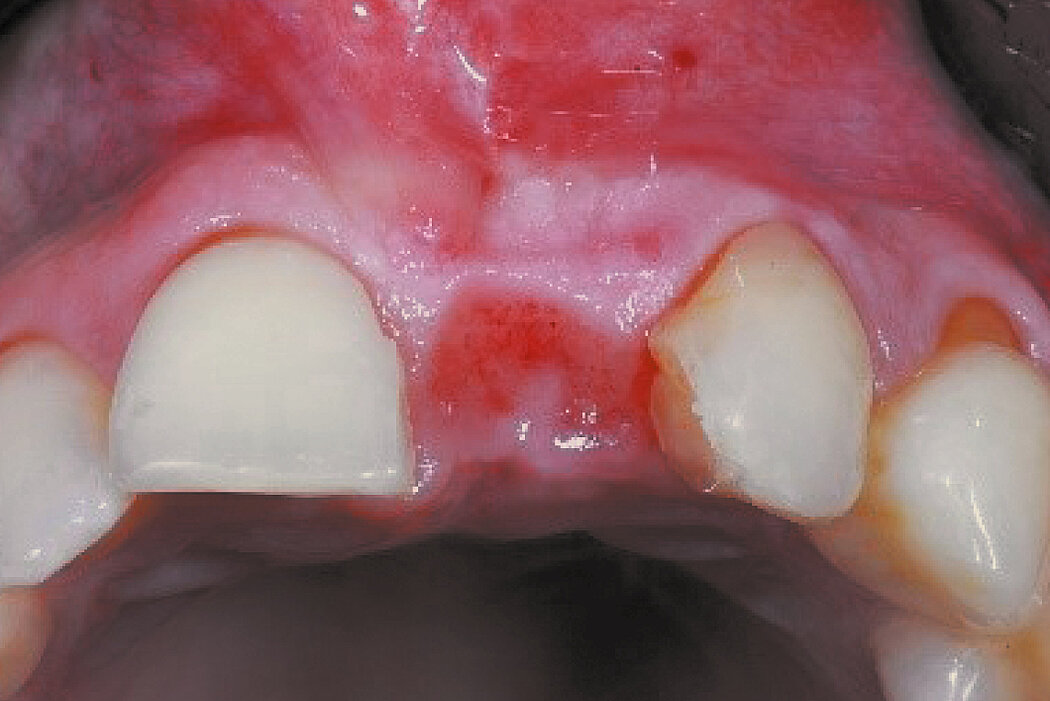
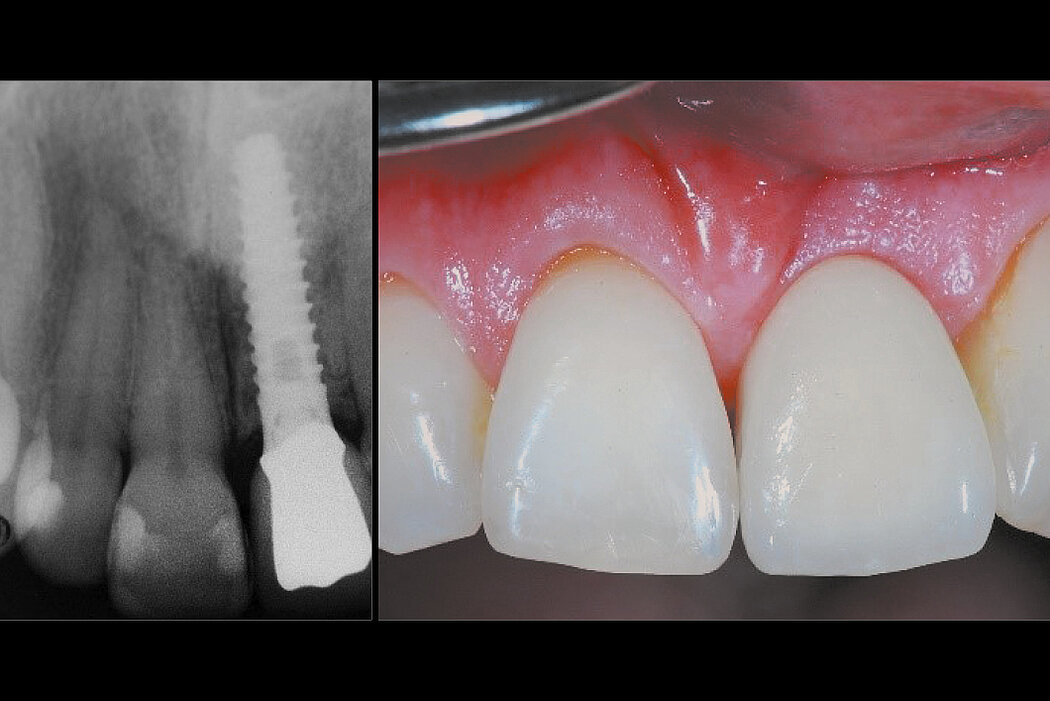
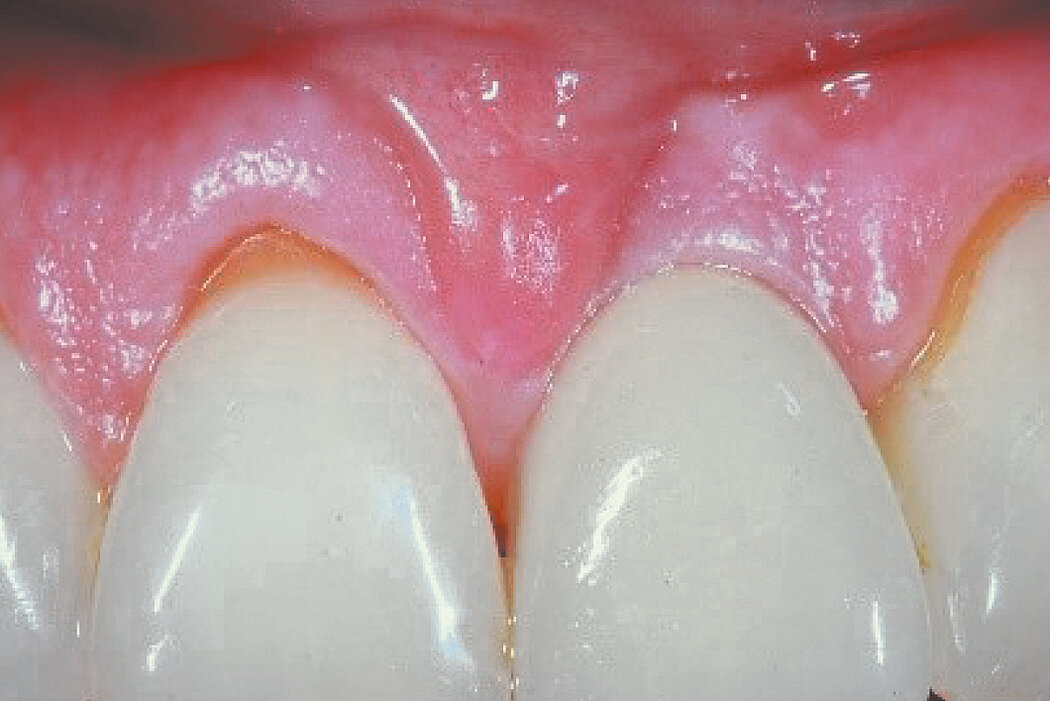
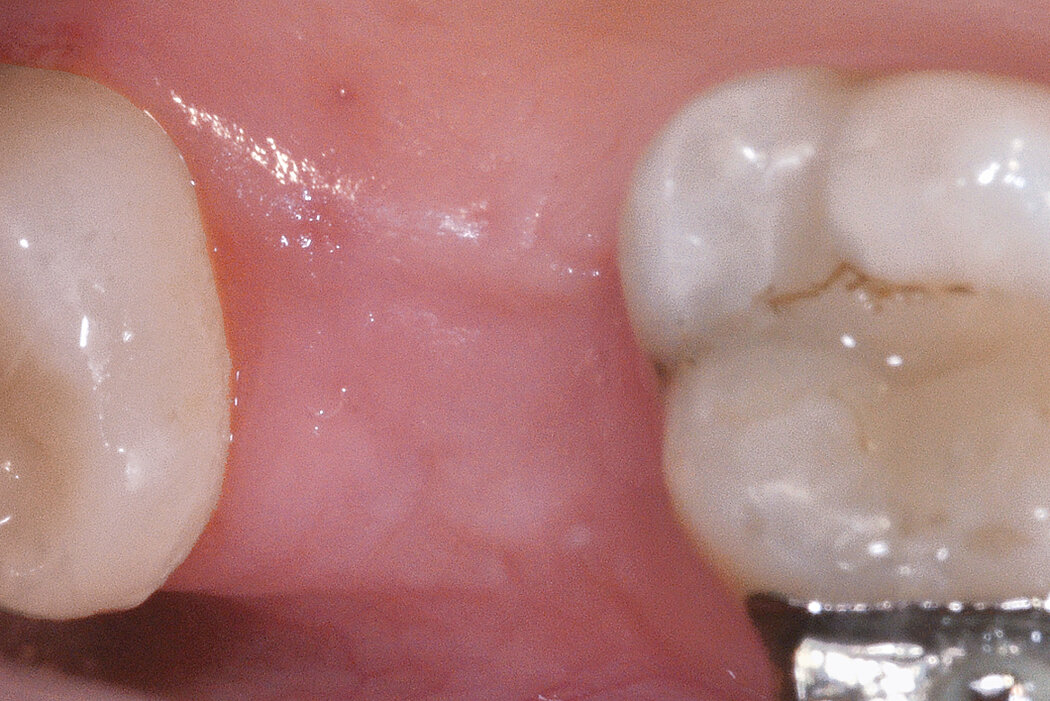
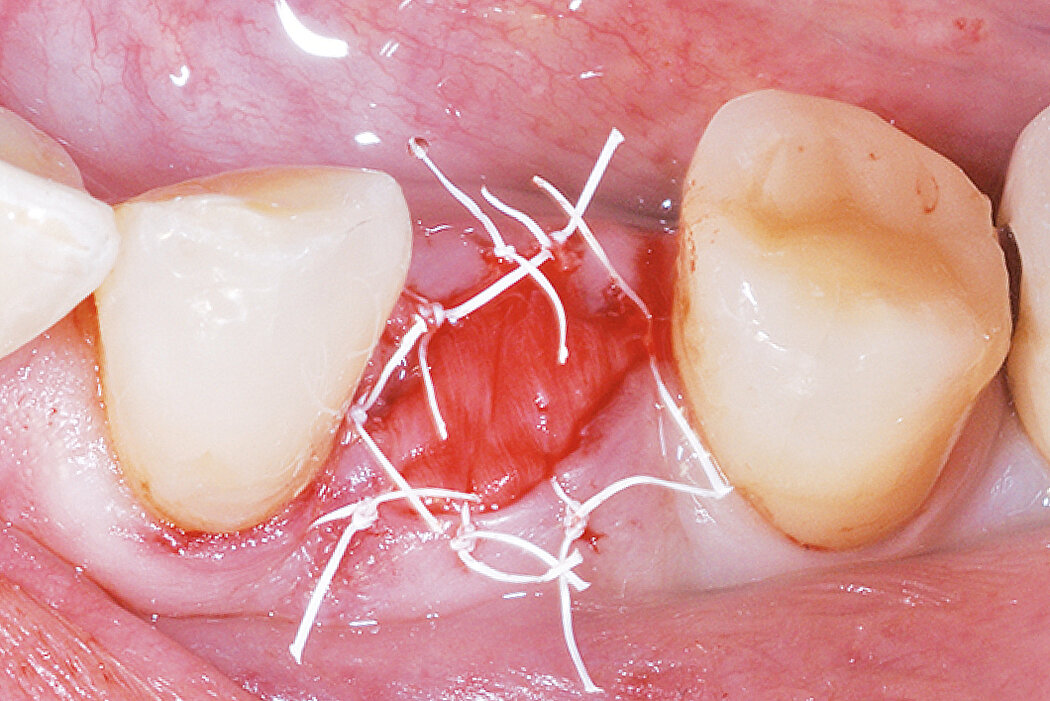
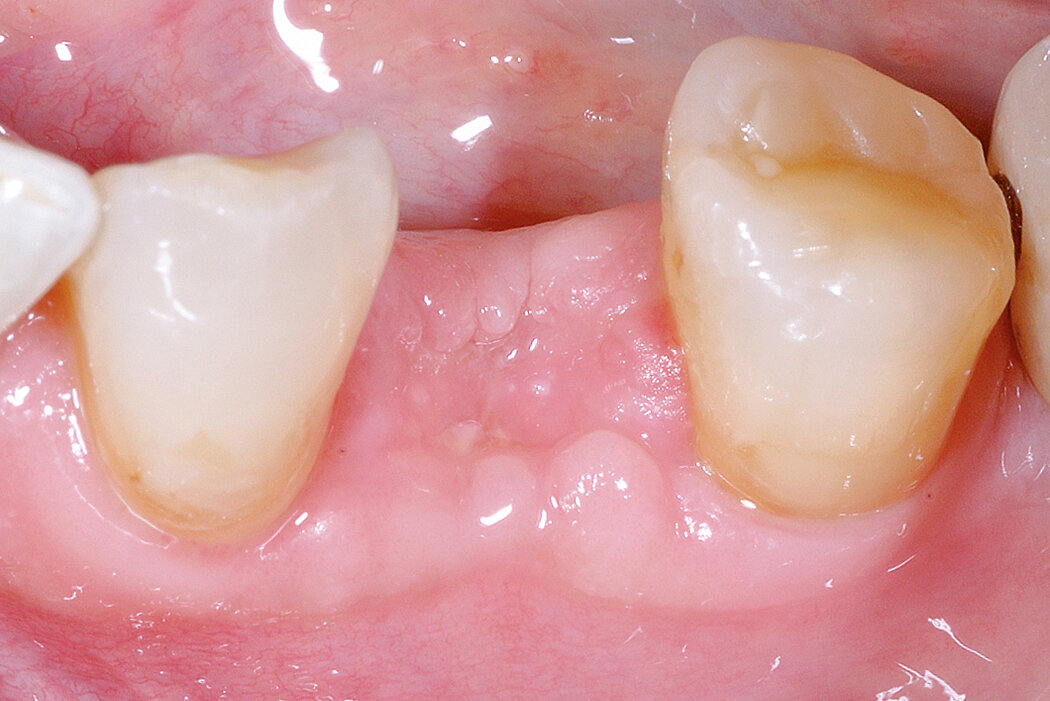
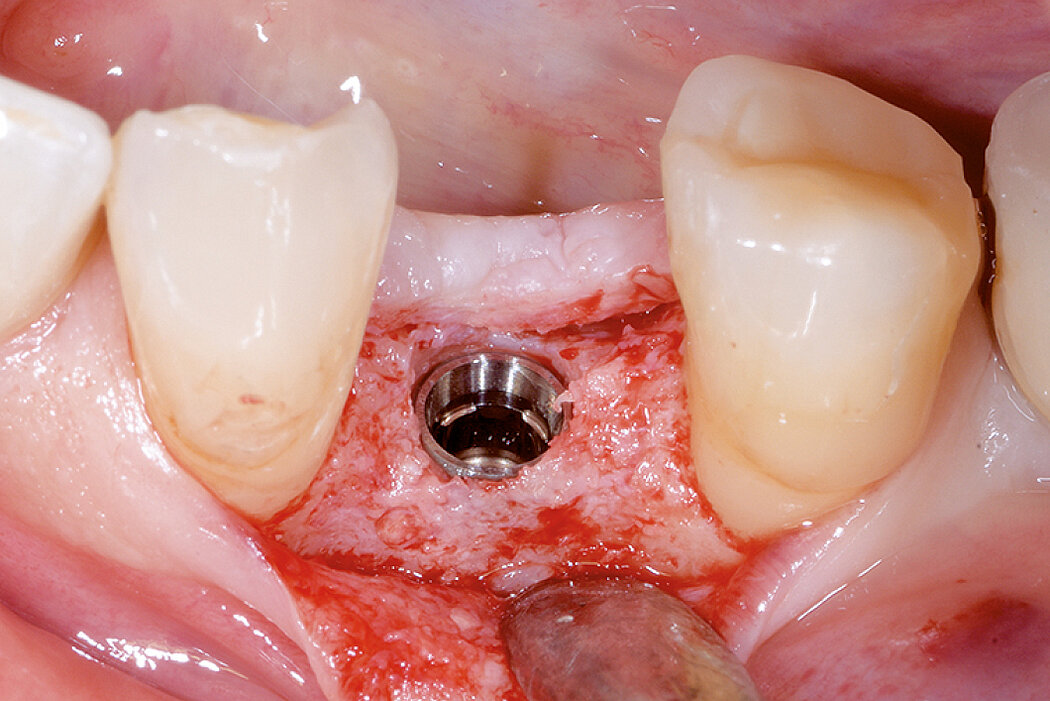
Conclusion
Geistlich Bio-Oss® Collagen and Geistlich Mucograft® Seal preserve the ridge for optimal implant placement 5 months post-op. At the central incisor, the buccal soft-tissue thickness is optimised with a connective tissue graft.
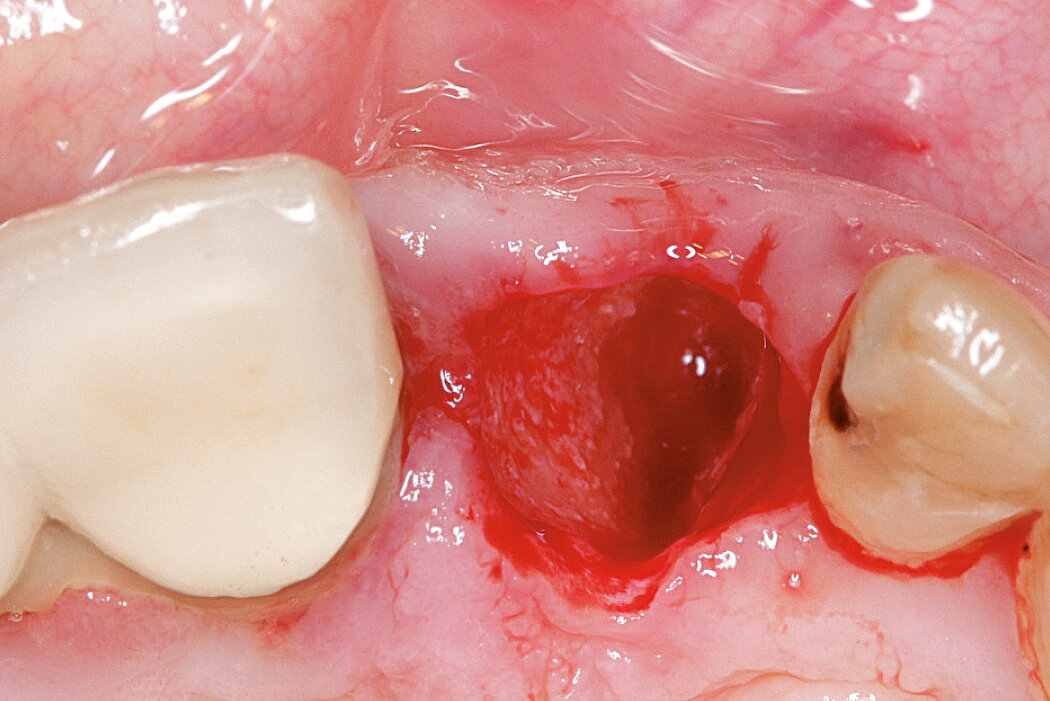
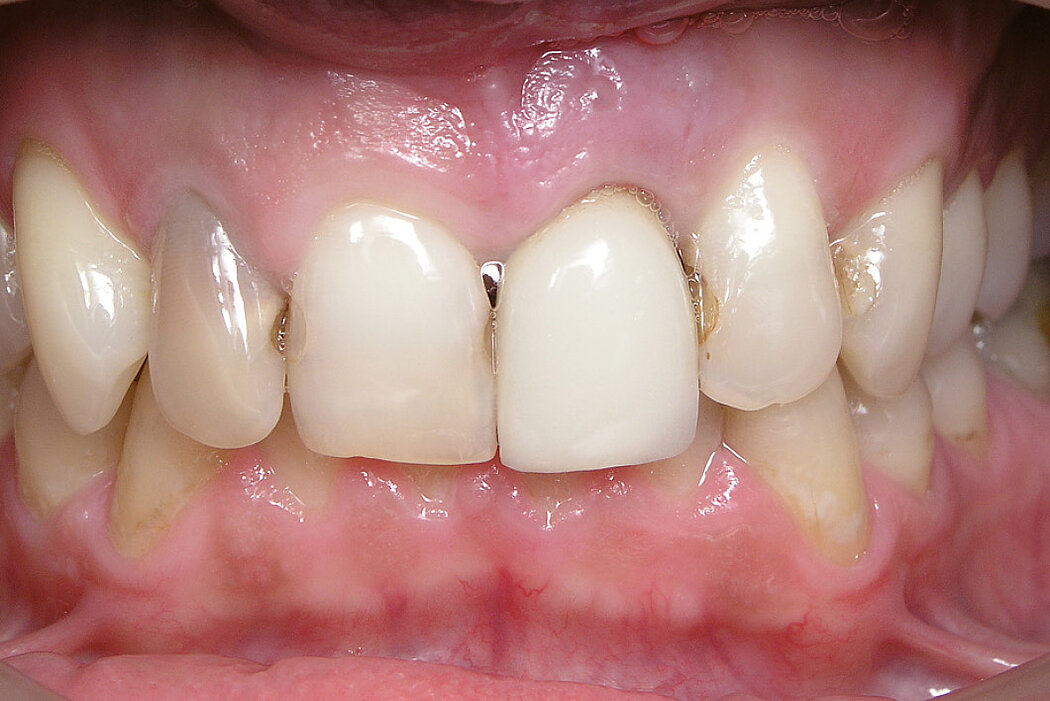
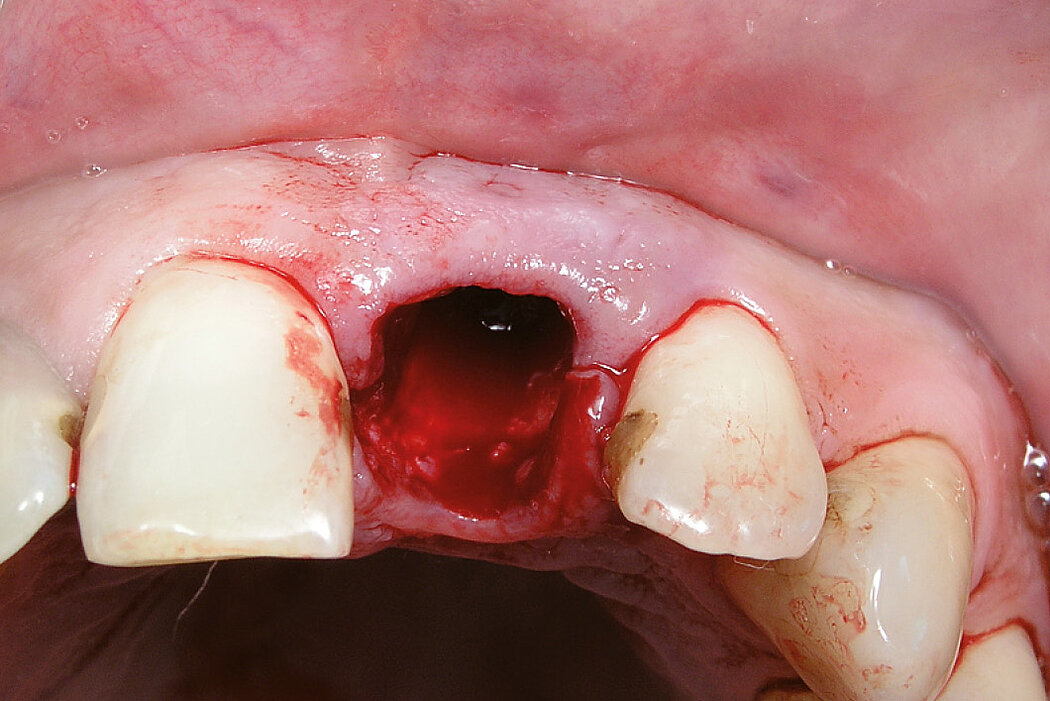
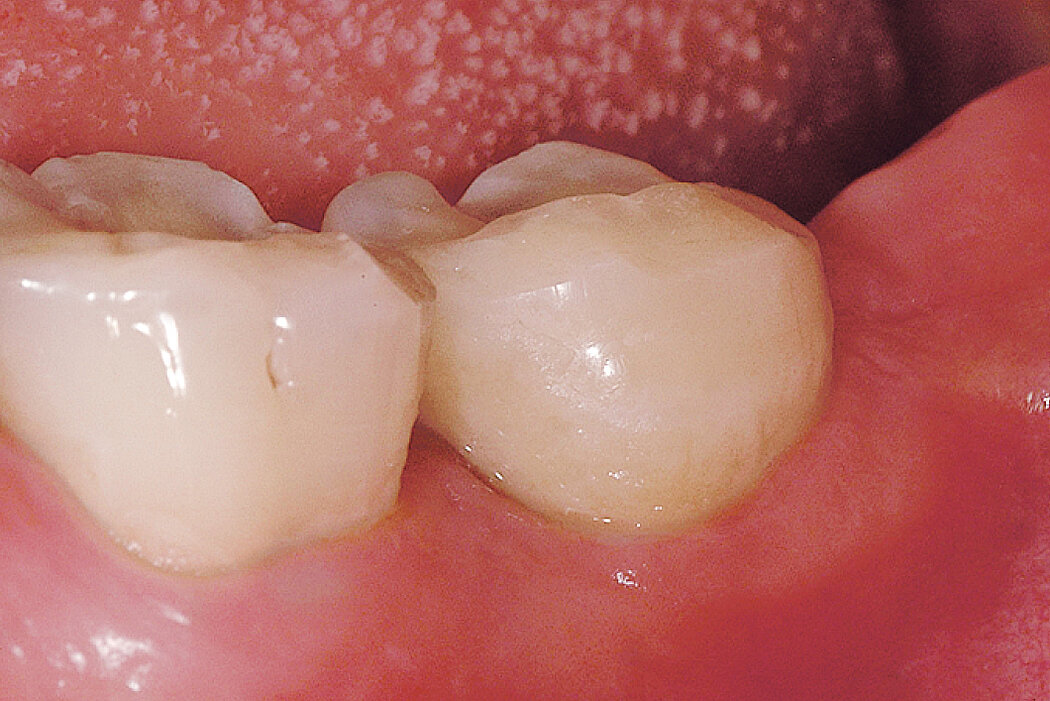
Ridge Preservation in socket with preserved buccal bone wall
Clinical challenge
Soft and hard tissues are well preserved without any scarring on the buccal or occlusal aspect.
Aim / Approach
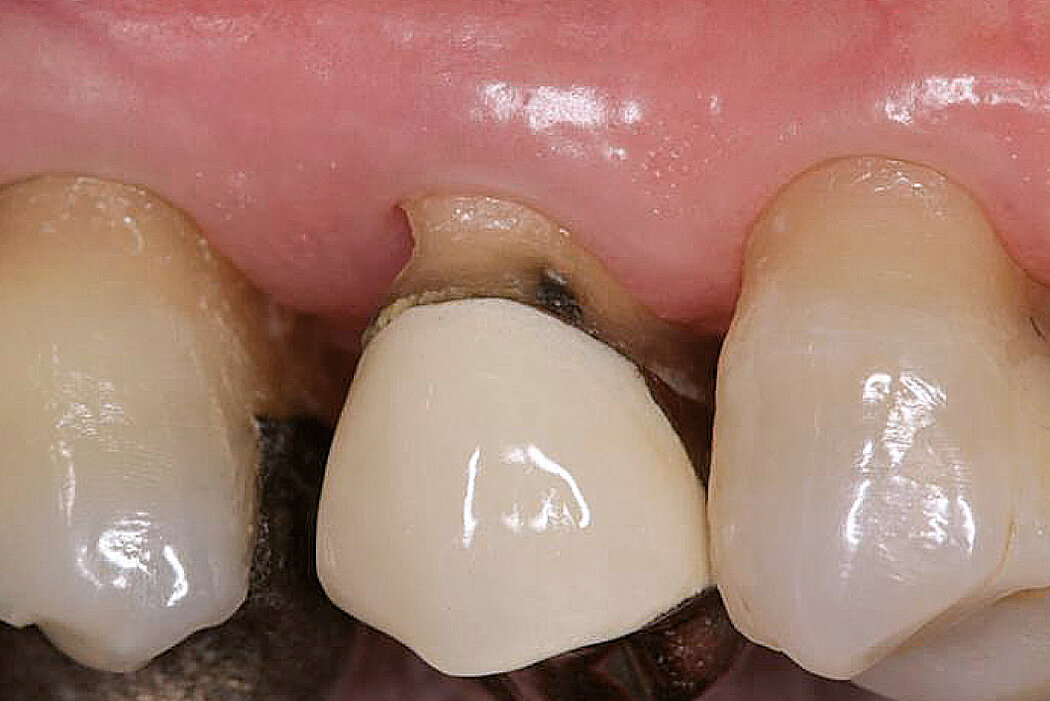
Delayed implant placement 4 months after extraction. Minimally invasive treatment of the socket.
Conclusion
Good/mature/solid bone obtained 4 months after treatment. Fast and scar-free soft tissue regeneration. Optimal clinical and esthetic result for the patient.
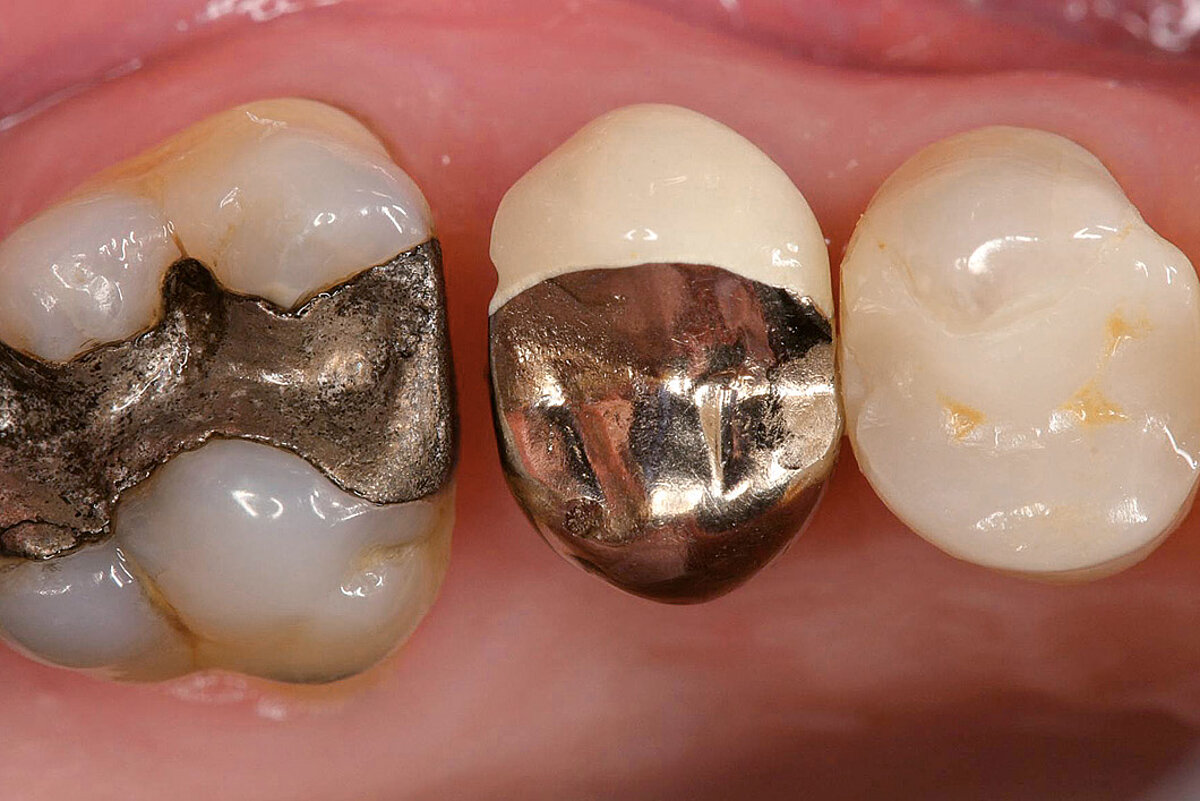
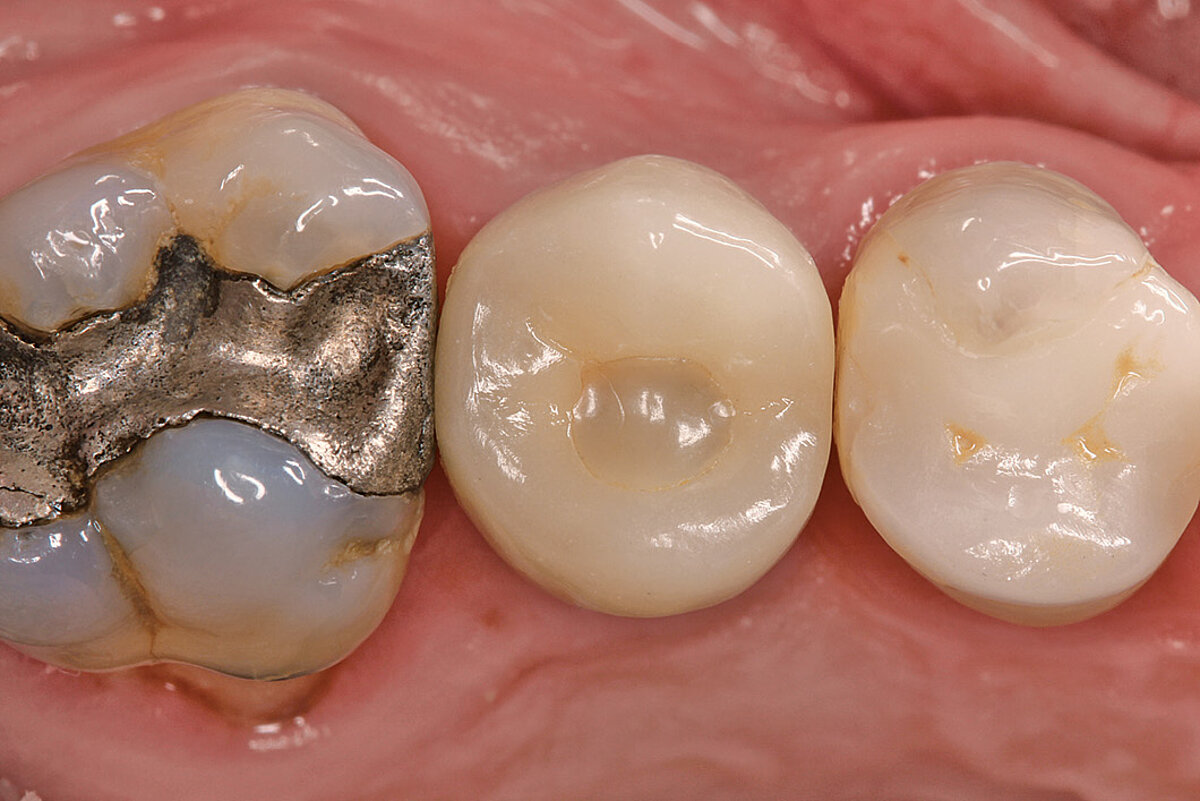
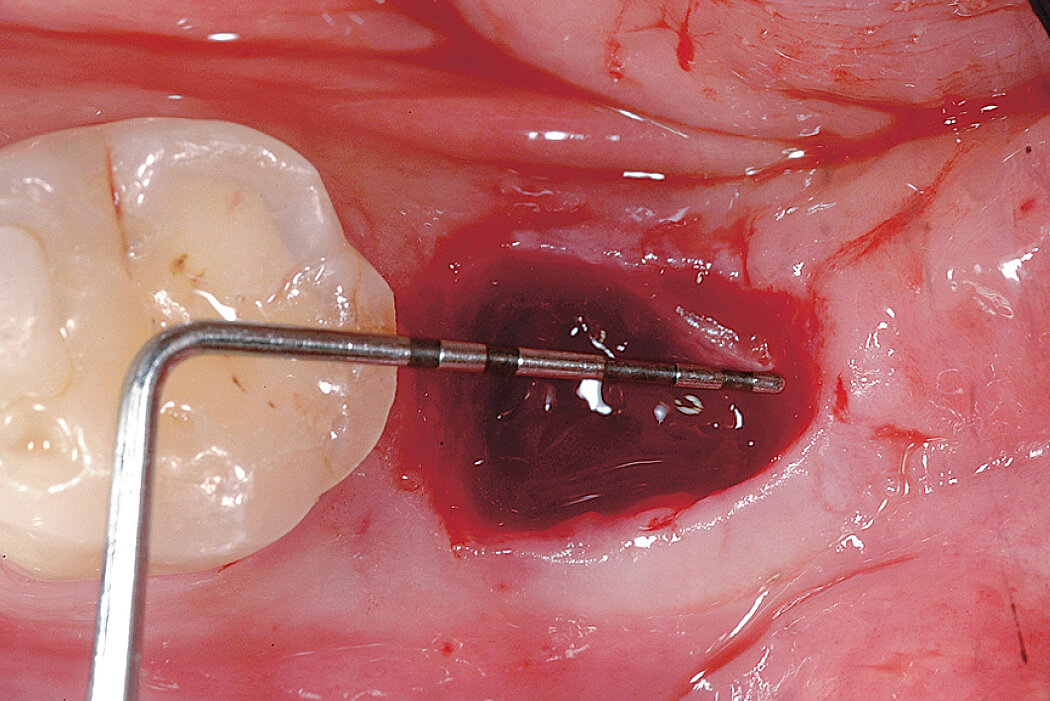
Ridge Preservation in defect extraction sockets (open-healing approach)
Clinical challenge
Whenever possible we prefer to preserve rather than to rebuild the bone later, specially in the front teeth.
Aim / Approach
Maintain hard and soft-tissue contour in esthetically demanding region. Late implant placement in single tooth gap.
Conclusion
Severe ridge resorption was prevented with Geistlich Biomaterials. A long-term pleasant outcome was achieved with additional contouring with Geistlich Biomaterials and a connective tissue graft at implant placement.
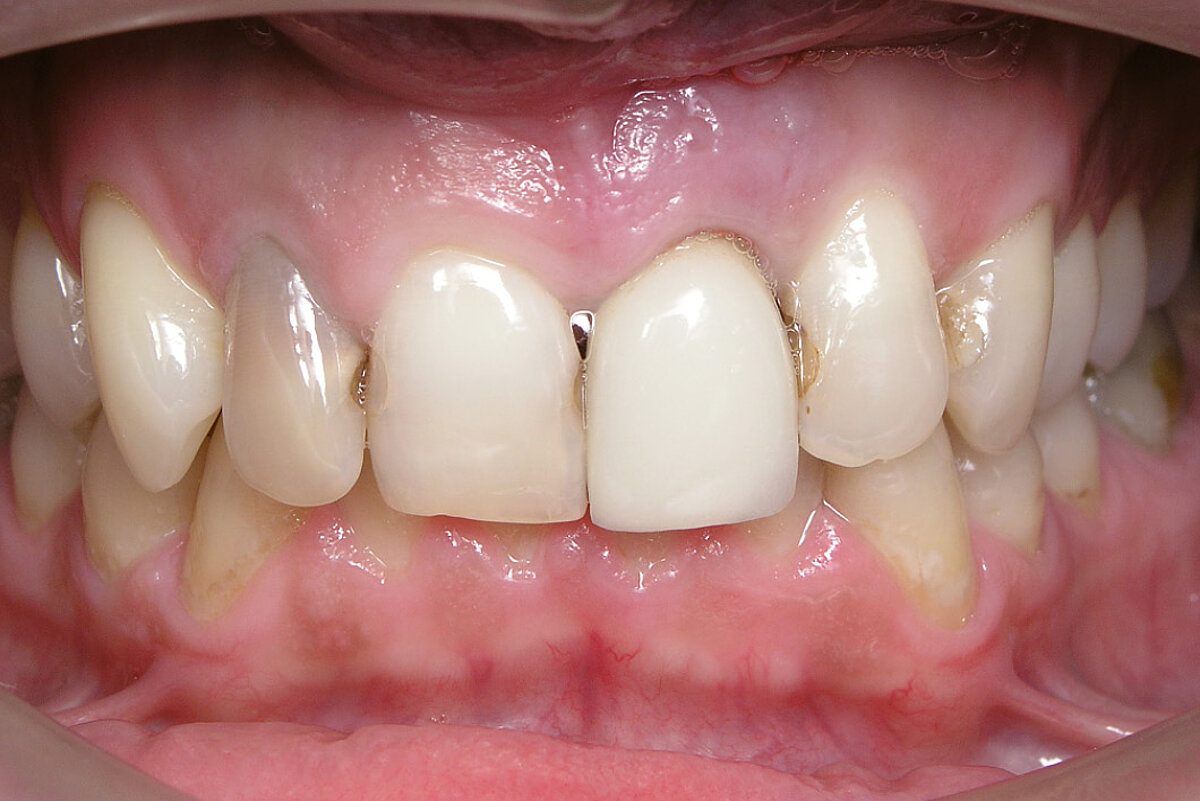
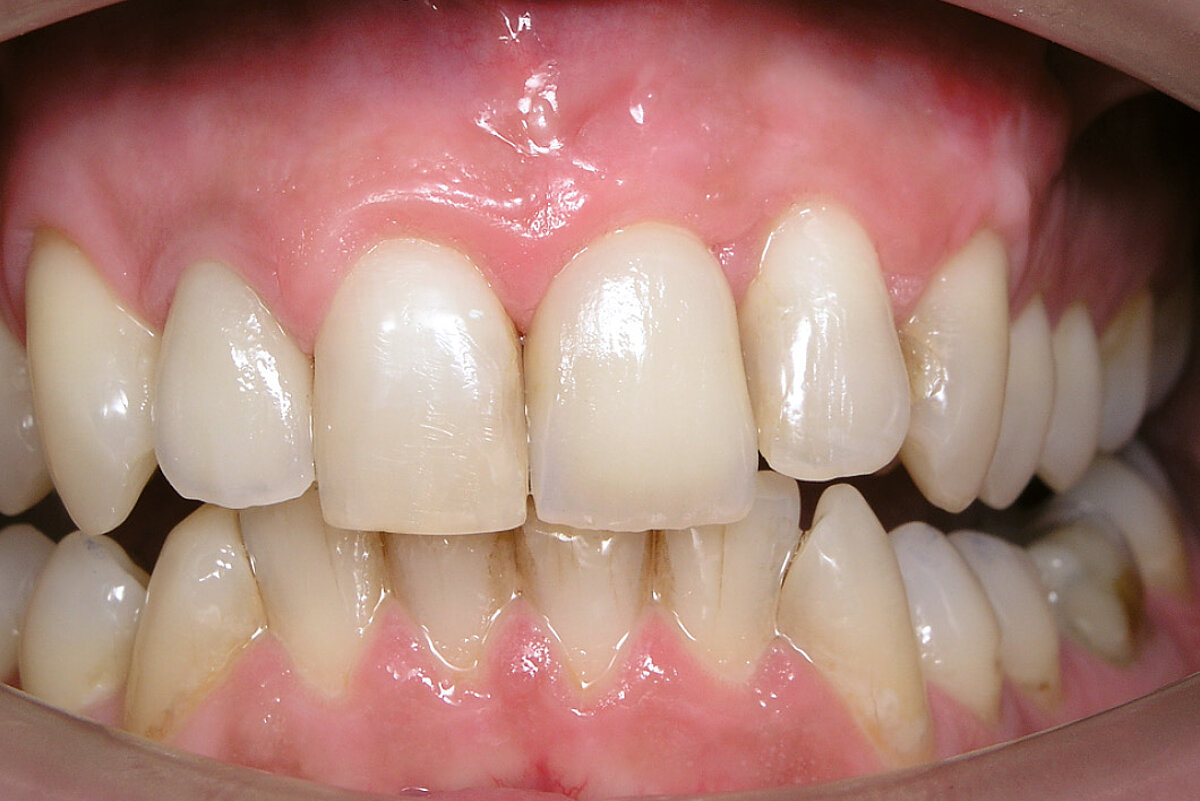
Ridge Preservation in the anterior region for late implantation
Aim / Approach
Preservation of hard and soft-tissue volume after extraction in the anterior region for late implant placement. Prevention of extensive guided bone regeneration procedures at implant placement.
Conclusion
Volume of hard and soft tissue can be preserved better with Geistlich Bio-Oss® Collagen and Geistlich Mucograft® Seal than with spontaneous healing. A minimally invasive GBR is peformed to contour the ridge at implant placement.
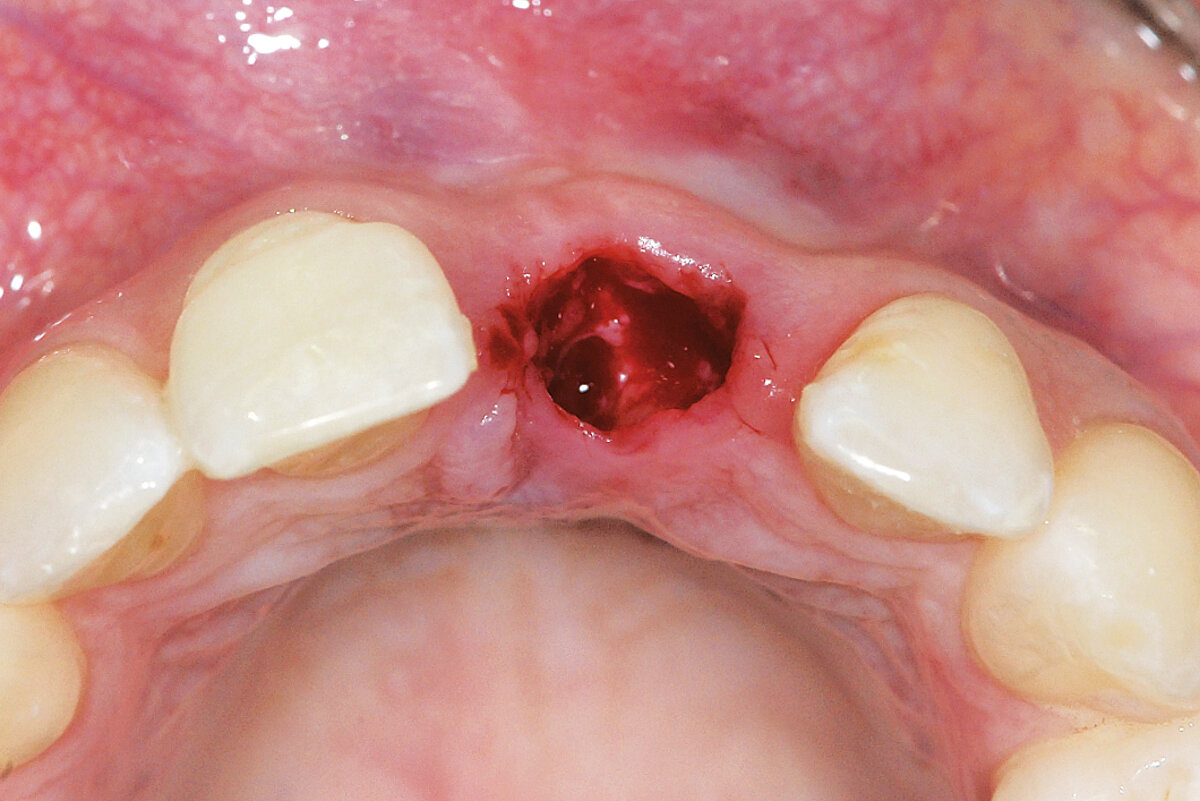
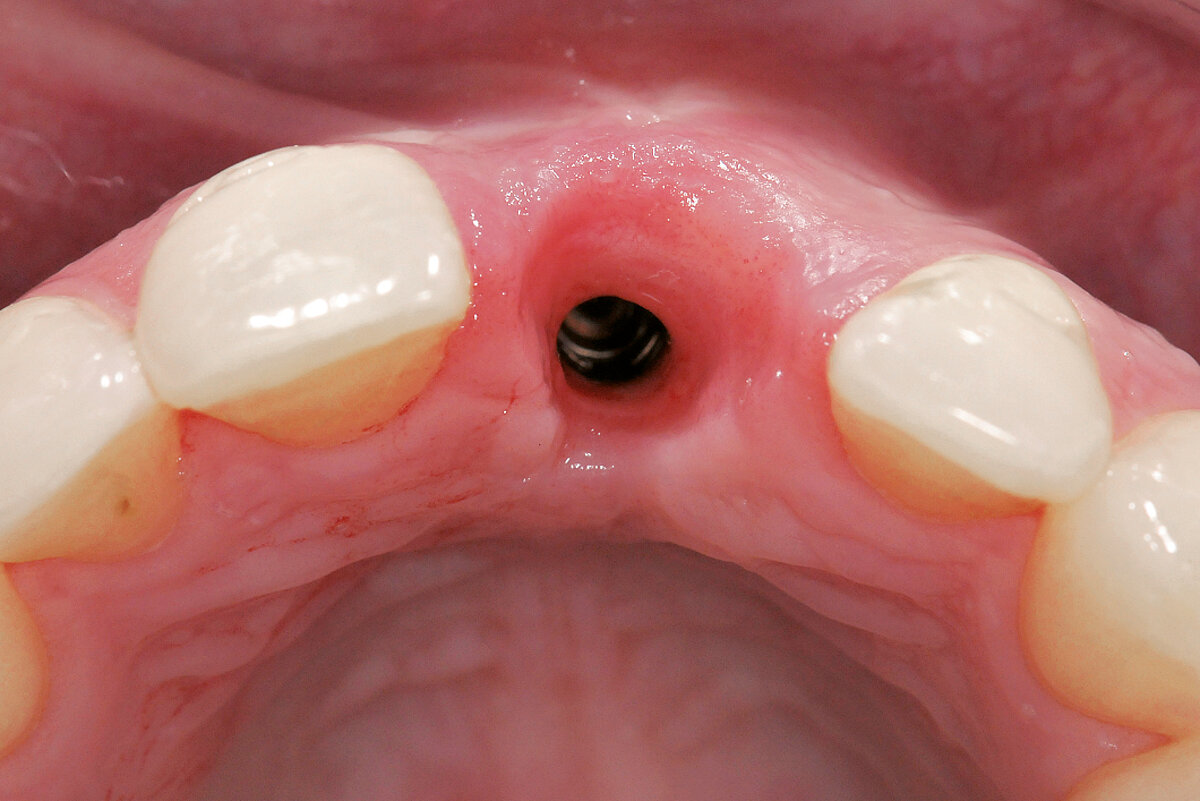
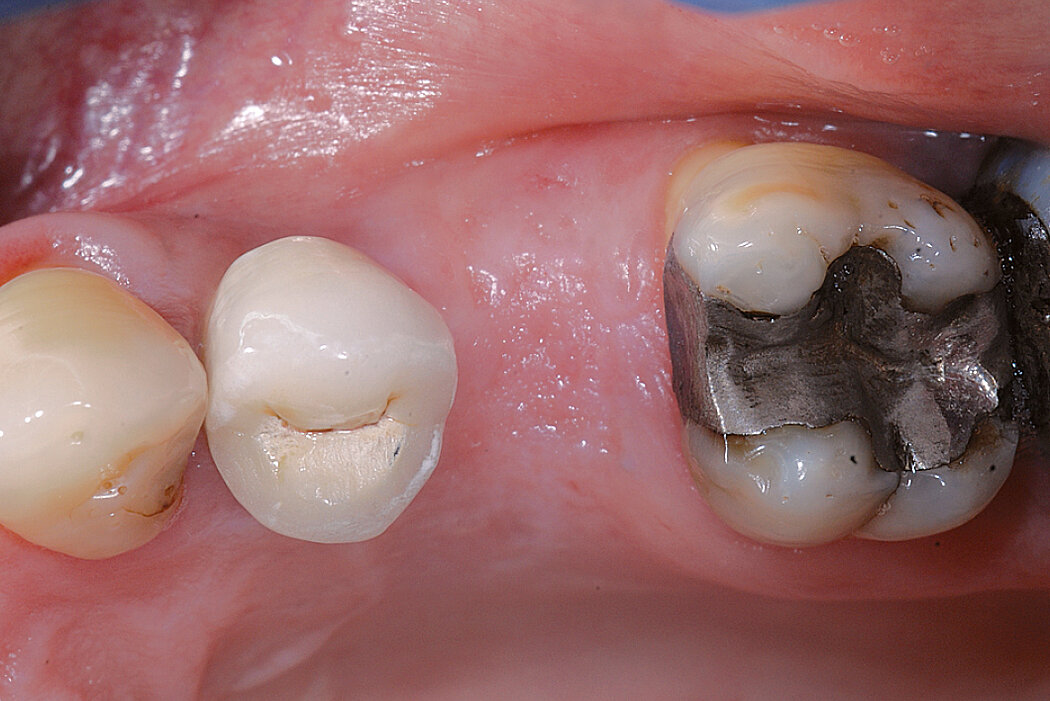
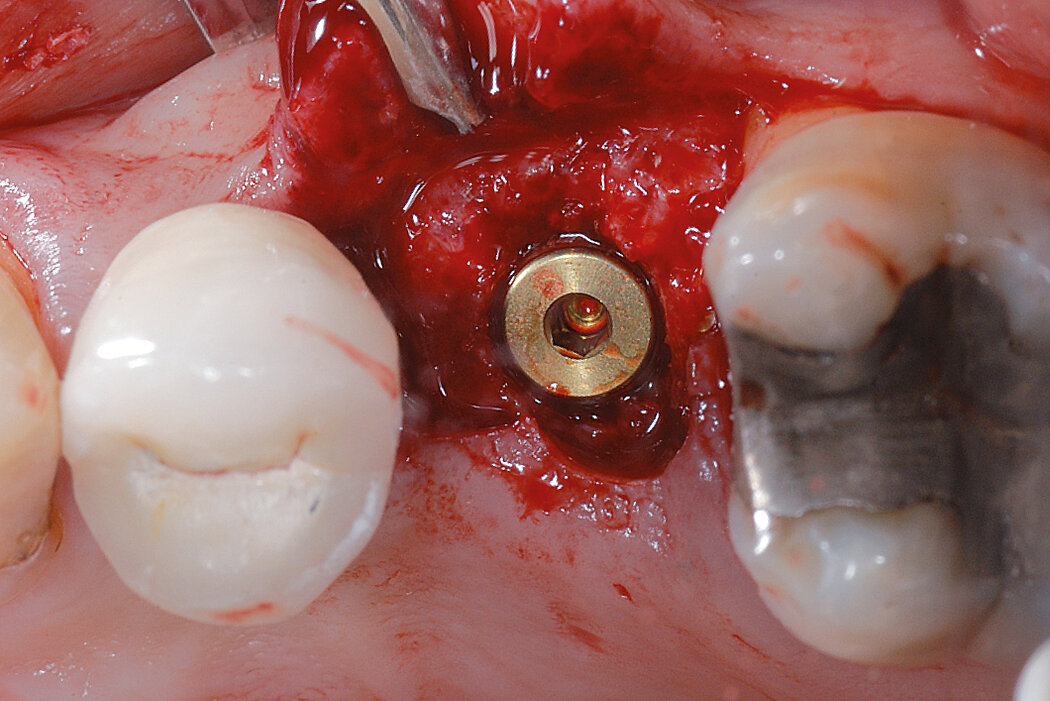
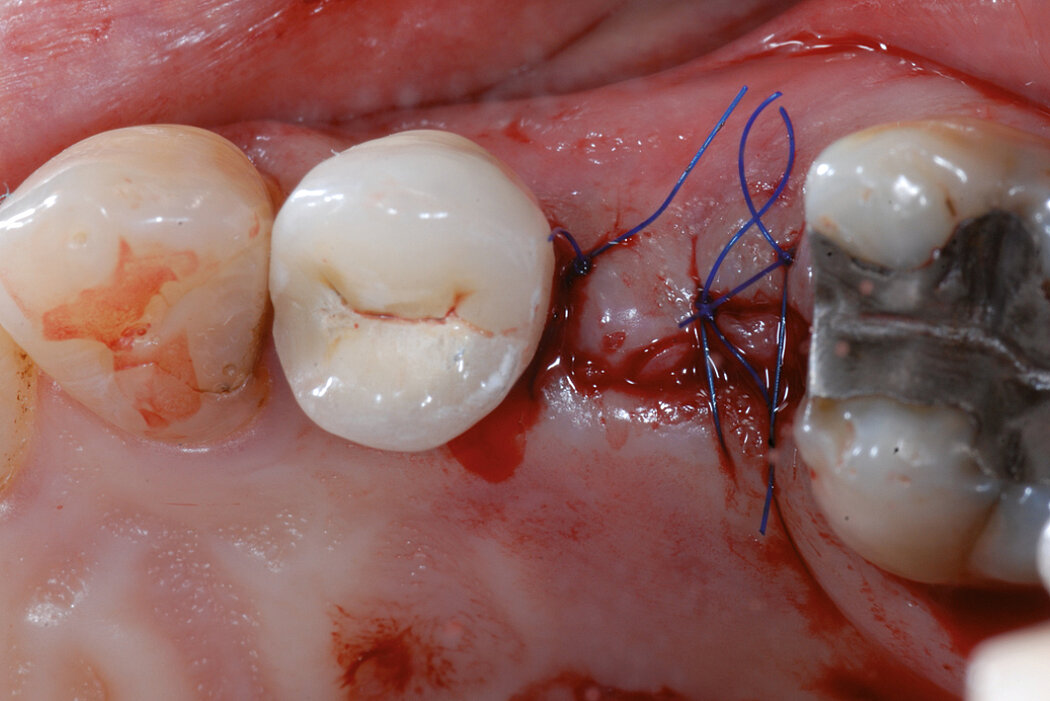
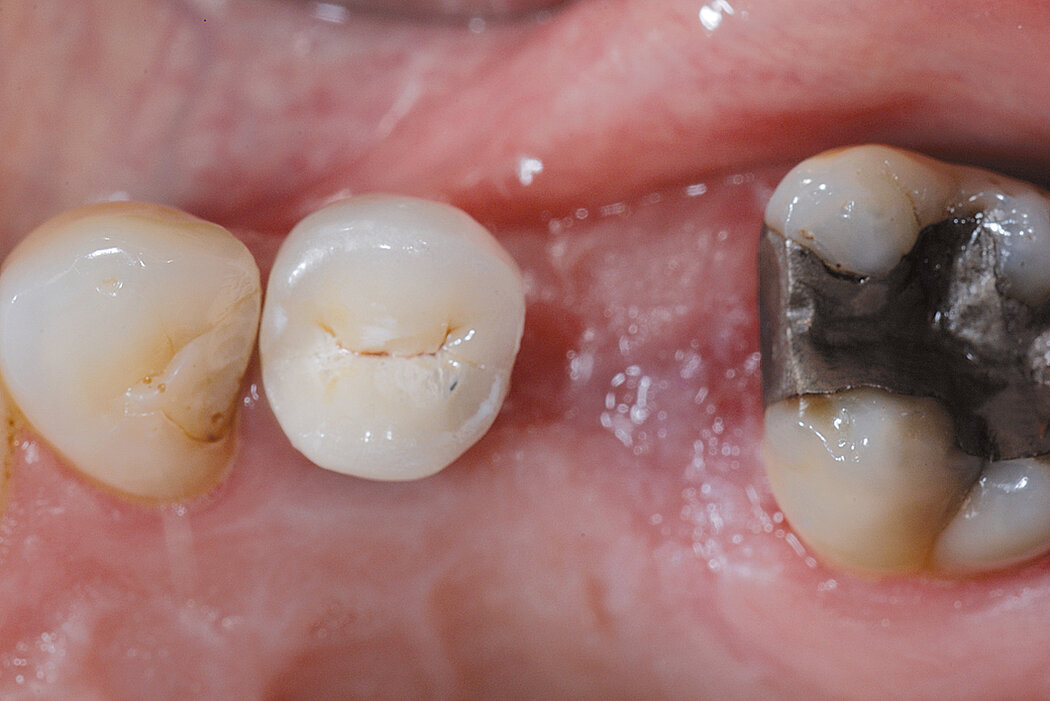
Ridge Preservation in the posterior region for late implantation
Clinical challenge
Geistlich Bio-Oss® and Geistlich Mucograft® Seal enable a flapless and effective Ridge Preservation.
Aim / Approach
Preservation of the ridge contour with minimal invasion. Late implant placement.
Conclusion
Geistlich Bio-Oss® and Geistlich Mucograft® Seal enable a flapless and effective Ridge Preservation. Hard and soft tissues are optimal for implant placement 6 months after Ridge Preservation procedure.
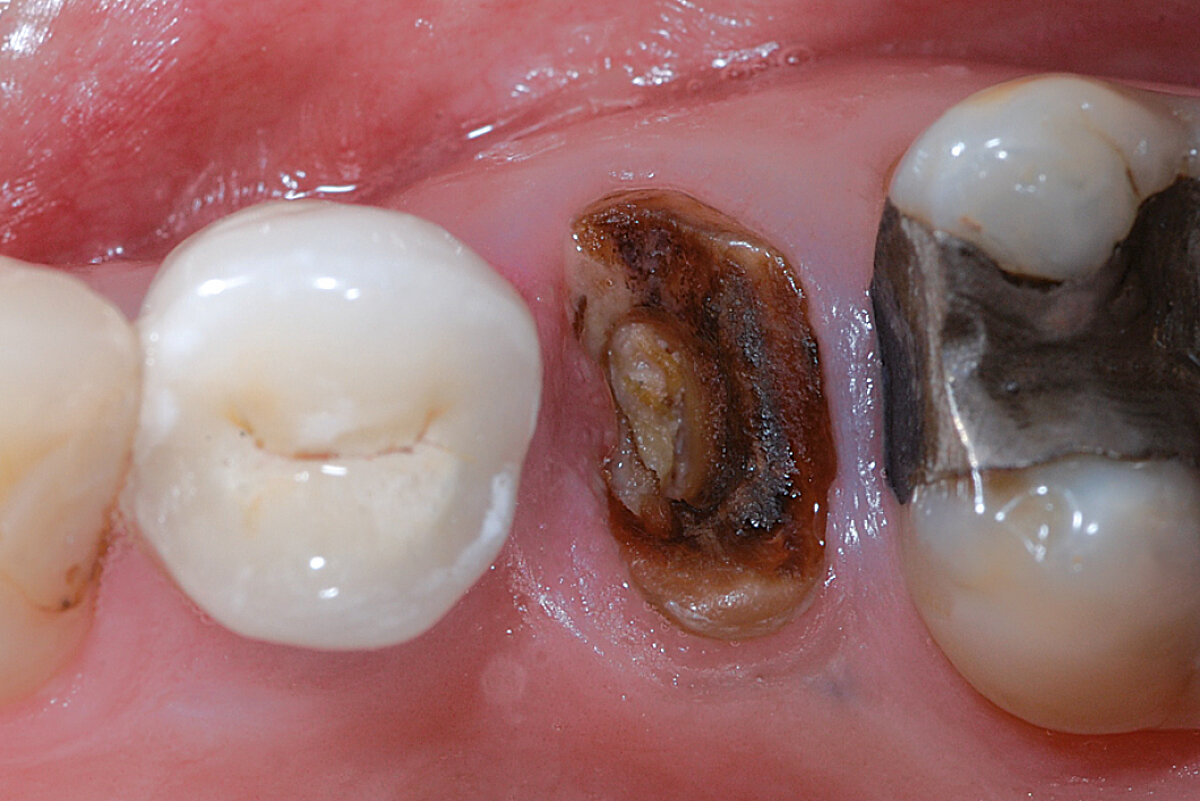
Ridge preservation of a fenestrated buccal bone wall (open-healing approach)
Clinical challenge
20 years of experience with Geistlich Bio-Oss® and Geistlich Bio-Gide® true to the motto ‘never change a winning team’ also for more complex indications.
Aim / Approach
Replace a hopeless central incisor with a vertical fracture of the tooth root and buccal bone fenestration. The vestibulum already showed a fistula.
Conclusion
Ridge Preservation techniques are effective in minimising volume loss.
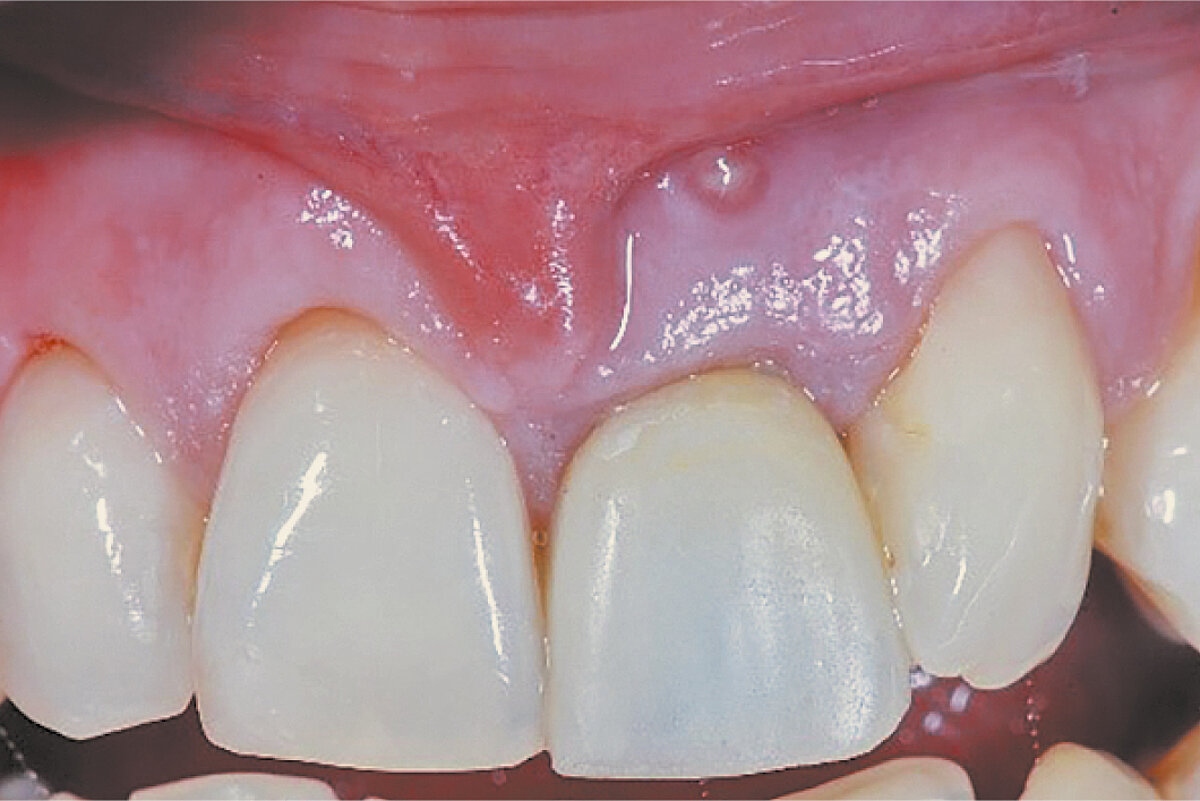
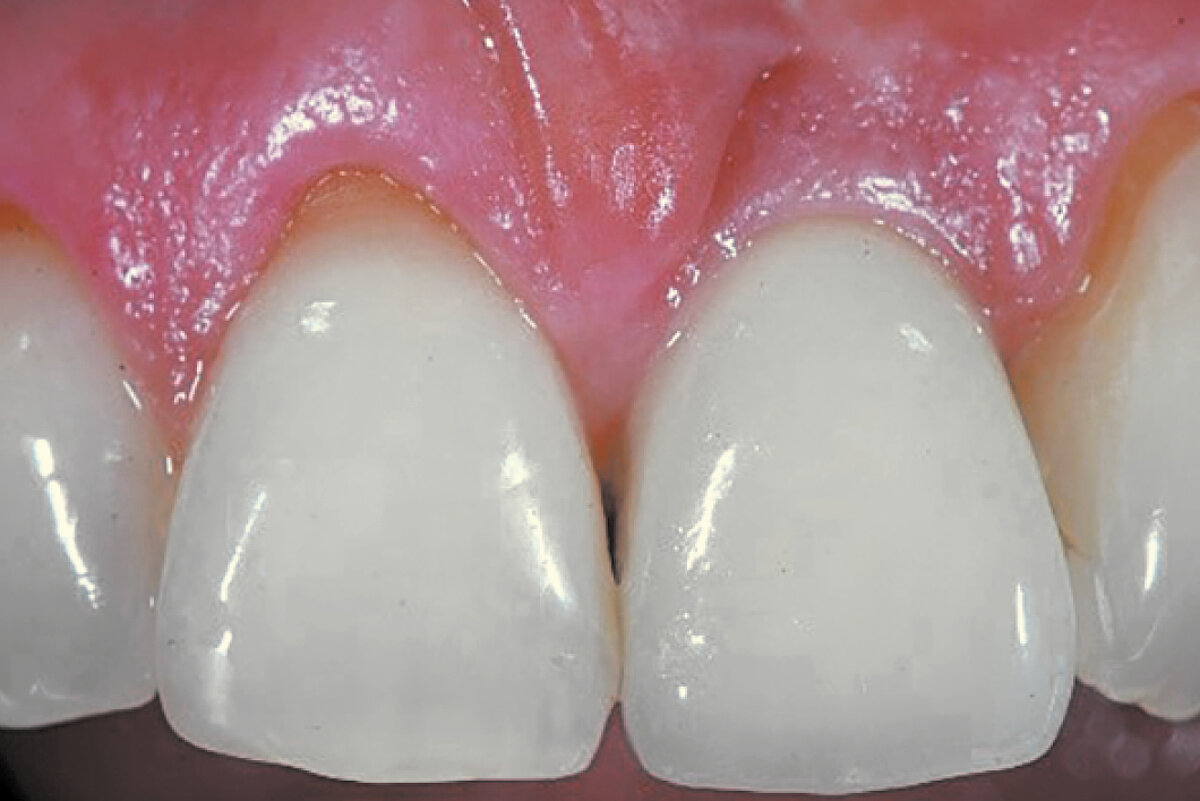
Ridge preservation in defect extraction socket (open-healing approach)
Clinical challenge
Ridge Preservation allows correct 3D implant placement reducing additional surgeries (i.e. sinus lift).
Aim / Approach
Prevent tissue collapse in the posterior area due to absence of the buccal bone wall. Avoid a possible sinus lift elevation.
Conclusion
Ridge preservation with Geistlich biomaterials preserved the alveolar ridge contour. A minimally invasive procedure provided enough ridge width for adequate implant placement and esthetic outcome.
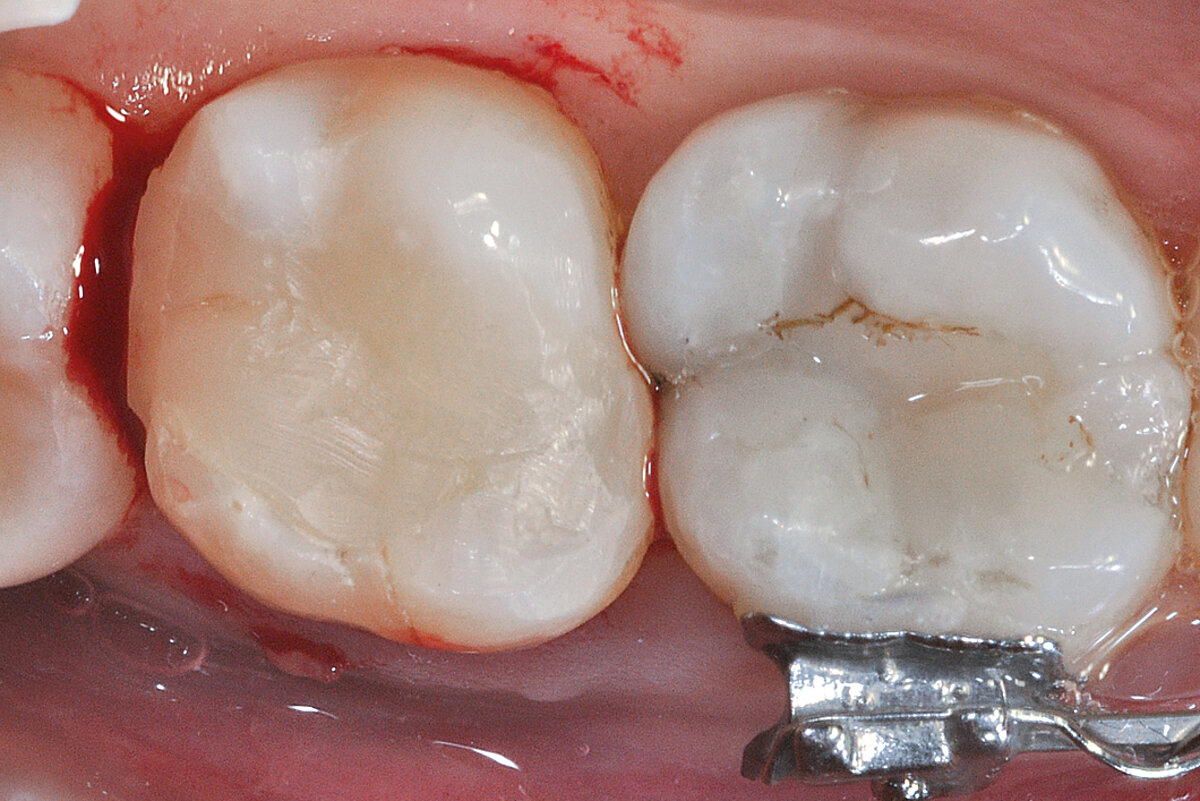
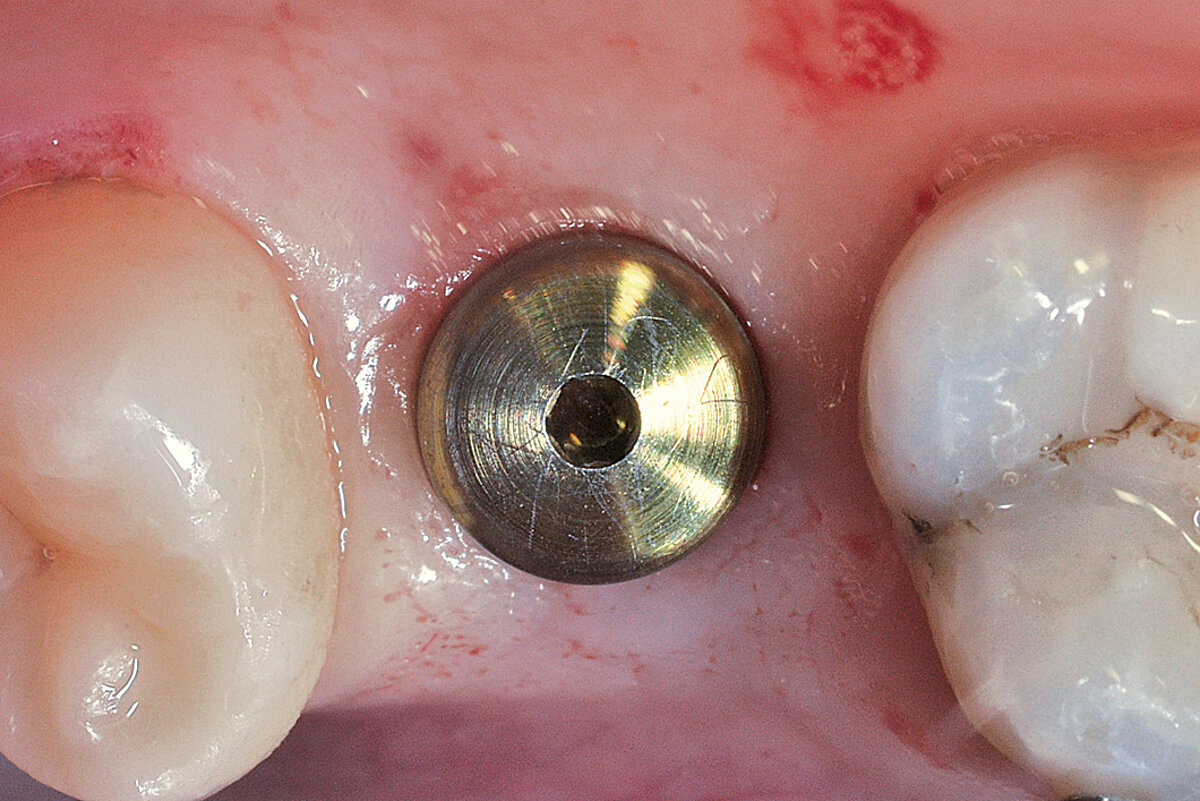
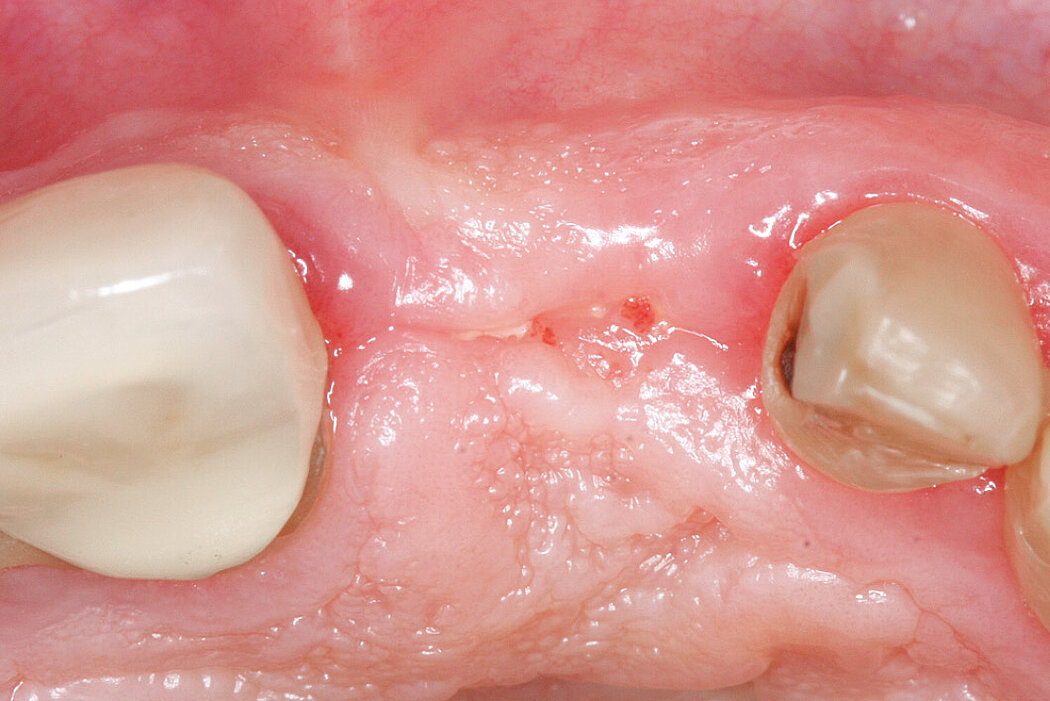
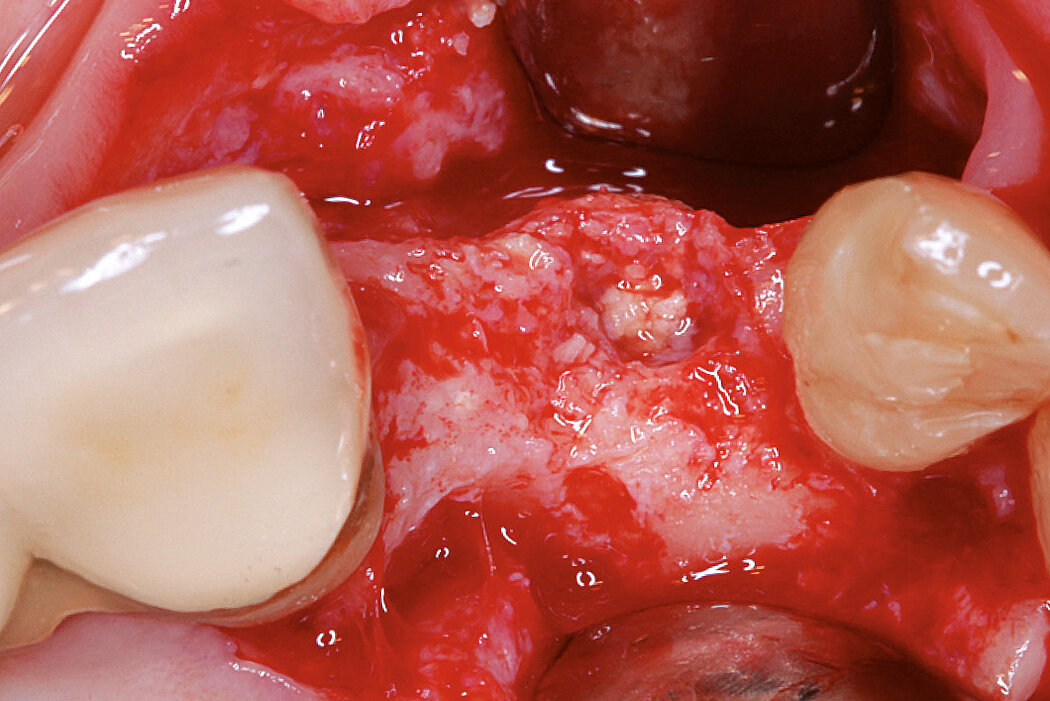
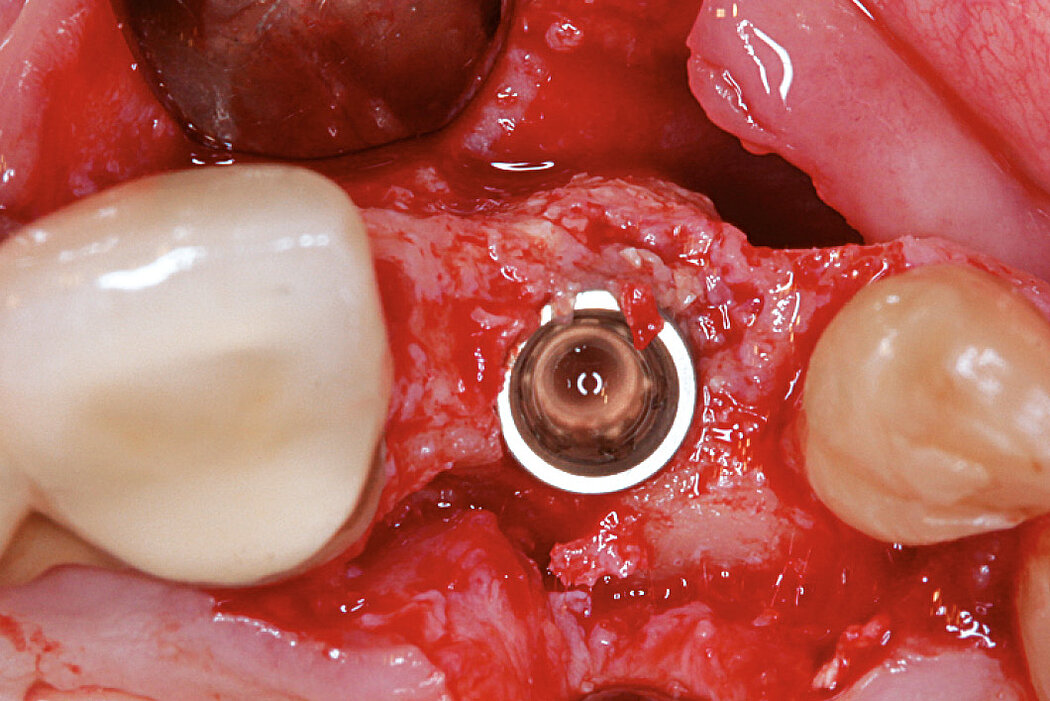
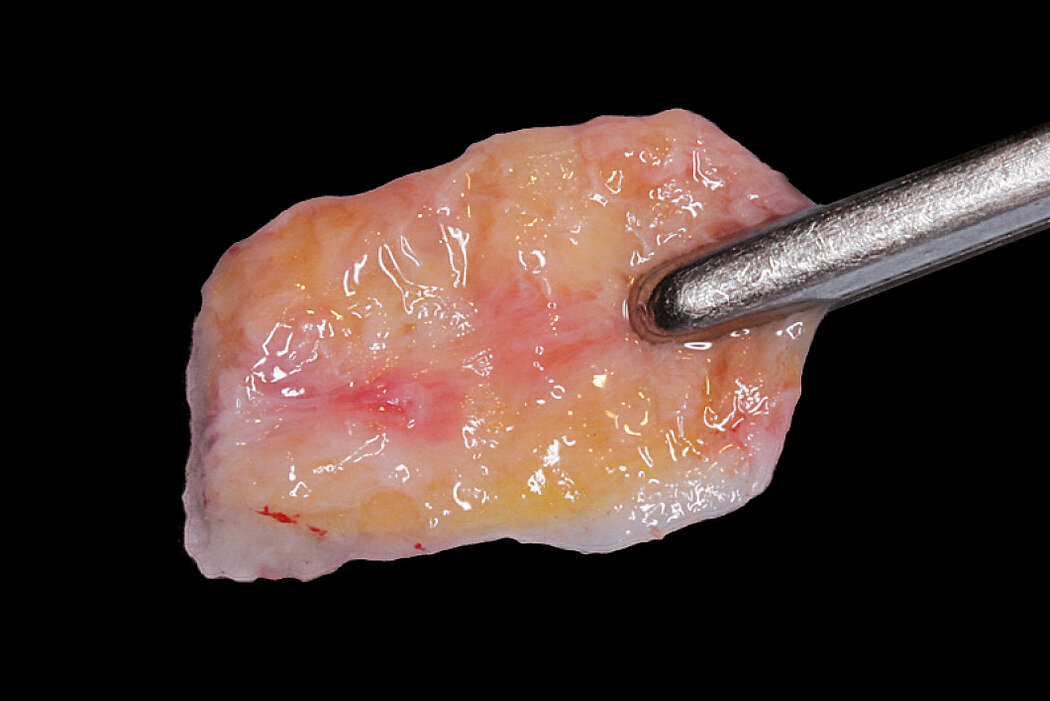
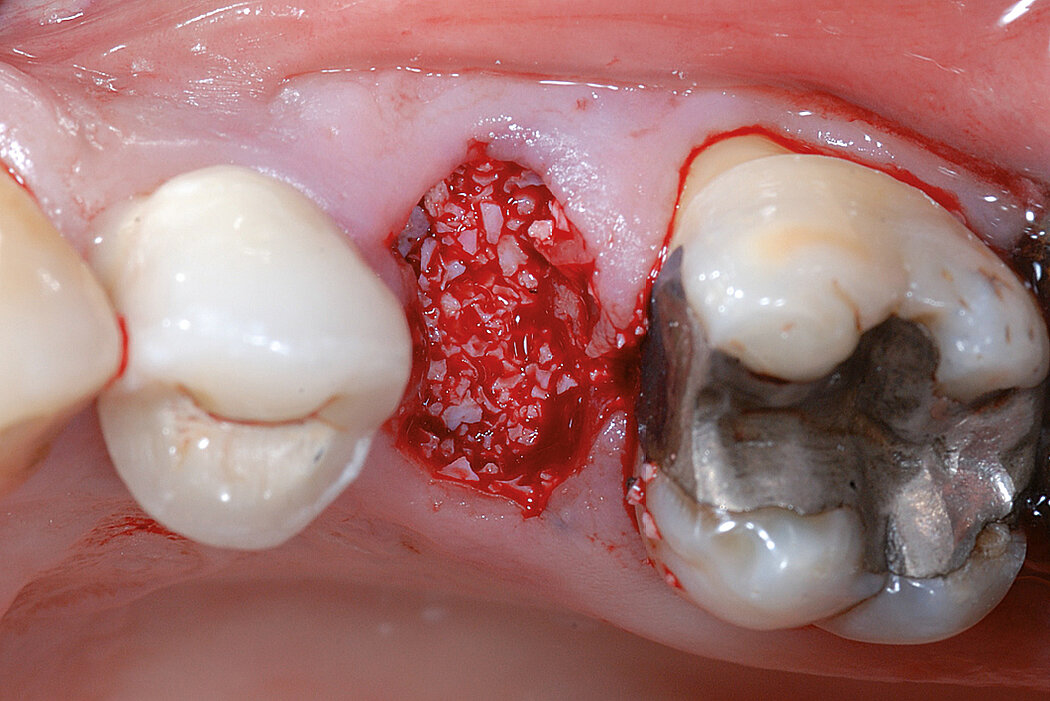
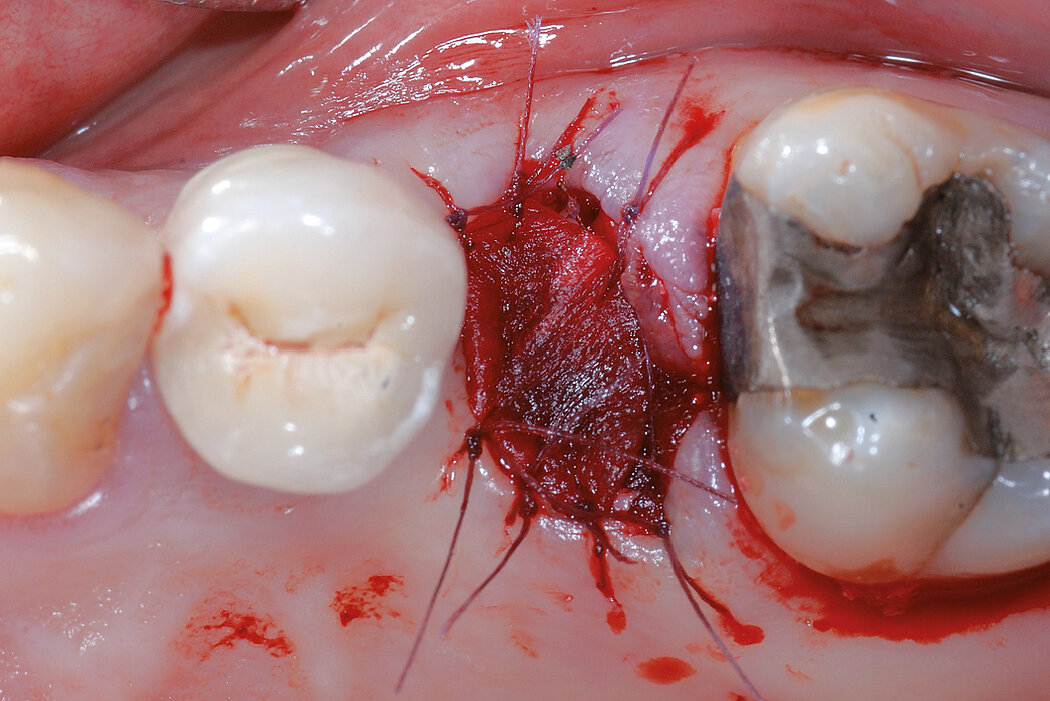
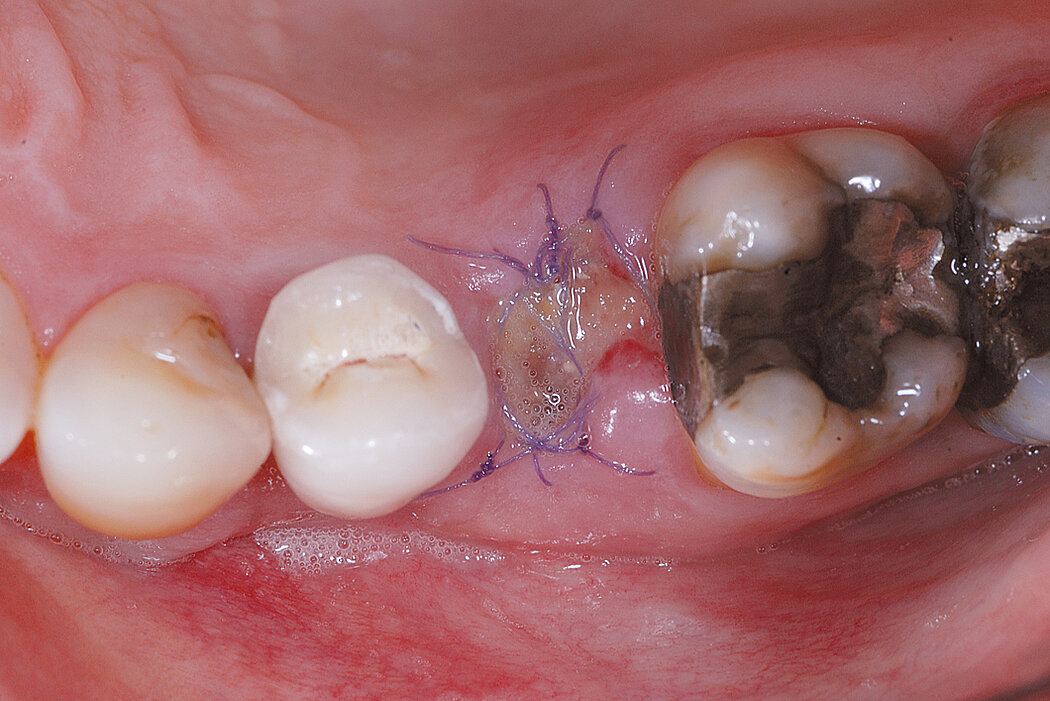
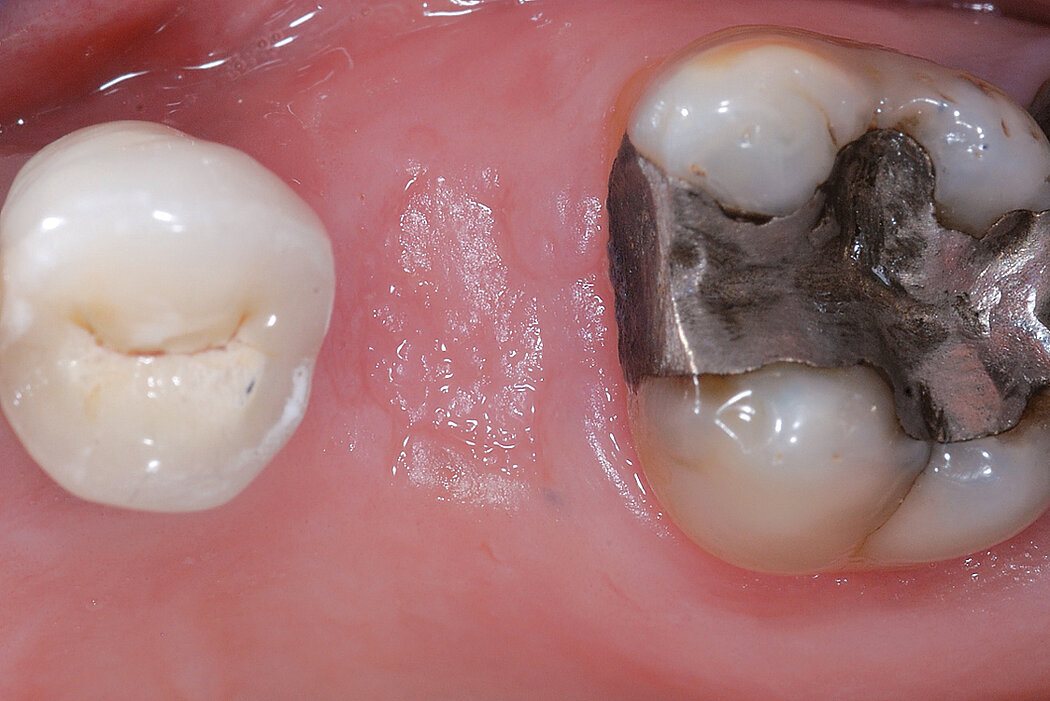
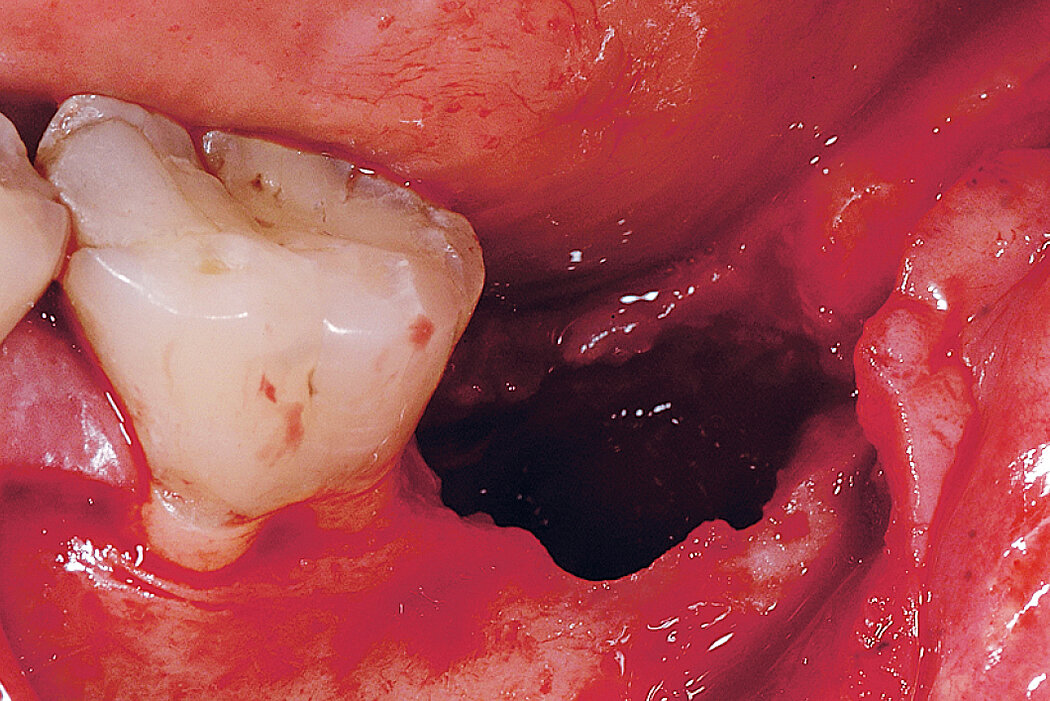
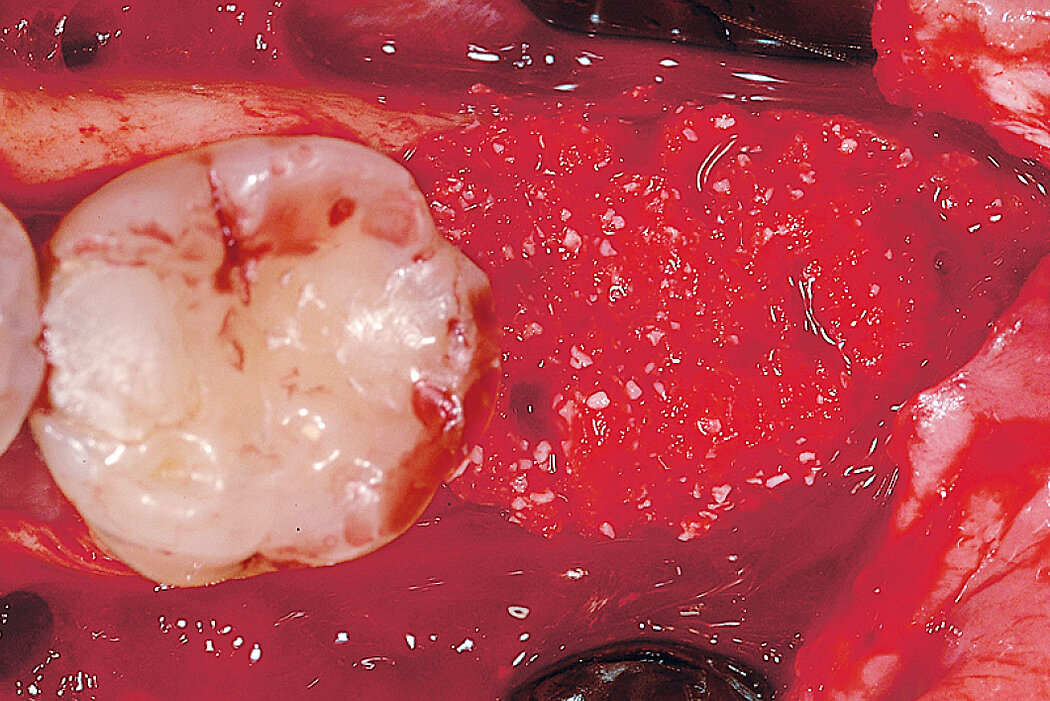
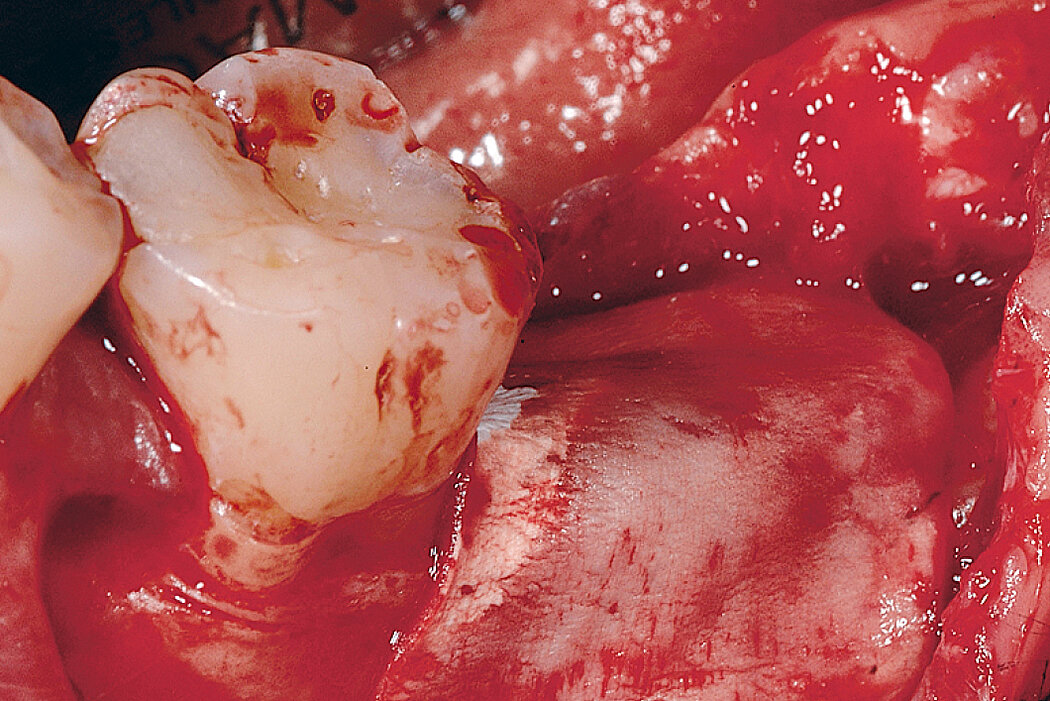
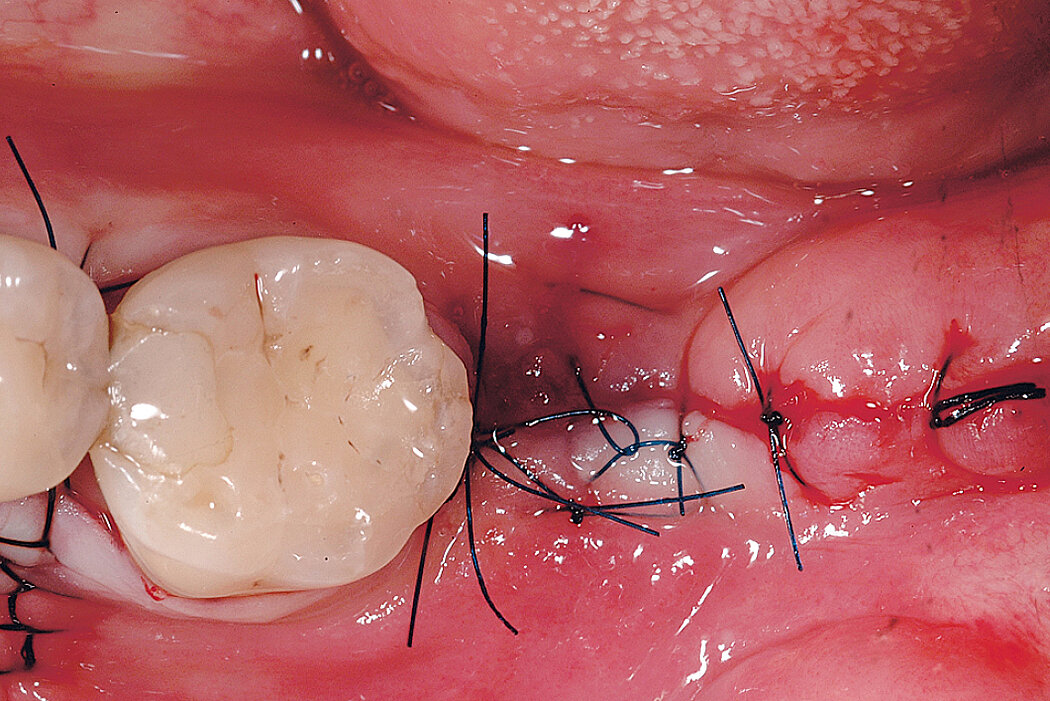
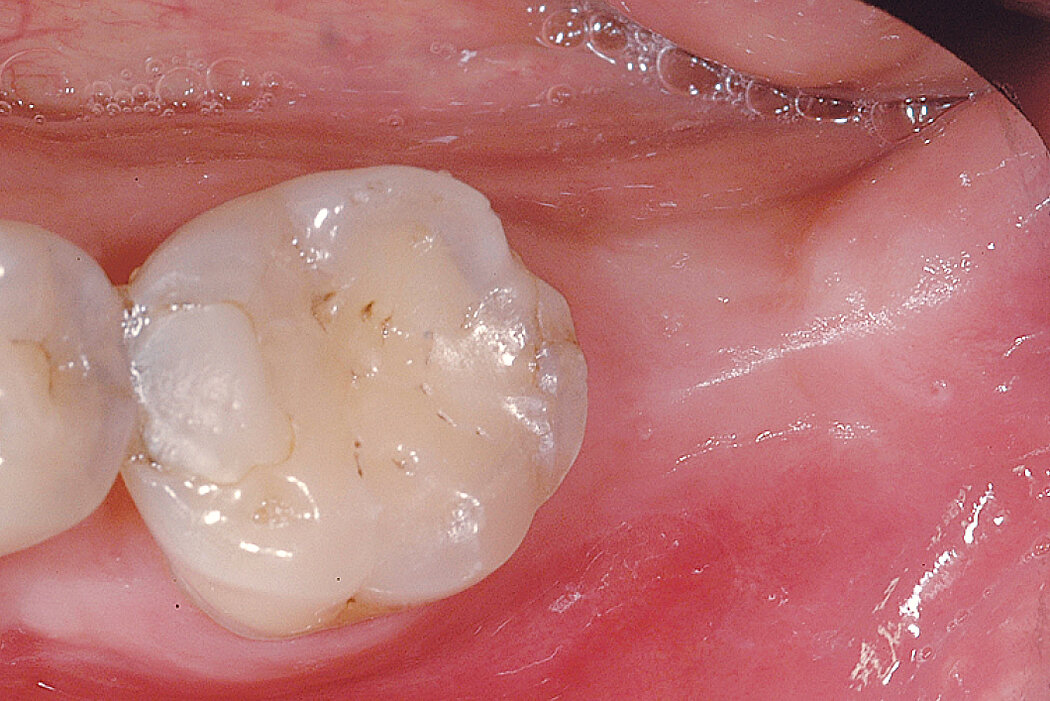
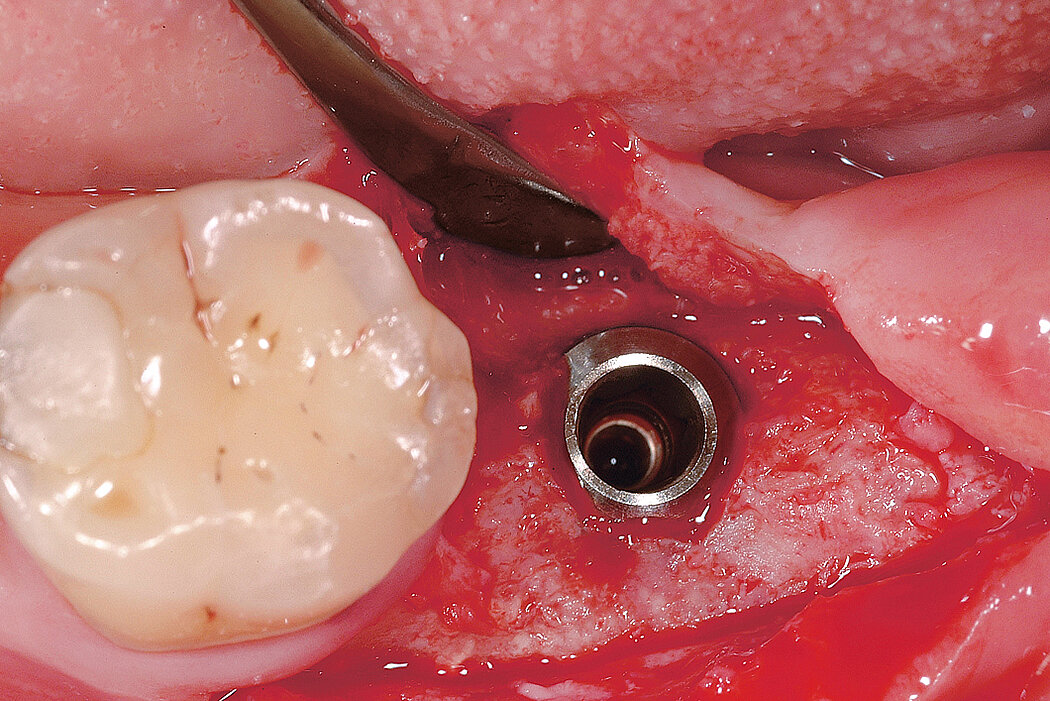
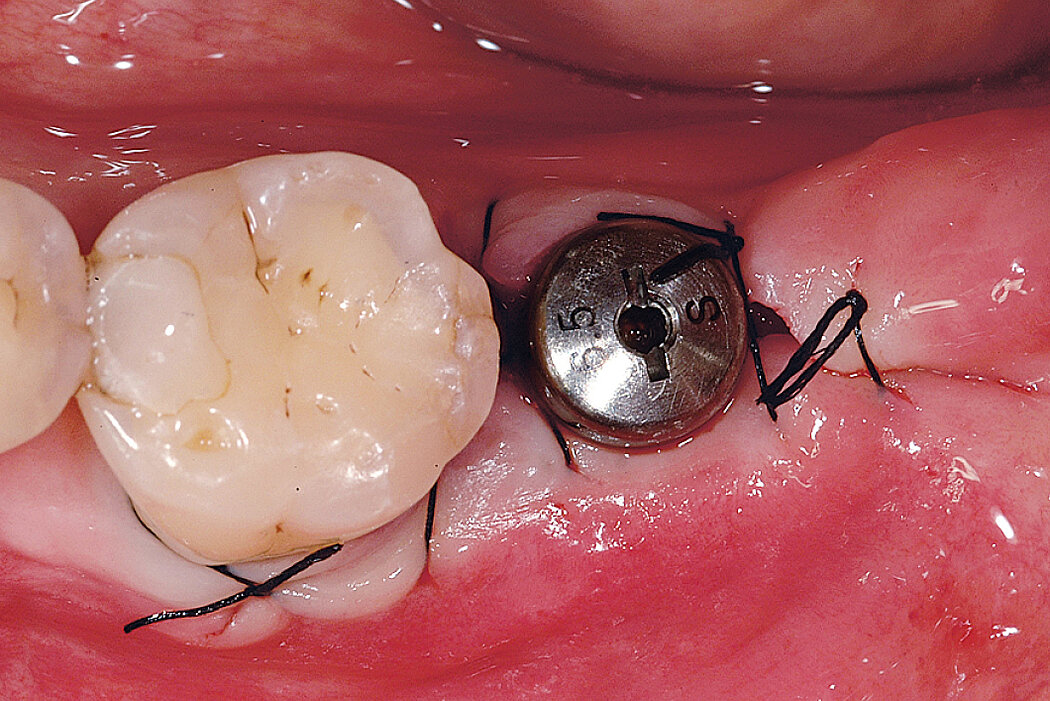
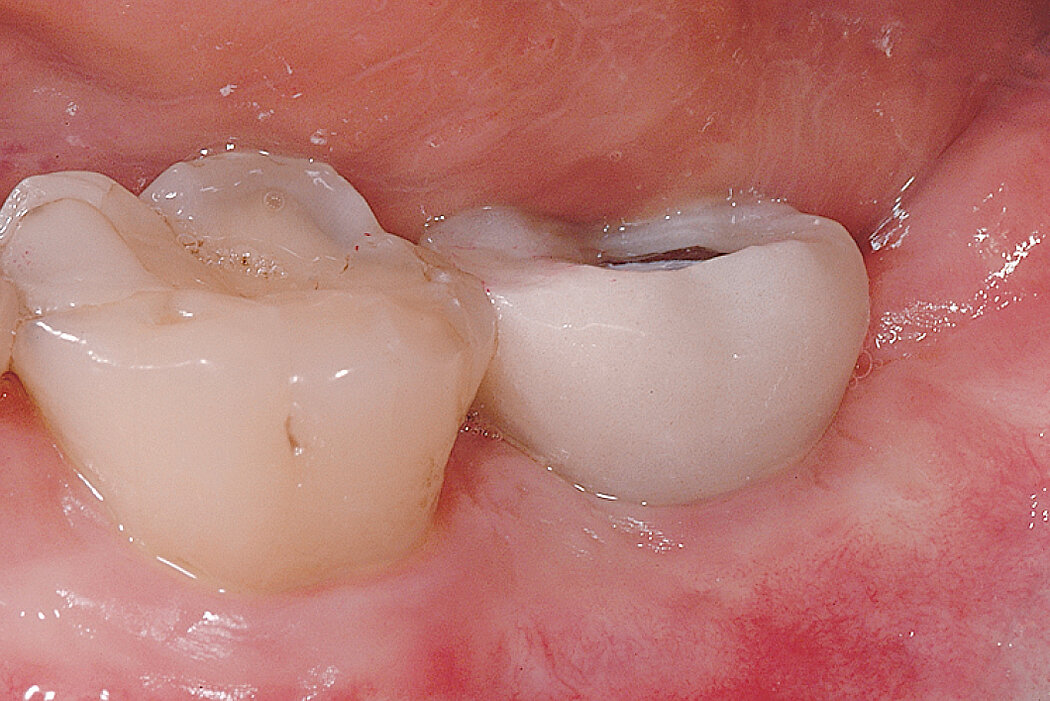
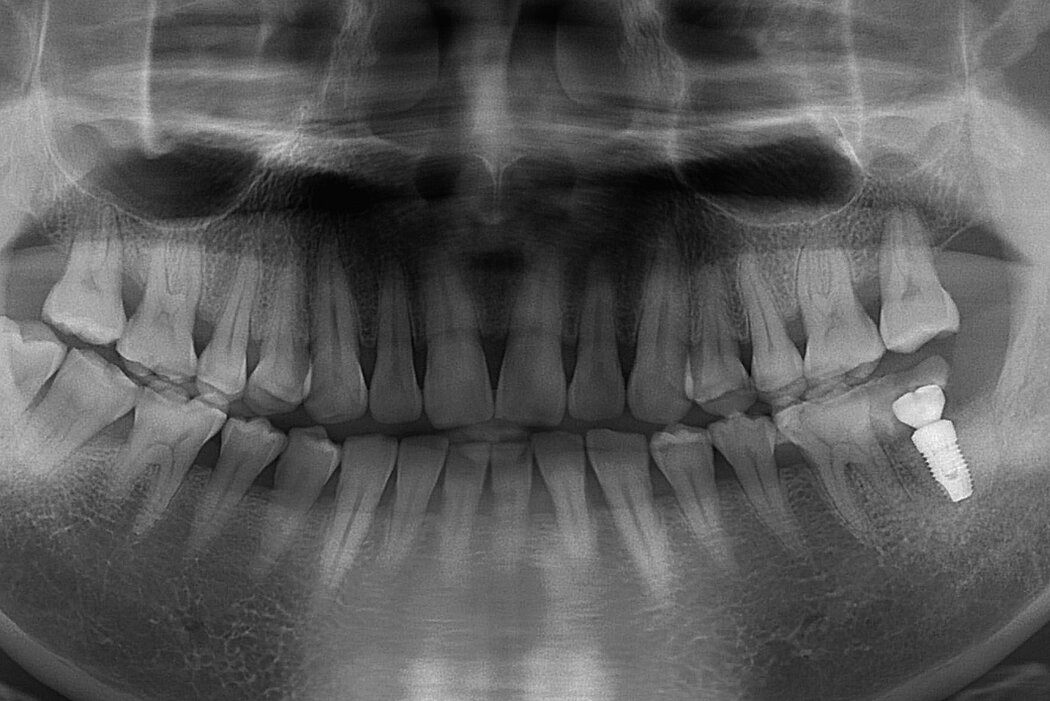
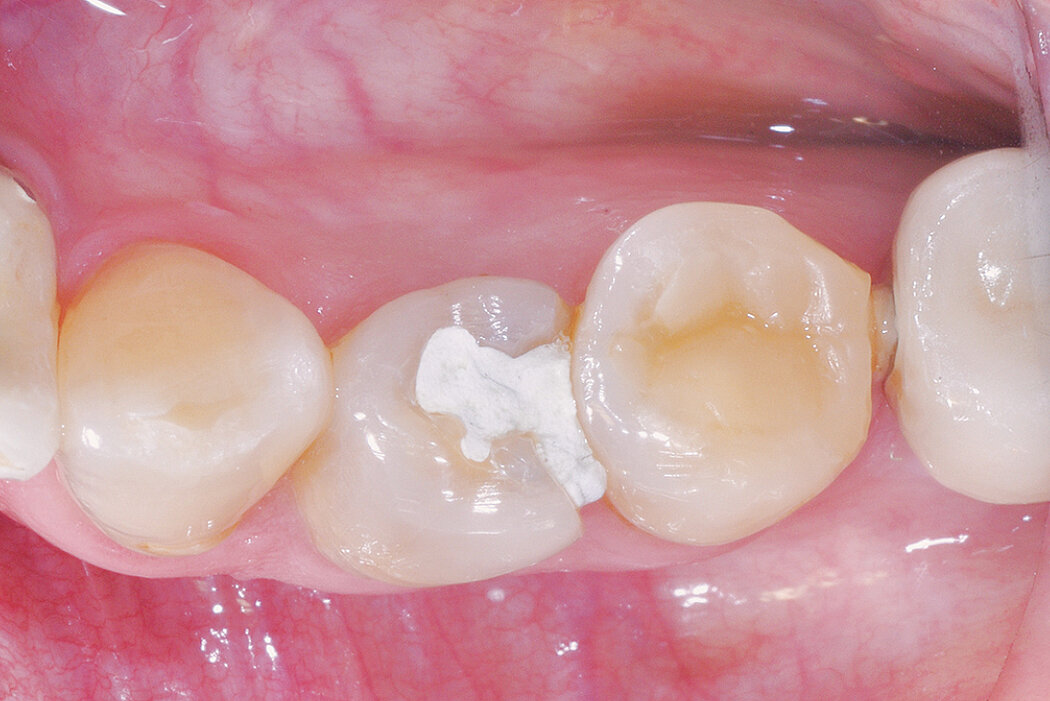
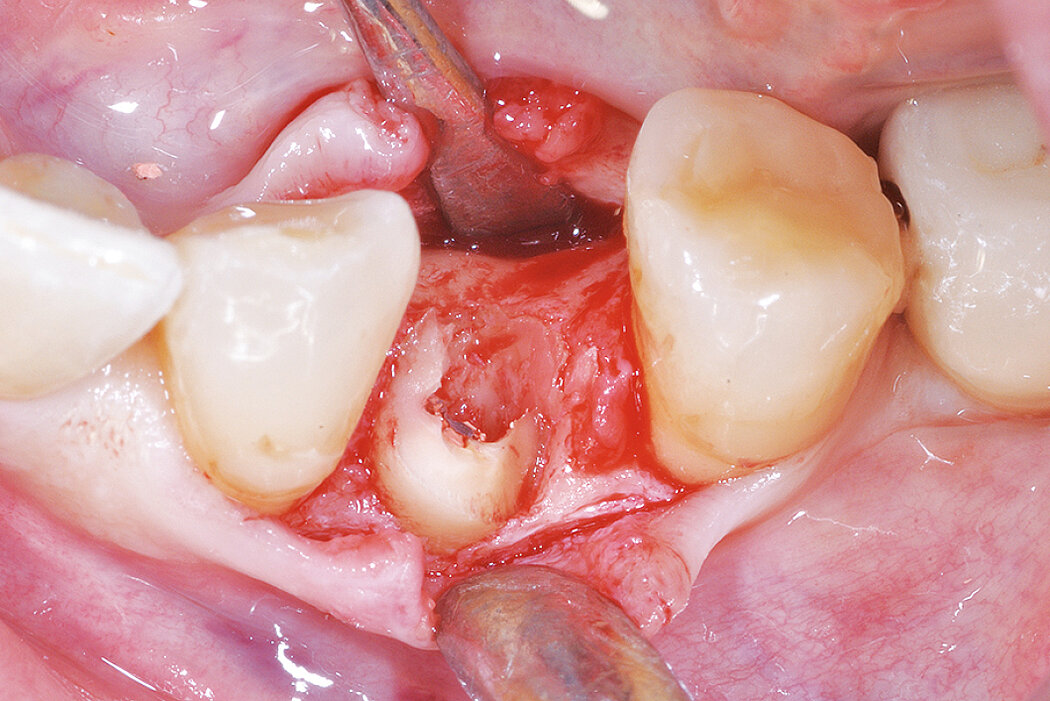
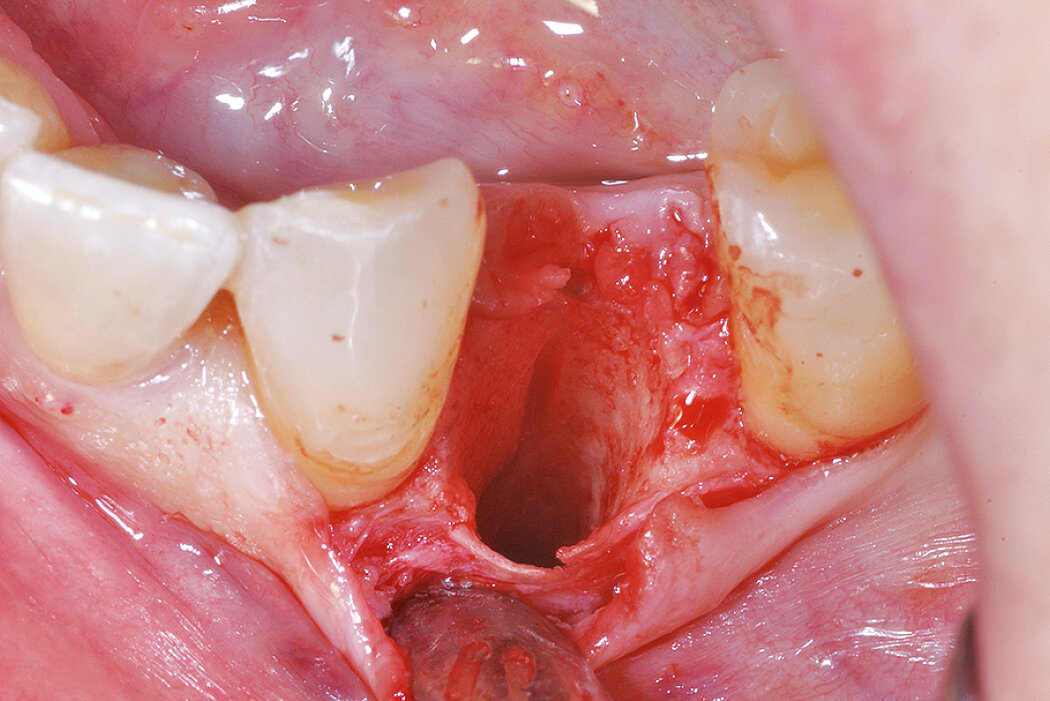
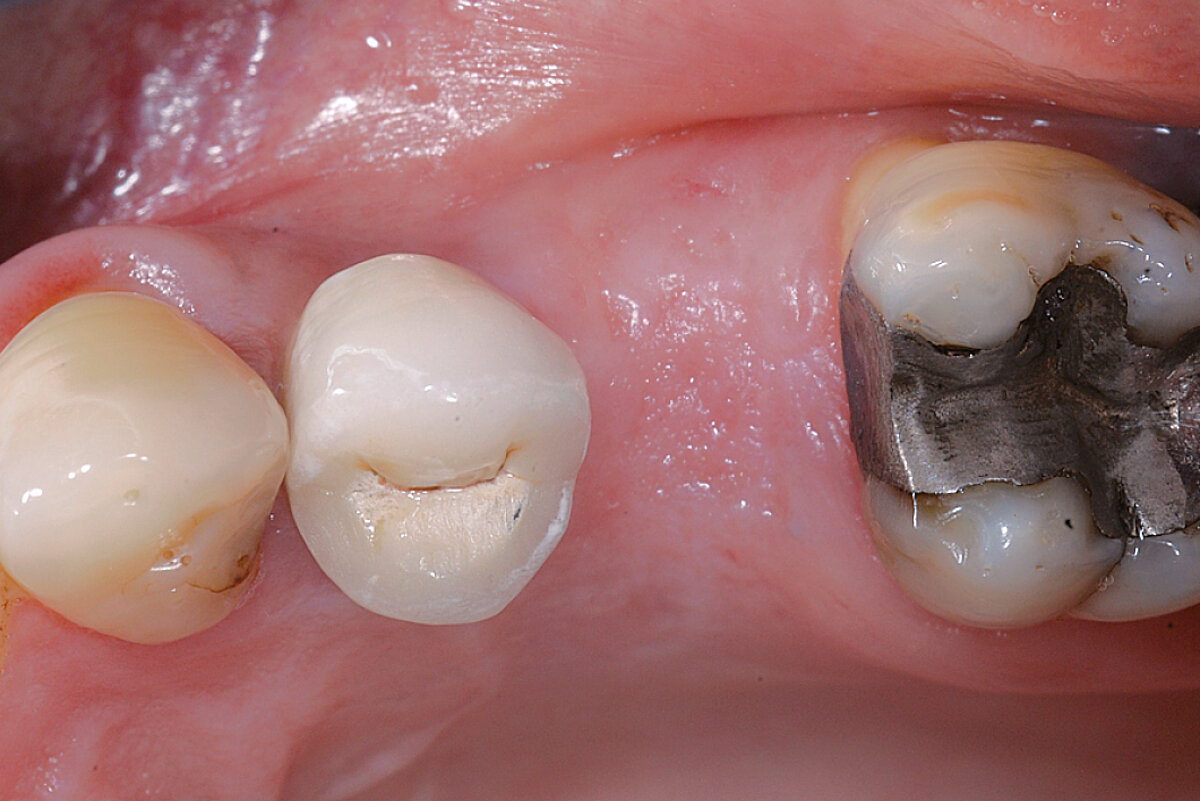
Ridge Preservation for delayed implant placement
Clinical challenge
After 6 months the defect was completely filled with newly-formed hard tissue.
Aim / Approach
Reconstruct alveolar bone with severe vertical loss from chronic periodontitis at the lower left second molar. Investigate the clinical and histological result by using Geistlich Combi-Kit Collagen after tooth extraction.
Conclusion
The defect was completely filled with newly-formed hard tissue after 6 months. Histomorphometric analysis revealed 45% of the hard tissue area including bone substitute material and 28% of the soft tissue area.
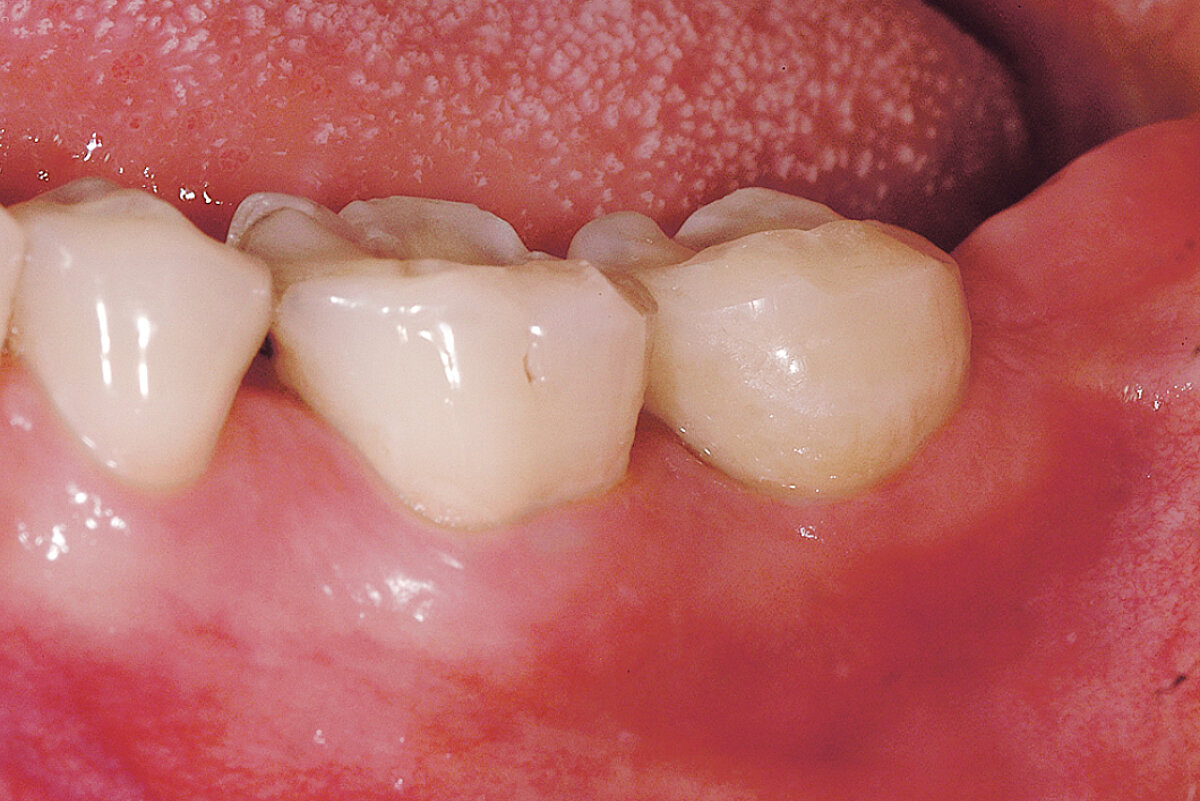
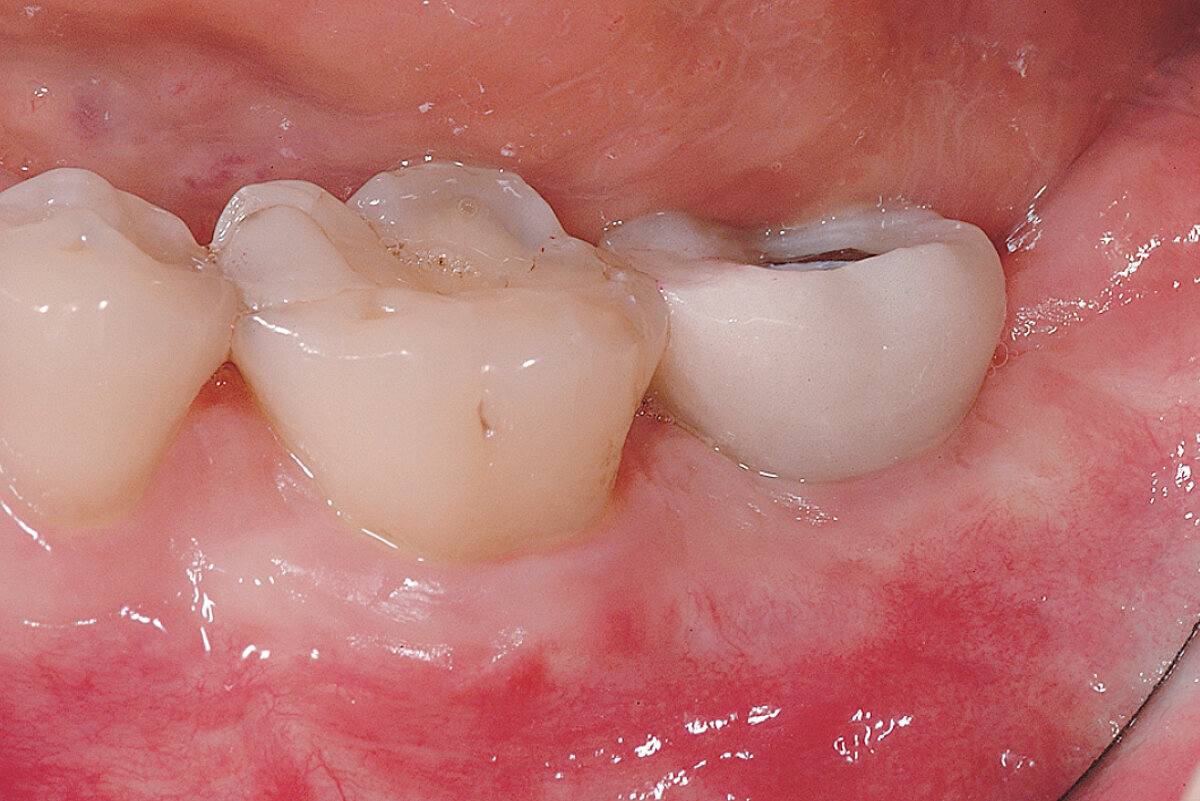
Delayed implant placement with a thin and defective buccal bone wall (open-healing approach)
Clinical challenge
Geistlich Bio-Gide® Shape is a really user-friendly product that can easily be used in the management of postextraction sites for ridge preservation.
Aim / Approach
Delayed implant placement to restore tooth 34. Minimally invasive procedure without mobilization of the flap to cover the graft: healing by secondary intention (open healing).
Conclusion
Geistlich Bio-Gide® Shape in combination with Geistlich Bio-Oss® Collagen preserved largely the ridge dimensions after tooth extraction. Implant can be placed without need of a second bone grafting at time of implant placement.